Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
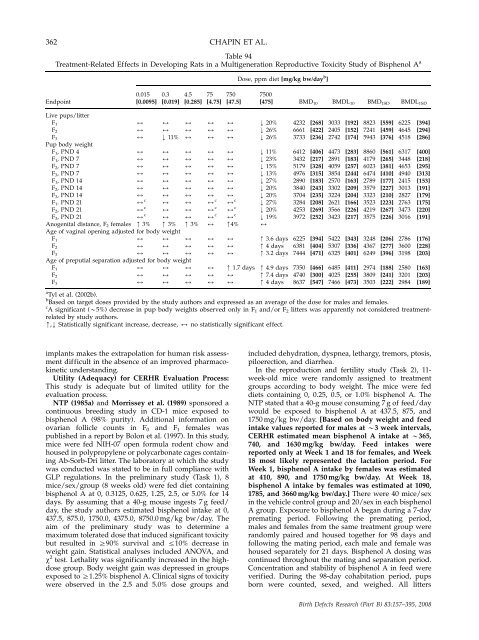
362 CHAPIN ET AL.<br />
Table 94<br />
Treatment-Related Effects in Developing Rats in a Multigenerati<strong>on</strong> <strong>Reproductive</strong> Toxicity Study of Bisphenol A a<br />
Endpoint<br />
0.015<br />
[0.0095]<br />
0.3<br />
[0.019]<br />
4.5<br />
[0.285]<br />
Live pups/litter<br />
F1 2 2 2<br />
F2 2 2 2<br />
F3 Pup body weight<br />
2 k 11% 2<br />
F1, PND 4 2 2 2<br />
F1, PND 7 2 2 2<br />
F2, PND 7 2 2 2<br />
F3, PND 7 2 2 2<br />
F1, PND 14 2 2 2<br />
F2, PND 14 2 2 2<br />
F3, PND 14 2 2 2<br />
2 c<br />
F1. PND 21 2 2<br />
F2, PND 21 2 2<br />
2 c<br />
2 c<br />
F 3, PND 21 2 2<br />
Anogenital distance, F 2 females m 3% m 3% m 3%<br />
Age of vaginal opening adjusted for body weight<br />
F 1 2 2 2<br />
F 2 2 2 2<br />
F 3 2 2 2<br />
Age of preputial separati<strong>on</strong> adjusted for body weight<br />
F1 2 2 2<br />
F2 2 2 2<br />
F 3 2 2 2<br />
75<br />
[4.75]<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2 c<br />
2 c<br />
2 c<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
Dose, ppm diet [mg/kg bw/day b ]<br />
750 7500<br />
[47.5] [475] BMD10 BMDL 10 BMD 1SD BMDL 1SD<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2 c<br />
2 c<br />
2 c<br />
m4%<br />
2<br />
2<br />
2<br />
m 1.7 days<br />
2<br />
2<br />
k 20%<br />
k 26%<br />
k 26%<br />
k 11%<br />
k 23%<br />
k 15%<br />
k 13%<br />
k 27%<br />
k 20%<br />
k 20%<br />
k 27%<br />
k 20%<br />
k 19%<br />
2<br />
m 3.6 days<br />
m 4 days<br />
m 3.2 days<br />
m 4.9 days<br />
m 7.4 days<br />
m 4 days<br />
a<br />
Tyl et al. (2002b).<br />
b<br />
Based <strong>on</strong> target doses provided by <strong>the</strong> study authors <strong>and</strong> expressed as an average of <strong>the</strong> dose for males <strong>and</strong> females.<br />
c<br />
A significant (B5%) decrease in pup body weights observed <strong>on</strong>ly in F1 <strong>and</strong>/or F2 litters was apparently not c<strong>on</strong>sidered treatmentrelated<br />
by study authors.<br />
m,k Statistically significant increase, decrease, 2 no statistically significant effect.<br />
implants makes <strong>the</strong> extrapolati<strong>on</strong> for human risk assessment<br />
difficult in <strong>the</strong> absence of an improved pharmacokinetic<br />
underst<strong>and</strong>ing.<br />
Utility (Adequacy) for CERHR Evaluati<strong>on</strong> Process:<br />
This study is adequate but of limited utility for <strong>the</strong><br />
evaluati<strong>on</strong> process.<br />
NTP (1985a) <strong>and</strong> Morrissey et al. (1989) sp<strong>on</strong>sored a<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tinuous breeding study in CD-1 mice exposed to<br />
bisphenol A (98% purity). Additi<strong>on</strong>al informati<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong><br />
ovarian follicle counts in F0 <strong>and</strong> F1 females was<br />
published in a report by Bol<strong>on</strong> et al. (1997). In this study,<br />
mice were fed NIH-07 open formula rodent chow <strong>and</strong><br />
housed in polypropylene or polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate cages c<strong>on</strong>taining<br />
Ab-Sorb-Dri litter. The laboratory at which <strong>the</strong> study<br />
was c<strong>on</strong>ducted was stated to be in full compliance with<br />
GLP regulati<strong>on</strong>s. In <strong>the</strong> preliminary study (Task 1), 8<br />
mice/sex/group (8 weeks old) were fed diet c<strong>on</strong>taining<br />
bisphenol A at 0, 0.3125, 0.625, 1.25, 2.5, or 5.0% for 14<br />
days. By assuming that a 40-g mouse ingests 7 g feed/<br />
day, <strong>the</strong> study authors estimated bisphenol intake at 0,<br />
437.5, 875.0, 1750.0, 4375.0, 8750.0 mg/kg bw/day. The<br />
aim of <strong>the</strong> preliminary study was to determine a<br />
maximum tolerated dose that induced significant toxicity<br />
but resulted in Z90% survival <strong>and</strong> r10% decrease in<br />
weight gain. Statistical analyses included ANOVA, <strong>and</strong><br />
w 2 test. Lethality was significantly increased in <strong>the</strong> highdose<br />
group. Body weight gain was depressed in groups<br />
exposed to Z1.25% bisphenol A. Clinical signs of toxicity<br />
