Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
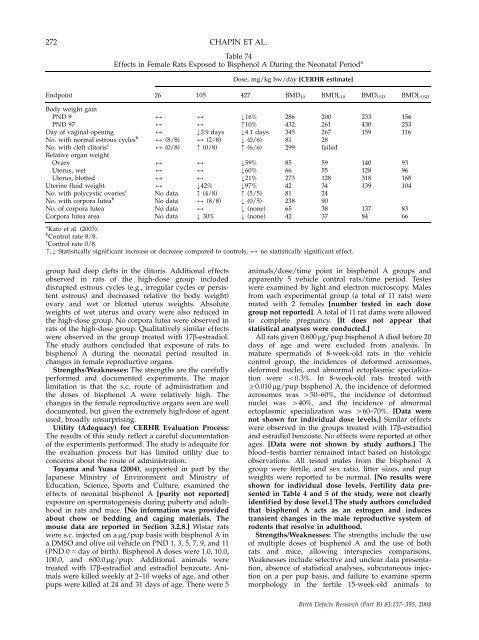
272 CHAPIN ET AL.<br />
Table 74<br />
Effects in Female Rats Exposed to Bisphenol A During <strong>the</strong> Ne<strong>on</strong>atal Period a<br />
Dose, mg/kg bw/day [CERHR estimate]<br />
Endpoint 26 105 427 BMD10 BMDL10 BMD1SD BMDL1SD<br />
Body weight gain<br />
PND 9 2 2 k16% 286 200 233 156<br />
PND 97 2 2 m10% 432 261 430 253<br />
Day of vaginal opening 2 k2.9 days k4.1 days 345 267 159 116<br />
No. with normal estrous cycles b 2 (8/8) 2 (2/8) k (0/6) 81 28<br />
No. with cleft clitoris c<br />
Relative organ weight<br />
2 (0/8) m (0/8) m (6/6) 299 failed<br />
Ovary 2 2 k59% 85 59 140 93<br />
Uterus, wet 2 2 k60% 66 55 128 96<br />
Uterus, blotted 2 2 k21% 273 128 318 168<br />
Uterine fluid weight 2 k42% k97% 42 34 139 104<br />
No. with polycystic ovaries c<br />
No data m (4/8) m (5/5) 81 24<br />
No. with corpora lutea b<br />
No data 2 (8/8) k (0/5) 238 90<br />
No. of corpora lutea No data 2 k (n<strong>on</strong>e) 65 38 137 83<br />
Corpora lutea area No data k 30% k (n<strong>on</strong>e) 42 37 84 66<br />
a Kato et al. (2003).<br />
b C<strong>on</strong>trol rate 8/8.<br />
c C<strong>on</strong>trol rate 0/8.<br />
m,k Statistically significant increase or decrease compared to c<strong>on</strong>trols; 2 no statistically significant effect.<br />
group had deep clefts in <strong>the</strong> clitoris. Additi<strong>on</strong>al effects<br />
observed in rats of <strong>the</strong> high-dose group included<br />
disrupted estrous cycles (e.g., irregular cycles or persistent<br />
estrous) <strong>and</strong> decreased relative (to body weight)<br />
ovary <strong>and</strong> wet or blotted uterus weights. Absolute<br />
weights of wet uterus <strong>and</strong> ovary were also reduced in<br />
<strong>the</strong> high-dose group. No corpora lutea were observed in<br />
rats of <strong>the</strong> high-dose group. Qualitatively similar effects<br />
were observed in <strong>the</strong> group treated with 17b-estradiol.<br />
The study authors c<strong>on</strong>cluded that exposure of rats to<br />
bisphenol A during <strong>the</strong> ne<strong>on</strong>atal period resulted in<br />
changes in female reproductive organs.<br />
Strengths/Weaknesses: The strengths are <strong>the</strong> carefully<br />
performed <strong>and</strong> documented experiments. The major<br />
limitati<strong>on</strong> is that <strong>the</strong> s.c. route of administrati<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> doses of bisphenol A were relatively high. The<br />
changes in <strong>the</strong> female reproductive organs seen are well<br />
documented, but given <strong>the</strong> extremely high-dose of agent<br />
used, broadly unsurprising.<br />
Utility (Adequacy) for CERHR Evaluati<strong>on</strong> Process:<br />
The results of this study reflect a careful documentati<strong>on</strong><br />
of <strong>the</strong> experiments performed. The study is adequate for<br />
<strong>the</strong> evaluati<strong>on</strong> process but has limited utility due to<br />
c<strong>on</strong>cerns about <strong>the</strong> route of administrati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
Toyama <strong>and</strong> Yuasa (2004), supported in part by <strong>the</strong><br />
Japanese Ministry of Envir<strong>on</strong>ment <strong>and</strong> Ministry of<br />
Educati<strong>on</strong>, Science, Sports <strong>and</strong> Culture, examined <strong>the</strong><br />
effects of ne<strong>on</strong>atal bisphenol A [purity not reported]<br />
exposure <strong>on</strong> spermatogenesis during puberty <strong>and</strong> adulthood<br />
in rats <strong>and</strong> mice. [No informati<strong>on</strong> was provided<br />
