Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
208 CHAPIN ET AL.<br />
60–100% in each dose group with <strong>the</strong> excepti<strong>on</strong> of<br />
females exposed to 250 ppm was c<strong>on</strong>sidered to be<br />
treatment-related. No histological alterati<strong>on</strong>s were observed<br />
in <strong>the</strong> cecum. Death in mice was limited to 2 of 10<br />
females in <strong>the</strong> 5000 ppm group. Weight gain was reduced<br />
by at least 14% in male mice exposed to Z15,000 ppm.<br />
N<strong>on</strong>-dose-related decreases in weight gain of 17% or<br />
more occurred in female mice of all dose groups. A doserelated<br />
increase in multinucleated giant hepatocytes was<br />
observed in all dose groups of male mice; <strong>the</strong> <strong>on</strong>ly<br />
incidence data reported for multinucleated giant hepatocytes<br />
were 0 of 10 female c<strong>on</strong>trols <strong>and</strong> 9 of 10 male mice<br />
of <strong>the</strong> 25,000 ppm group. [A complete set of data for<br />
histopathological findings was not presented for rats or<br />
mice.]<br />
Yamasaki et al. (2002a) examined <strong>the</strong> effects of<br />
bisphenol A exposure <strong>on</strong> male <strong>and</strong> female CD rats in a<br />
study c<strong>on</strong>ducted according to Good Laboratory Practices<br />
(GLP). [Because this study included a number of<br />
reproductive organ <strong>and</strong> horm<strong>on</strong>e endpoints, it is also<br />
discussed in Secti<strong>on</strong>s 4.2.1.1 <strong>and</strong> 4.2.2.1.] Rats were fed a<br />
commercial diet (MF Oriental Yeast Co.) <strong>and</strong> housed in<br />
stainless steel wire-mesh cages. Rats were groups<br />
according to body weight <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong>n r<strong>and</strong>omly assigned<br />
to treatment groups. Ten 7-week-old rats/sex/group<br />
were gavaged with bisphenol A at 0 (olive oil vehicle),<br />
40, 200, or 1000 mg/kg bw/day for 28 days. Due to <strong>the</strong><br />
death of 1 animal exhibiting clinical signs in <strong>the</strong><br />
1000 mg/kg bw/day group, <strong>the</strong> high-dose was reduced<br />
to 600 mg/kg bw/day <strong>on</strong> Study Day 8. In an additi<strong>on</strong>al<br />
study, rats were exposed to ethinyl estradiol at 0, 10, 50,<br />
or 200 mg/kg bw/day for 28 days. Endpoints examined<br />
during <strong>the</strong> study were clinical signs, body weight gain,<br />
<strong>and</strong> food intake. Estrous cyclicity was examined in<br />
females for 2 weeks beginning <strong>on</strong> Study Day 15. Males<br />
were killed <strong>on</strong> Study Day 29 <strong>and</strong> females were killed in<br />
diestrus <strong>on</strong> Study Day 30, 31, or 32. Hematology <strong>and</strong><br />
clinical chemistry endpoints were assessed, <strong>and</strong> blood<br />
horm<strong>on</strong>e c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s were measured by immunoassay<br />
systems. Sperm motility <strong>and</strong> viability were evaluated.<br />
Organs, including those of <strong>the</strong> reproductive system,<br />
were weighed <strong>and</strong> subjected to histopathological evaluati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
With <strong>the</strong> excepti<strong>on</strong> of <strong>the</strong> testis <strong>and</strong> epididymis,<br />
which were fixed in Bouin soluti<strong>on</strong>, <strong>the</strong> organs were<br />
fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin. Statistical<br />
analyses included Bartlett test for homogeneity of<br />
variance, ANOVA, Dunnett test, <strong>and</strong>/or Kruskall–Wallis<br />
test.<br />
One female <strong>and</strong> 3 males from <strong>the</strong> high-dose group<br />
died; clinical signs observed in those animals included<br />
soft stools, decreased mobility, reduced respirati<strong>on</strong> rate,<br />
<strong>and</strong> decreased body temperature. Soft stools were also<br />
observed in surviving males <strong>and</strong> females of <strong>the</strong> mid- <strong>and</strong><br />
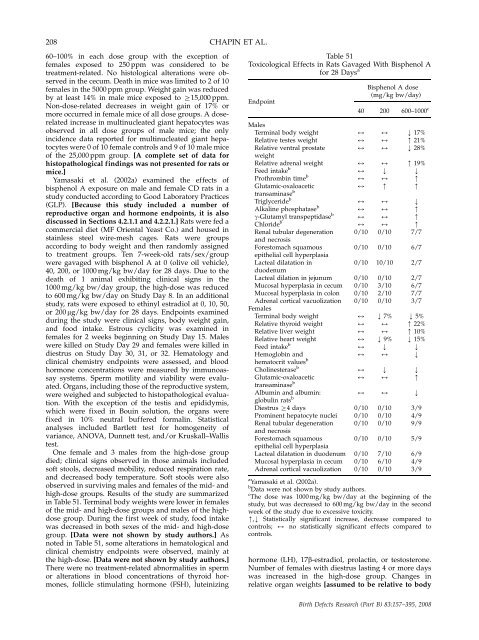
