Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
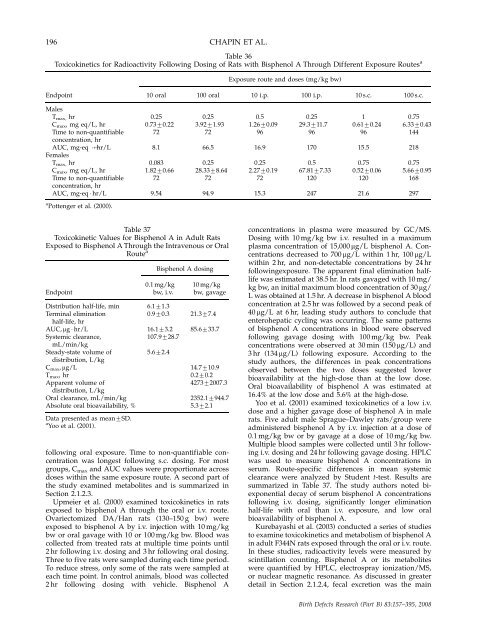
196 CHAPIN ET AL.<br />
Table 36<br />
Toxicokinetics for Radioactivity Following Dosing of Rats with Bisphenol A Through Different Exposure Routes a<br />
Exposure route <strong>and</strong> doses (mg/kg bw)<br />
Endpoint 10 oral 100 oral 10 i.p. 100 i.p. 10 s.c. 100 s.c.<br />
Males<br />
T max, hr 0.25 0.25 0.5 0.25 1 0.75<br />
Cmax, mg eq/L, hr 0.7370.22 3.9271.93 1.2670.09 29.3711.7 0.6170.24 6.3370.43<br />
Time to n<strong>on</strong>-quantifiable 72 72 96 96 96 144<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>, hr<br />
AUC, mg-eq � hr/L 8.1 66.5 16.9 170 15.5 218<br />
Females<br />
Tmax, hr 0.083 0.25 0.25 0.5 0.75 0.75<br />
Cmax, mg eq/L, hr 1.8270.66 28.3378.64 2.2770.19 67.8177.33 0.5270.06 5.6670.95<br />
Time to n<strong>on</strong>-quantifiable 72 72 72 120 120 168<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>, hr<br />
AUC, mg-eq � hr/L 9.54 94.9 15.3 247 21.6 297<br />
a Pottenger et al. (2000).<br />
Table 37<br />
Toxicokinetic Values for Bisphenol A in Adult Rats<br />
Exposed to Bisphenol A Through <strong>the</strong> Intravenous or Oral<br />
Route a<br />
Bisphenol A dosing<br />
0.1 mg/kg 10 mg/kg<br />
Endpoint bw, i.v. bw, gavage<br />
Distributi<strong>on</strong> half-life, min 6.171.3<br />
Terminal eliminati<strong>on</strong> 0.970.3 21.377.4<br />
half-life, hr<br />
AUC, mg � hr/L 16.173.2 85.6733.7<br />
Systemic clearance, 107.9728.7<br />
mL/min/kg<br />
Steady-state volume of 5.672.4<br />
distributi<strong>on</strong>, L/kg<br />
Cmax, mg/L 14.7710.9<br />
Tmax, hr 0.270.2<br />
Apparent volume of 427372007.3<br />
distributi<strong>on</strong>, L/kg<br />
Oral clearance, mL/min/kg 2352.17944.7<br />
Absolute oral bioavailability, % 5.372.1<br />
Data presented as mean7SD.<br />
a Yoo et al. (2001).<br />
following oral exposure. Time to n<strong>on</strong>-quantifiable c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong><br />
was l<strong>on</strong>gest following s.c. dosing. For most<br />
groups, C max <strong>and</strong> AUC values were proporti<strong>on</strong>ate across<br />
doses within <strong>the</strong> same exposure route. A sec<strong>on</strong>d part of<br />
<strong>the</strong> study examined metabolites <strong>and</strong> is summarized in<br />
Secti<strong>on</strong> 2.1.2.3.<br />
Upmeier et al. (2000) examined toxicokinetics in rats<br />
exposed to bisphenol A through <strong>the</strong> oral or i.v. route.<br />
Ovariectomized DA/Han rats (130–150 g bw) were<br />
exposed to bisphenol A by i.v. injecti<strong>on</strong> with 10 mg/kg<br />
bw or oral gavage with 10 or 100 mg/kg bw. Blood was<br />
collected from treated rats at multiple time points until<br />
2 hr following i.v. dosing <strong>and</strong> 3 hr following oral dosing.<br />
Three to five rats were sampled during each time period.<br />
To reduce stress, <strong>on</strong>ly some of <strong>the</strong> rats were sampled at<br />
each time point. In c<strong>on</strong>trol animals, blood was collected<br />
2 hr following dosing with vehicle. Bisphenol A<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s in plasma were measured by GC/MS.<br />
Dosing with 10 mg/kg bw i.v. resulted in a maximum<br />
