Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
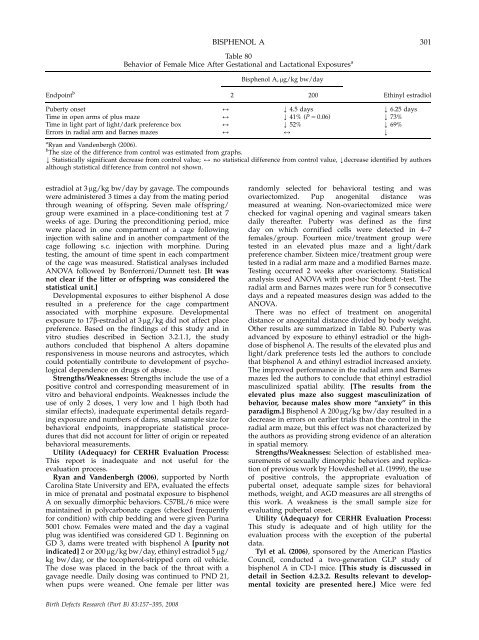
Endpoint b<br />
BISPHENOL A 301<br />
Table 80<br />
Behavior of Female Mice After Gestati<strong>on</strong>al <strong>and</strong> Lactati<strong>on</strong>al Exposures a<br />
Bisphenol A, mg/kg bw/day<br />
2 200 Ethinyl estradiol<br />
Puberty <strong>on</strong>set 2 k 4.5 days k 6.25 days<br />
Time in open arms of plus maze 2 k 41% (P 5 0.06) k 73%<br />
Time in light part of light/dark preference box 2 k 52% k 69%<br />
Errors in radial arm <strong>and</strong> Barnes mazes 2 2 k<br />
a Ryan <strong>and</strong> V<strong>and</strong>enbergh (2006).<br />
b The size of <strong>the</strong> difference from c<strong>on</strong>trol was estimated from graphs.<br />
k Statistically significant decrease from c<strong>on</strong>trol value; 2 no statistical difference from c<strong>on</strong>trol value, kdecrease identified by authors<br />
although statistical difference from c<strong>on</strong>trol not shown.<br />
estradiol at 3 mg/kg bw/day by gavage. The compounds<br />
were administered 3 times a day from <strong>the</strong> mating period<br />
through weaning of offspring. Seven male offspring/<br />
group were examined in a place-c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>ing test at 7<br />
weeks of age. During <strong>the</strong> prec<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>ing period, mice<br />
were placed in <strong>on</strong>e compartment of a cage following<br />
injecti<strong>on</strong> with saline <strong>and</strong> in ano<strong>the</strong>r compartment of <strong>the</strong><br />
cage following s.c. injecti<strong>on</strong> with morphine. During<br />
testing, <strong>the</strong> amount of time spent in each compartment<br />
of <strong>the</strong> cage was measured. Statistical analyses included<br />
ANOVA followed by B<strong>on</strong>ferr<strong>on</strong>i/Dunnett test. [It was<br />
not clear if <strong>the</strong> litter or offspring was c<strong>on</strong>sidered <strong>the</strong><br />
statistical unit.]<br />
Developmental exposures to ei<strong>the</strong>r bisphenol A dose<br />
resulted in a preference for <strong>the</strong> cage compartment<br />
associated with morphine exposure. Developmental<br />
exposure to 17b-estradiol at 3 mg/kg did not affect place<br />
preference. Based <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong> findings of this study <strong>and</strong> in<br />
vitro studies described in Secti<strong>on</strong> 3.2.1.1, <strong>the</strong> study<br />
authors c<strong>on</strong>cluded that bisphenol A alters dopamine<br />
resp<strong>on</strong>siveness in mouse neur<strong>on</strong>s <strong>and</strong> astrocytes, which<br />
could potentially c<strong>on</strong>tribute to development of psychological<br />
dependence <strong>on</strong> drugs of abuse.<br />
Strengths/Weaknesses: Strengths include <strong>the</strong> use of a<br />
positive c<strong>on</strong>trol <strong>and</strong> corresp<strong>on</strong>ding measurement of in<br />
vitro <strong>and</strong> behavioral endpoints. Weaknesses include <strong>the</strong><br />
use of <strong>on</strong>ly 2 doses, 1 very low <strong>and</strong> 1 high (both had<br />
similar effects), inadequate experimental details regarding<br />
exposure <strong>and</strong> numbers of dams, small sample size for<br />
behavioral endpoints, inappropriate statistical procedures<br />
that did not account for litter of origin or repeated<br />
behavioral measurements.<br />
Utility (Adequacy) for CERHR Evaluati<strong>on</strong> Process:<br />
This report is inadequate <strong>and</strong> not useful for <strong>the</strong><br />
evaluati<strong>on</strong> process.<br />
Ryan <strong>and</strong> V<strong>and</strong>enbergh (2006), supported by North<br />
Carolina State University <strong>and</strong> EPA, evaluated <strong>the</strong> effects<br />
in mice of prenatal <strong>and</strong> postnatal exposure to bisphenol<br />
A <strong>on</strong> sexually dimorphic behaviors. C57BL/6 mice were<br />
maintained in polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate cages (checked frequently<br />
for c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>) with chip bedding <strong>and</strong> were given Purina<br />