about chow or bedding <strong>and</strong> caging materials. The<br />
mouse data are reported in Secti<strong>on</strong> 3.2.8.] Wistar rats<br />
were s.c. injected <strong>on</strong> a mg/pup basis with bisphenol A in<br />
a DMSO <strong>and</strong> olive oil vehicle <strong>on</strong> PND 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, <strong>and</strong> 11<br />
(PND 0 5 day of birth). Bisphenol A doses were 1.0, 10.0,<br />
100.0, <strong>and</strong> 600.0 mg/pup. Additi<strong>on</strong>al animals were<br />
treated with 17b-estradiol <strong>and</strong> estradiol benzoate. Animals<br />
were killed weekly at 2–10 weeks of age, <strong>and</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r<br />
pups were killed at 24 <strong>and</strong> 31 days of age. There were 5<br />
animals/dose/time point in bisphenol A groups <strong>and</strong><br />
apparently 5 vehicle c<strong>on</strong>trol rats/time period. Testes<br />
were examined by light <strong>and</strong> electr<strong>on</strong> microscopy. Males<br />
from each experimental group (a total of 11 rats) were<br />
mated with 2 females [number tested in each dose<br />
group not reported]. A total of 11 rat dams were allowed<br />
to complete pregnancy. [It does not appear that<br />
statistical analyses were c<strong>on</strong>ducted.]<br />
All rats given 0.600 mg/pup bisphenol A died before 20<br />
days of age <strong>and</strong> were excluded from analysis. In<br />
mature spermatids of 8-week-old rats in <strong>the</strong> vehicle<br />
c<strong>on</strong>trol group, <strong>the</strong> incidences of deformed acrosomes,<br />
deformed nuclei, <strong>and</strong> abnormal ectoplasmic specializati<strong>on</strong><br />
were o0.3%. In 8-week-old rats treated with<br />
Z0.010 mg/pup bisphenol A, <strong>the</strong> incidence of deformed<br />
acrosomes was 450–60%, <strong>the</strong> incidence of deformed<br />
nuclei was 440%, <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> incidence of abnormal<br />
ectoplasmic specializati<strong>on</strong> was 460–70%. [Data were<br />
not shown for individual dose levels.] Similar effects<br />
were observed in <strong>the</strong> groups treated with 17b-estradiol<br />
<strong>and</strong> estradiol benzoate. No effects were reported at o<strong>the</strong>r<br />
ages. [Data were not shown by study authors.] The<br />
blood–testis barrier remained intact based <strong>on</strong> histologic<br />
observati<strong>on</strong>s. All tested males from <strong>the</strong> bisphenol A<br />
group were fertile, <strong>and</strong> sex ratio, litter sizes, <strong>and</strong> pup<br />
weights were reported to be normal. [No results were<br />
shown for individual dose levels. Fertility data presented<br />
in Table 4 <strong>and</strong> 5 of <strong>the</strong> study, were not clearly<br />
identified by dose level.] The study authors c<strong>on</strong>cluded<br />
that bisphenol A acts as an estrogen <strong>and</strong> induces<br />
transient changes in <strong>the</strong> male reproductive system of<br />
rodents that resolve in adulthood.<br />
Strengths/Weaknesses: The strengths include <strong>the</strong> use<br />
of multiple doses of bisphenol A <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> use of both<br />
rats <strong>and</strong> mice, allowing interspecies comparis<strong>on</strong>s.<br />
Weaknesses include selective <strong>and</strong> unclear data presentati<strong>on</strong>,<br />
absence of statistical analyses, subcutaneous injecti<strong>on</strong><br />
<strong>on</strong> a per pup basis, <strong>and</strong> failure to examine sperm<br />
morphology in <strong>the</strong> fertile 15-week-old animals to<br />
Birth Defects Research (Part B) 83:157–395, 2008