plasma c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> of 15,000 mg/L bisphenol A. C<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
decreased to 700 mg/L within 1 hr, 100 mg/L<br />
within 2 hr, <strong>and</strong> n<strong>on</strong>-detectable c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s by 24 hr<br />
followingexposure. The apparent final eliminati<strong>on</strong> halflife<br />
was estimated at 38.5 hr. In rats gavaged with 10 mg/<br />
kg bw, an initial maximum blood c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> of 30 mg/<br />
L was obtained at 1.5 hr. A decrease in bisphenol A blood<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> at 2.5 hr was followed by a sec<strong>on</strong>d peak of<br />
40 mg/L at 6 hr, leading study authors to c<strong>on</strong>clude that<br />
enterohepatic cycling was occurring. The same patterns<br />
of bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s in blood were observed<br />
following gavage dosing with 100 mg/kg bw. Peak<br />
c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s were observed at 30 min (150 mg/L) <strong>and</strong><br />
3 hr (134 mg/L) following exposure. According to <strong>the</strong><br />
study authors, <strong>the</strong> differences in peak c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
observed between <strong>the</strong> two doses suggested lower<br />
bioavailability at <strong>the</strong> high-dose than at <strong>the</strong> low dose.<br />
Oral bioavailability of bisphenol A was estimated at<br />
16.4% at <strong>the</strong> low dose <strong>and</strong> 5.6% at <strong>the</strong> high-dose.<br />
Yoo et al. (2001) examined toxicokinetics of a low i.v.<br />
dose <strong>and</strong> a higher gavage dose of bisphenol A in male<br />
rats. Five adult male Sprague–Dawley rats/group were<br />
administered bisphenol A by i.v. injecti<strong>on</strong> at a dose of<br />
0.1 mg/kg bw or by gavage at a dose of 10 mg/kg bw.<br />
Multiple blood samples were collected until 3 hr following<br />
i.v. dosing <strong>and</strong> 24 hr following gavage dosing. HPLC<br />
was used to measure bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s in<br />
serum. Route-specific differences in mean systemic<br />
clearance were analyzed by Student t-test. Results are<br />
summarized in Table 37. The study authors noted biexp<strong>on</strong>ential<br />
decay of serum bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
following i.v. dosing, significantly l<strong>on</strong>ger eliminati<strong>on</strong><br />
half-life with oral than i.v. exposure, <strong>and</strong> low oral<br />
bioavailability of bisphenol A.<br />
Kurebayashi et al. (2003) c<strong>on</strong>ducted a series of studies<br />
to examine toxicokinetics <strong>and</strong> metabolism of bisphenol A<br />
in adult F344N rats exposed through <strong>the</strong> oral or i.v. route.<br />
In <strong>the</strong>se studies, radioactivity levels were measured by<br />
scintillati<strong>on</strong> counting. Bisphenol A or its metabolites<br />
were quantified by HPLC, electrospray i<strong>on</strong>izati<strong>on</strong>/MS,<br />
or nuclear magnetic res<strong>on</strong>ance. As discussed in greater<br />
detail in Secti<strong>on</strong> 2.1.2.4, fecal excreti<strong>on</strong> was <strong>the</strong> main<br />
Birth Defects Research (Part B) 83:157–395, 2008