Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
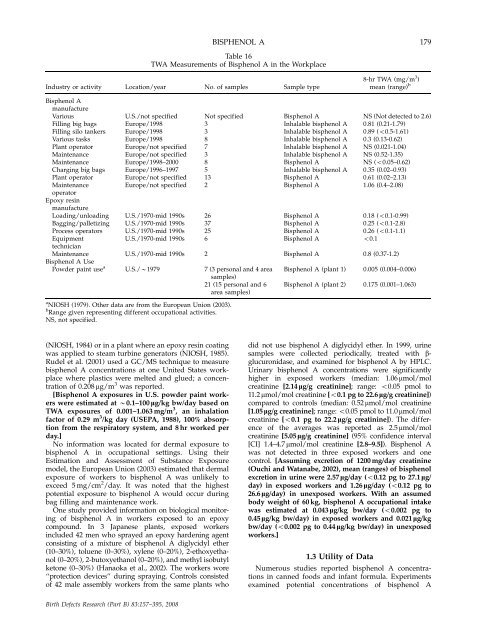
BISPHENOL A 179<br />
Table 16<br />
TWA Measurements of Bisphenol A in <strong>the</strong> Workplace<br />
8-hr TWA (mg/m 3 )<br />
Industry or activity Locati<strong>on</strong>/year No. of samples Sample type mean (range) b<br />
Bisphenol A<br />
manufacture<br />
Various U.S./not specified Not specified Bisphenol A NS (Not detected to 2.6)<br />
Filling big bags Europe/1998 3 Inhalable bisphenol A 0.81 (0.21-1.79)<br />
Filling silo tankers Europe/1998 3 Inhalable bisphenol A 0.89 (o0.5-1.61)<br />
Various tasks Europe/1998 8 Inhalable bisphenol A 0.3 (0.13-0.62)<br />
Plant operator Europe/not specified 7 Inhalable bisphenol A NS (0.021-1.04)<br />
Maintenance Europe/not specified 3 Inhalable bisphenol A NS (0.52-1.35)<br />
Maintenance Europe/1998–2000 8 Bisphenol A NS (o0.05–0.62)<br />
Charging big bags Europe/1996–1997 5 Inhalable bisphenol A 0.35 (0.02–0.93)<br />
Plant operator Europe/not specified 13 Bisphenol A 0.61 (0.02–2.13)<br />
Maintenance Europe/not specified 2 Bisphenol A 1.06 (0.4–2.08)<br />
operator<br />
Epoxy resin<br />
manufacture<br />
Loading/unloading U.S./1970-mid 1990s 26 Bisphenol A 0.18 (o0.1-0.99)<br />
Bagging/palletizing U.S./1970-mid 1990s 37 Bisphenol A 0.25 (o0.1-2.8)<br />
Process operators U.S./1970-mid 1990s 25 Bisphenol A 0.26 (o0.1-1.1)<br />
Equipment U.S./1970-mid 1990s 6 Bisphenol A o0.1<br />
technician<br />
Maintenance U.S./1970-mid 1990s 2 Bisphenol A 0.8 (0.37-1.2)<br />
Bisphenol A Use<br />
Powder paint use a<br />
U.S./B1979 7 (3 pers<strong>on</strong>al <strong>and</strong> 4 area Bisphenol A (plant 1) 0.005 (0.004–0.006)<br />
samples)<br />
21 (15 pers<strong>on</strong>al <strong>and</strong> 6 Bisphenol A (plant 2) 0.175 (0.001–1.063)<br />
area samples)<br />
a<br />
NIOSH (1979). O<strong>the</strong>r data are from <strong>the</strong> European Uni<strong>on</strong> (2003).<br />
b<br />
Range given representing different occupati<strong>on</strong>al activities.<br />
NS, not specified.<br />
(NIOSH, 1984) or in a plant where an epoxy resin coating<br />
was applied to steam turbine generators (NIOSH, 1985).<br />
Rudel et al. (2001) used a GC/MS technique to measure<br />
bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s at <strong>on</strong>e United States workplace<br />
where plastics were melted <strong>and</strong> glued; a c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong><br />
of 0.208 mg/m 3 was reported.<br />
[Bisphenol A exposures in U.S. powder paint workers<br />
were estimated at B0.1–100 lg/kg bw/day based <strong>on</strong><br />
TWA exposures of 0.001–1.063 mg/m 3 , an inhalati<strong>on</strong><br />
factor of 0.29 m 3 /kg day (USEPA, 1988), 100% absorpti<strong>on</strong><br />
from <strong>the</strong> respiratory system, <strong>and</strong> 8 hr worked per<br />
day.]<br />
No informati<strong>on</strong> was located for dermal exposure to<br />
bisphenol A in occupati<strong>on</strong>al settings. Using <strong>the</strong>ir<br />
Estimati<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong> Assessment of Substance Exposure<br />