high-dose groups. Results of <strong>the</strong> study are summarized<br />
in Table 51. Terminal body weights were lower in females<br />
of <strong>the</strong> mid- <strong>and</strong> high-dose groups <strong>and</strong> males of <strong>the</strong> highdose<br />
group. During <strong>the</strong> first week of study, food intake<br />
was decreased in both sexes of <strong>the</strong> mid- <strong>and</strong> high-dose<br />
group. [Data were not shown by study authors.] As<br />
noted in Table 51, some alterati<strong>on</strong>s in hematological <strong>and</strong><br />
clinical chemistry endpoints were observed, mainly at<br />
<strong>the</strong> high-dose. [Data were not shown by study authors.]<br />
There were no treatment-related abnormalities in sperm<br />
or alterati<strong>on</strong>s in blood c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s of thyroid horm<strong>on</strong>es,<br />
follicle stimulating horm<strong>on</strong>e (FSH), luteinizing<br />
Table 51<br />
Toxicological Effects in Rats Gavaged With Bisphenol A<br />
for 28 Days a<br />
Endpoint<br />
Males<br />
Terminal body weight<br />
Relative testes weight<br />
Relative ventral prostate<br />
weight<br />
Relative adrenal weight<br />
Feed intake b<br />
Prothrombin time b<br />
Glutamic-oxaloacetic<br />
transaminase b<br />
Triglyceride b<br />
Alkaline phosphatase b<br />
g-Glutamyl transpeptidase b<br />
Chloride b<br />
Renal tubular degenerati<strong>on</strong><br />
<strong>and</strong> necrosis<br />
Forestomach squamous<br />
epi<strong>the</strong>lial cell hyperplasia<br />
Lacteal dilatati<strong>on</strong> in<br />
duodenum<br />
Lacteal dilati<strong>on</strong> in jejunum<br />
Mucosal hyperplasia in cecum<br />
Mucosal hyperplasia in col<strong>on</strong><br />
Adrenal cortical vacuolizati<strong>on</strong><br />
Females<br />
Terminal body weight<br />
Relative thyroid weight<br />
Relative liver weight<br />
Relative heart weight<br />
Feed intake b<br />
Hemoglobin <strong>and</strong><br />
hematocrit values b<br />
Cholinesterase b<br />
Glutamic-oxaloacetic<br />
transaminase b<br />
Albumin <strong>and</strong> albumin:<br />
globulin rats b<br />
Diestrus Z4 days<br />
Prominent hepatocyte nuclei<br />
Renal tubular degenerati<strong>on</strong><br />
<strong>and</strong> necrosis<br />
Forestomach squamous<br />
epi<strong>the</strong>lial cell hyperplasia<br />
Lacteal dilatati<strong>on</strong> in duodenum<br />
Mucosal hyperplasia in cecum<br />
Adrenal cortical vacuolizati<strong>on</strong><br />
Bisphenol A dose<br />
(mg/kg bw/day)<br />
40 200 600–1000 c<br />
2 2<br />
2 2<br />
2 2<br />
2 2<br />
2 k<br />
2 2<br />
2 m<br />
2 2<br />
2 2<br />
2 2<br />
2 2<br />
0/10 0/10<br />
0/10 0/10<br />
0/10 10/10<br />
0/10 0/10<br />
0/10 3/10<br />
0/10 2/10<br />
0/10 0/10<br />
2 k 7%<br />
2 2<br />
2 2<br />
2 k 9%<br />
2 k<br />
2 2<br />
2 k<br />
2 2<br />
2 2<br />
0/10 0/10<br />
0/10 0/10<br />
0/10 0/10<br />
0/10 0/10<br />
0/10 7/10<br />
0/10 6/10<br />
0/10 0/10<br />
k 17%<br />
m 21%<br />
k 28%<br />
m 19%<br />
k<br />
m<br />
m<br />
k<br />
m<br />
m<br />
m<br />
7/7<br />
6/7<br />
2/7<br />
2/7<br />
6/7<br />
7/7<br />
3/7<br />
k 5%<br />
m 22%<br />
m 10%<br />
k 15%<br />
k<br />
k<br />
a Yamasaki et al. (2002a).<br />
b Data were not shown by study authors.<br />
c The dose was 1000 mg/kg bw/day at <strong>the</strong> beginning of <strong>the</strong><br />
study, but was decreased to 600 mg/kg bw/day in <strong>the</strong> sec<strong>on</strong>d<br />
week of <strong>the</strong> study due to excessive toxicity.<br />
m,k Statistically significant increase, decrease compared to<br />
c<strong>on</strong>trols; 2 no statistically significant effects compared to<br />
c<strong>on</strong>trols.<br />
horm<strong>on</strong>e (LH), 17b-estradiol, prolactin, or testoster<strong>on</strong>e.<br />
Number of females with diestrus lasting 4 or more days<br />
was increased in <strong>the</strong> high-dose group. Changes in<br />
relative organ weights [assumed to be relative to body<br />
k<br />
m<br />
k<br />
3/9<br />
4/9<br />
9/9<br />
5/9<br />
6/9<br />
4/9<br />
3/9<br />
Birth Defects Research (Part B) 83:157–395, 2008