5001 chow. Females were mated <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> day a vaginal<br />
plug was identified was c<strong>on</strong>sidered GD 1. Beginning <strong>on</strong><br />
GD 3, dams were treated with bisphenol A [purity not<br />
indicated] 2 or 200 mg/kg bw/day, ethinyl estradiol 5 mg/<br />
kg bw/day, or <strong>the</strong> tocopherol-stripped corn oil vehicle.<br />
The dose was placed in <strong>the</strong> back of <strong>the</strong> throat with a<br />
gavage needle. Daily dosing was c<strong>on</strong>tinued to PND 21,<br />
when pups were weaned. One female per litter was<br />
Birth Defects Research (Part B) 83:157–395, 2008<br />
r<strong>and</strong>omly selected for behavioral testing <strong>and</strong> was<br />
ovariectomized. Pup anogenital distance was<br />
measured at weaning. N<strong>on</strong>-ovariectomized mice were<br />
checked for vaginal opening <strong>and</strong> vaginal smears taken<br />
daily <strong>the</strong>reafter. Puberty was defined as <strong>the</strong> first<br />
day <strong>on</strong> which cornified cells were detected in 4–7<br />
females/group. Fourteen mice/treatment group were<br />
tested in an elevated plus maze <strong>and</strong> a light/dark<br />
preference chamber. Sixteen mice/treatment group were<br />
tested in a radial arm maze <strong>and</strong> a modified Barnes maze.<br />
Testing occurred 2 weeks after ovariectomy. Statistical<br />
analysis used ANOVA with post-hoc Student t-test. The<br />
radial arm <strong>and</strong> Barnes mazes were run for 5 c<strong>on</strong>secutive<br />
days <strong>and</strong> a repeated measures design was added to <strong>the</strong><br />
ANOVA.<br />
There was no effect of treatment <strong>on</strong> anogenital<br />
distance or anogenital distance divided by body weight.<br />
O<strong>the</strong>r results are summarized in Table 80. Puberty was<br />
advanced by exposure to ethinyl estradiol or <strong>the</strong> highdose<br />
of bisphenol A. The results of <strong>the</strong> elevated plus <strong>and</strong><br />
light/dark preference tests led <strong>the</strong> authors to c<strong>on</strong>clude<br />
that bisphenol A <strong>and</strong> ethinyl estradiol increased anxiety.<br />
The improved performance in <strong>the</strong> radial arm <strong>and</strong> Barnes<br />
mazes led <strong>the</strong> authors to c<strong>on</strong>clude that ethinyl estradiol<br />
masculinized spatial ability. [The results from <strong>the</strong><br />
elevated plus maze also suggest masculinizati<strong>on</strong> of<br />
behavior, because males show more ‘‘anxiety’’ in this<br />
paradigm.] Bisphenol A 200 mg/kg bw/day resulted in a<br />
decrease in errors <strong>on</strong> earlier trials than <strong>the</strong> c<strong>on</strong>trol in <strong>the</strong><br />
radial arm maze, but this effect was not characterized by<br />
<strong>the</strong> authors as providing str<strong>on</strong>g evidence of an alterati<strong>on</strong><br />
in spatial memory.<br />
Strengths/Weaknesses: Selecti<strong>on</strong> of established measurements<br />
of sexually dimorphic behaviors <strong>and</strong> replicati<strong>on</strong><br />
of previous work by Howdeshell et al. (1999), <strong>the</strong> use<br />
of positive c<strong>on</strong>trols, <strong>the</strong> appropriate evaluati<strong>on</strong> of<br />
pubertal <strong>on</strong>set, adequate sample sizes for behavioral<br />
methods, weight, <strong>and</strong> AGD measures are all strengths of<br />
this work. A weakness is <strong>the</strong> small sample size for<br />
evaluating pubertal <strong>on</strong>set.<br />
Utility (Adequacy) for CERHR Evaluati<strong>on</strong> Process:<br />
This study is adequate <strong>and</strong> of high utility for <strong>the</strong><br />
evaluati<strong>on</strong> process with <strong>the</strong> excepti<strong>on</strong> of <strong>the</strong> pubertal<br />
data.<br />
Tyl et al. (2006), sp<strong>on</strong>sored by <strong>the</strong> American Plastics<br />
Council, c<strong>on</strong>ducted a two-generati<strong>on</strong> GLP study of<br />
bisphenol A in CD-1 mice. [This study is discussed in<br />
detail in Secti<strong>on</strong> 4.2.3.2. Results relevant to developmental<br />
toxicity are presented here.] Mice were fed