were observed in <strong>the</strong> 2.5 <strong>and</strong> 5.0% dose groups <strong>and</strong><br />
4232<br />
6661<br />
3733<br />
6412<br />
3432<br />
5179<br />
4976<br />
2890<br />
3840<br />
3704<br />
3284<br />
4253<br />
3972<br />
6225<br />
6381<br />
7444<br />
7350<br />
4740<br />
8637<br />
[268]<br />
[422]<br />
[236]<br />
[406]<br />
[217]<br />
[328]<br />
[315]<br />
[183]<br />
[243]<br />
[235]<br />
[208]<br />
[269]<br />
[252]<br />
[394]<br />
[404]<br />
[471]<br />
[466]<br />
[300]<br />
[547]<br />
3033<br />
2405<br />
2742<br />
4473<br />
2891<br />
4059<br />
3854<br />
2570<br />
3302<br />
3224<br />
2621<br />
3566<br />
3423<br />
5422<br />
5307<br />
6325<br />
6485<br />
4025<br />
7466<br />
[192]<br />
[152]<br />
[174]<br />
[283]<br />
[183]<br />
[257]<br />
[244]<br />
[163]<br />
[209]<br />
[204]<br />
[166]<br />
[226]<br />
[217]<br />
[343]<br />
[336]<br />
[401]<br />
[411]<br />
[255]<br />
[473]<br />
8823<br />
7241<br />
5943<br />
8860<br />
4179<br />
6023<br />
6474<br />
2789<br />
3579<br />
3323<br />
3523<br />
4219<br />
3575<br />
3248<br />
4367<br />
6249<br />
2974<br />
3809<br />
3503<br />
[559]<br />
[459]<br />
[376]<br />
[561]<br />
[265]<br />
[381]<br />
[410]<br />
[177]<br />
[227]<br />
[210]<br />
[223]<br />
[267]<br />
[226]<br />
[206]<br />
[277]<br />
[396]<br />
[188]<br />
[241]<br />
[222]<br />
6225<br />
4645<br />
4518<br />
6317<br />
3448<br />
4653<br />
4940<br />
2415<br />
3013<br />
2827<br />
2763<br />
3473<br />
3016<br />
2786<br />
3600<br />
3198<br />
2580<br />
3201<br />
2984<br />
[394]<br />
[294]<br />
[286]<br />
[400]<br />
[218]<br />
[295]<br />
[313]<br />
[153]<br />
[191]<br />
[179]<br />
[175]<br />
[220]<br />
[191]<br />
[176]<br />
[228]<br />
[203]<br />
[163]<br />
[203]<br />
[189]<br />
included dehydrati<strong>on</strong>, dyspnea, lethargy, tremors, ptosis,<br />
piloerecti<strong>on</strong>, <strong>and</strong> diarrhea.<br />
In <strong>the</strong> reproducti<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong> fertility study (Task 2), 11week-old<br />
mice were r<strong>and</strong>omly assigned to treatment<br />
groups according to body weight. The mice were fed<br />
diets c<strong>on</strong>taining 0, 0.25, 0.5, or 1.0% bisphenol A. The<br />
NTP stated that a 40-g mouse c<strong>on</strong>suming 7 g of feed/day<br />
would be exposed to bisphenol A at 437.5, 875, <strong>and</strong><br />
1750 mg/kg bw/day. [Based <strong>on</strong> body weight <strong>and</strong> feed<br />
intake values reported for males at B3 week intervals,<br />
CERHR estimated mean bisphenol A intake at B365,<br />
740, <strong>and</strong> 1630 mg/kg bw/day. Feed intakes were<br />
reported <strong>on</strong>ly at Week 1 <strong>and</strong> 18 for females, <strong>and</strong> Week<br />
18 most likely represented <strong>the</strong> lactati<strong>on</strong> period. For<br />
Week 1, bisphenol A intake by females was estimated<br />
at 410, 890, <strong>and</strong> 1750 mg/kg bw/day. At Week 18,<br />
bisphenol A intake by females was estimated at 1090,<br />
1785, <strong>and</strong> 3660 mg/kg bw/day.] There were 40 mice/sex<br />
in <strong>the</strong> vehicle c<strong>on</strong>trol group <strong>and</strong> 20/sex in each bisphenol<br />
A group. Exposure to bisphenol A began during a 7-day<br />
premating period. Following <strong>the</strong> premating period,<br />
males <strong>and</strong> females from <strong>the</strong> same treatment group were<br />
r<strong>and</strong>omly paired <strong>and</strong> housed toge<strong>the</strong>r for 98 days <strong>and</strong><br />
following <strong>the</strong> mating period, each male <strong>and</strong> female was<br />
housed separately for 21 days. Bisphenol A dosing was<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tinued throughout <strong>the</strong> mating <strong>and</strong> separati<strong>on</strong> period.<br />
C<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong> stability of bisphenol A in feed were<br />
verified. During <strong>the</strong> 98-day cohabitati<strong>on</strong> period, pups<br />
born were counted, sexed, <strong>and</strong> weighed. All litters<br />
Birth Defects Research (Part B) 83:157–395, 2008