Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
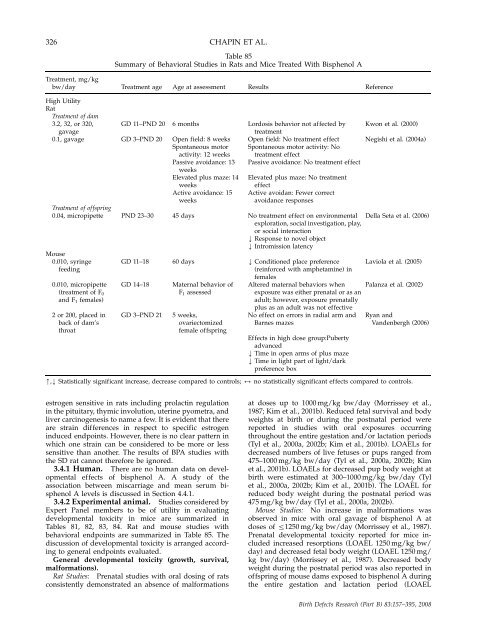
326 CHAPIN ET AL.<br />
Table 85<br />
Summary of Behavioral Studies in Rats <strong>and</strong> Mice Treated With Bisphenol A<br />
Treatment, mg/kg<br />
bw/day Treatment age Age at assessment Results Reference<br />
High Utility<br />
Rat<br />
Treatment of dam<br />
3.2, 32, or 320, GD 11–PND 20 6 m<strong>on</strong>ths Lordosis behavior not affected by Kw<strong>on</strong> et al. (2000)<br />
gavage treatment<br />
0.1, gavage GD 3–PND 20 Open field: 8 weeks Open field: No treatment effect Negishi et al. (2004a)<br />
Sp<strong>on</strong>taneous motor Sp<strong>on</strong>taneous motor activity: No<br />
activity: 12 weeks treatment effect<br />
Passive avoidance: 13 Passive avoidance: No treatment effect<br />
weeks<br />
Elevated plus maze: 14 Elevated plus maze: No treatment<br />
weeks effect<br />
Active avoidance: 15 Active avoidan: Fewer correct<br />
weeks avoidance resp<strong>on</strong>ses<br />
Treatment of offspring<br />
0.04, micropipette PND 23–30 45 days No treatment effect <strong>on</strong> envir<strong>on</strong>mental Della Seta et al. (2006)<br />
explorati<strong>on</strong>, social investigati<strong>on</strong>, play,<br />
or social interacti<strong>on</strong><br />
k Resp<strong>on</strong>se to novel object<br />
k Intromissi<strong>on</strong> latency<br />
Mouse<br />
0.010, syringe GD 11–18 60 days k C<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>ed place preference Laviola et al. (2005)<br />
feeding (reinforced with amphetamine) in<br />
females<br />
0.010, micropipette GD 14–18 Maternal behavior of Altered maternal behaviors when Palanza et al. (2002)<br />
(treatment of F0 F1 assessed exposure was ei<strong>the</strong>r prenatal or as an<br />
<strong>and</strong> F1 females) adult; however, exposure prenatally<br />
plus as an adult was not effective<br />
2 or 200, placed in GD 3–PND 21 5 weeks, No effect <strong>on</strong> errors in radial arm <strong>and</strong> Ryan <strong>and</strong><br />
back of dam’s ovariectomized Barnes mazes V<strong>and</strong>enbergh (2006)<br />
throat female offspring<br />
Effects in high dose group:Puberty<br />
advanced<br />
k Time in open arms of plus maze<br />
k Time in light part of light/dark<br />
preference box<br />
m,k Statistically significant increase, decrease compared to c<strong>on</strong>trols; 2 no statistically significant effects compared to c<strong>on</strong>trols.<br />
estrogen sensitive in rats including prolactin regulati<strong>on</strong><br />
in <strong>the</strong> pituitary, thymic involuti<strong>on</strong>, uterine pyometra, <strong>and</strong><br />
liver carcinogenesis to name a few. It is evident that <strong>the</strong>re<br />
are strain differences in respect to specific estrogen<br />
induced endpoints. However, <strong>the</strong>re is no clear pattern in<br />
which <strong>on</strong>e strain can be c<strong>on</strong>sidered to be more or less<br />
sensitive than ano<strong>the</strong>r. The results of BPA studies with<br />
<strong>the</strong> SD rat cannot <strong>the</strong>refore be ignored.<br />
3.4.1 <strong>Human</strong>. There are no human data <strong>on</strong> developmental<br />
effects of bisphenol A. A study of <strong>the</strong><br />
associati<strong>on</strong> between miscarriage <strong>and</strong> mean serum bisphenol<br />
A levels is discussed in Secti<strong>on</strong> 4.4.1.<br />
3.4.2 Experimental animal. Studies c<strong>on</strong>sidered by<br />
Expert Panel members to be of utility in evaluating<br />
developmental toxicity in mice are summarized in<br />
Tables 81, 82, 83, 84. Rat <strong>and</strong> mouse studies with<br />
behavioral endpoints are summarized in Table 85. The<br />
discussi<strong>on</strong> of developmental toxicity is arranged according<br />
to general endpoints evaluated.<br />
General developmental toxicity (growth, survival,<br />
malformati<strong>on</strong>s).<br />
Rat Studies: Prenatal studies with oral dosing of rats<br />
c<strong>on</strong>sistently dem<strong>on</strong>strated an absence of malformati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
at doses up to 1000 mg/kg bw/day (Morrissey et al.,<br />
1987; Kim et al., 2001b). Reduced fetal survival <strong>and</strong> body<br />
weights at birth or during <strong>the</strong> postnatal period were<br />
reported in studies with oral exposures occurring<br />
throughout <strong>the</strong> entire gestati<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong>/or lactati<strong>on</strong> periods<br />
(Tyl et al., 2000a, 2002b; Kim et al., 2001b). LOAELs for<br />
decreased numbers of live fetuses or pups ranged from<br />
475–1000 mg/kg bw/day (Tyl et al., 2000a, 2002b; Kim<br />
et al., 2001b). LOAELs for decreased pup body weight at<br />
birth were estimated at 300–1000 mg/kg bw/day (Tyl<br />
et al., 2000a, 2002b; Kim et al., 2001b). The LOAEL for<br />
reduced body weight during <strong>the</strong> postnatal period was<br />
475 mg/kg bw/day (Tyl et al., 2000a, 2002b).<br />
Mouse Studies: No increase in malformati<strong>on</strong>s was<br />
observed in mice with oral gavage of bisphenol A at<br />
doses of r1250 mg/kg bw/day (Morrissey et al., 1987).<br />
Prenatal developmental toxicity reported for mice included<br />
increased resorpti<strong>on</strong>s (LOAEL 1250 mg/kg bw/<br />
day) <strong>and</strong> decreased fetal body weight (LOAEL 1250 mg/<br />
kg bw/day) (Morrissey et al., 1987). Decreased body<br />
weight during <strong>the</strong> postnatal period was also reported in<br />
offspring of mouse dams exposed to bisphenol A during<br />
<strong>the</strong> entire gestati<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong> lactati<strong>on</strong> period (LOAEL<br />
Birth Defects Research (Part B) 83:157–395, 2008