model, <strong>the</strong> European Uni<strong>on</strong> (2003) estimated that dermal<br />
exposure of workers to bisphenol A was unlikely to<br />
exceed 5 mg/cm 2 /day. It was noted that <strong>the</strong> highest<br />
potential exposure to bisphenol A would occur during<br />
bag filling <strong>and</strong> maintenance work.<br />
One study provided informati<strong>on</strong> <strong>on</strong> biological m<strong>on</strong>itoring<br />
of bisphenol A in workers exposed to an epoxy<br />
compound. In 3 Japanese plants, exposed workers<br />
included 42 men who sprayed an epoxy hardening agent<br />
c<strong>on</strong>sisting of a mixture of bisphenol A diglycidyl e<strong>the</strong>r<br />
(10–30%), toluene (0–30%), xylene (0–20%), 2-ethoxyethanol<br />
(0–20%), 2-butoxyethanol (0–20%), <strong>and</strong> methyl isobutyl<br />
ket<strong>on</strong>e (0–30%) (Hanaoka et al., 2002). The workers wore<br />
‘‘protecti<strong>on</strong> devices’’ during spraying. C<strong>on</strong>trols c<strong>on</strong>sisted<br />
of 42 male assembly workers from <strong>the</strong> same plants who<br />
Birth Defects Research (Part B) 83:157–395, 2008<br />
did not use bisphenol A diglycidyl e<strong>the</strong>r. In 1999, urine<br />
samples were collected periodically, treated with bglucur<strong>on</strong>idase,<br />
<strong>and</strong> examined for bisphenol A by HPLC.<br />
Urinary bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s were significantly<br />
higher in exposed workers (median: 1.06 mmol/mol<br />
creatinine [2.14 lg/g creatinine]; range: o0.05 pmol to<br />
11.2 mmol/mol creatinine [o0.1 pgto22.6 lg/g creatinine])<br />
compared to c<strong>on</strong>trols (median: 0.52 mmol/mol creatinine<br />
[1.05 lg/g creatinine];range: o0.05 pmol to 11.0 mmol/mol<br />
creatinine [o0.1 pg to 22.2 lg/g creatinine]). The difference<br />
of <strong>the</strong> averages was reported as 2.5 mmol/mol<br />
creatinine [5.05 lg/g creatinine] (95% c<strong>on</strong>fidence interval<br />
[CI] 1.4–4.7 mmol/mol creatinine [2.8–9.5]). Bisphenol A<br />
was not detected in three exposed workers <strong>and</strong> <strong>on</strong>e<br />
c<strong>on</strong>trol. [Assuming excreti<strong>on</strong> of 1200 mg/day creatinine<br />
(Ouchi <strong>and</strong> Watanabe, 2002), mean (ranges) of bisphenol<br />
excreti<strong>on</strong> in urine were 2.57 lg/day (o0.12 pg to 27.1 lg/<br />
day) in exposed workers <strong>and</strong> 1.26 lg/day (o0.12 pg to<br />
26.6 lg/day) in unexposed workers. With an assumed<br />
body weight of 60 kg, bisphenol A occupati<strong>on</strong>al intake<br />
was estimated at 0.043 lg/kg bw/day (o0.002 pg to<br />
0.45 lg/kg bw/day) in exposed workers <strong>and</strong> 0.021 lg/kg<br />
bw/day (o0.002 pg to 0.44 lg/kg bw/day) in unexposed<br />
workers.]<br />
1.3 Utility of Data<br />
Numerous studies reported bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
in canned foods <strong>and</strong> infant formula. Experiments<br />
examined potential c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s of bisphenol A