Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
Monograph on the Potential Human Reproductive and ... - OEHHA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
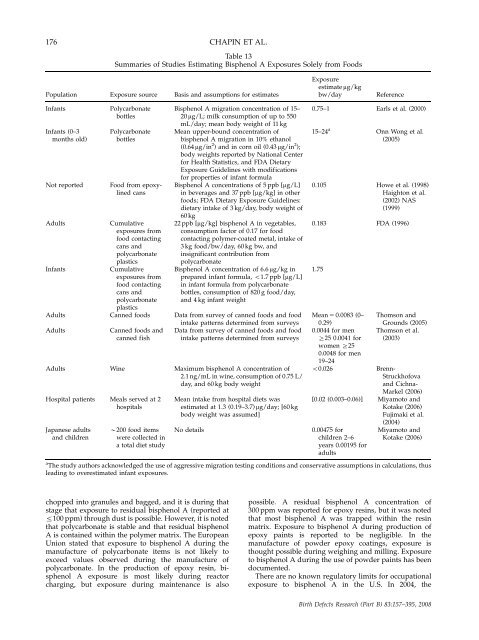
176 CHAPIN ET AL.<br />
Table 13<br />
Summaries of Studies Estimating Bisphenol A Exposures Solely from Foods<br />
Exposure<br />
estimate mg/kg<br />
Populati<strong>on</strong> Exposure source Basis <strong>and</strong> assumpti<strong>on</strong>s for estimates bw/day Reference<br />
Infants Polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate<br />
bottles<br />
Infants (0–3 Polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate<br />
m<strong>on</strong>ths old) bottles<br />
Not reported Food from epoxylined<br />
cans<br />
Adults Cumulative<br />
exposures from<br />
food c<strong>on</strong>tacting<br />
cans <strong>and</strong><br />
polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate<br />
plastics<br />
Infants Cumulative<br />
exposures from<br />
food c<strong>on</strong>tacting<br />
cans <strong>and</strong><br />
polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate<br />
plastics<br />
Adults Canned foods<br />
Adults Canned foods <strong>and</strong><br />
canned fish<br />
Adults Wine<br />
Hospital patients Meals served at 2<br />
hospitals<br />
Japanese adults B200 food items<br />
<strong>and</strong> children were collected in<br />
a total diet study<br />
Bisphenol A migrati<strong>on</strong> c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> of 15–<br />
20 mg/L; milk c<strong>on</strong>sumpti<strong>on</strong> of up to 550<br />
mL/day; mean body weight of 11 kg<br />
Mean upper-bound c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> of<br />
bisphenol A migrati<strong>on</strong> in 10% ethanol<br />
(0.64 mg/in 2 ) <strong>and</strong> in corn oil (0.43 mg/in 2 );<br />
body weights reported by Nati<strong>on</strong>al Center<br />
for Health Statistics, <strong>and</strong> FDA Dietary<br />
Exposure Guidelines with modificati<strong>on</strong>s<br />
for properties of infant formula<br />
Bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong>s of 5 ppb [mg/L]<br />
in beverages <strong>and</strong> 37 ppb [mg/kg] in o<strong>the</strong>r<br />
foods; FDA Dietary Exposure Guidelines:<br />
dietary intake of 3 kg/day, body weight of<br />
60 kg<br />
22 ppb [mg/kg] bisphenol A in vegetables,<br />
c<strong>on</strong>sumpti<strong>on</strong> factor of 0.17 for food<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tacting polymer-coated metal, intake of<br />
3 kg food/bw/day, 60 kg bw, <strong>and</strong><br />
insignificant c<strong>on</strong>tributi<strong>on</strong> from<br />
polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate<br />
Bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> of 6.6 mg/kg in<br />
prepared infant formula, o1.7 ppb [mg/L]<br />
in infant formula from polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate<br />
bottles, c<strong>on</strong>sumpti<strong>on</strong> of 820 g food/day,<br />
<strong>and</strong> 4 kg infant weight<br />
Data from survey of canned foods <strong>and</strong> food<br />
intake patterns determined from surveys<br />
Data from survey of canned foods <strong>and</strong> food<br />
intake patterns determined from surveys<br />
Maximum bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> of<br />
2.1 ng/mL in wine, c<strong>on</strong>sumpti<strong>on</strong> of 0.75 L/<br />
day, <strong>and</strong> 60 kg body weight<br />
Mean intake from hospital diets was<br />
estimated at 1.3 (0.19–3.7) mg/day; [60 kg<br />
body weight was assumed]<br />
No details<br />
0.75–1 Earls et al. (2000)<br />
15–24 a<br />
Onn W<strong>on</strong>g et al.<br />
(2005)<br />
0.105 Howe et al. (1998)<br />
Haight<strong>on</strong> et al.<br />
(2002) NAS<br />
(1999)<br />
0.183 FDA (1996)<br />
1.75<br />
Mean 5 0.0083 (0– Thoms<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong><br />
0.29) Grounds (2005)<br />
0.0044 for men Thoms<strong>on</strong> et al.<br />
Z25 0.0041 for (2003)<br />
women Z25<br />
0.0048 for men<br />
19–24<br />
o0.026 Brenn-<br />
Struckhofova<br />
<strong>and</strong> Cichna-<br />
Markel (2006)<br />
[0.02 (0.003–0.06)] Miyamoto <strong>and</strong><br />
Kotake (2006)<br />
Fujimaki et al.<br />
(2004)<br />
0.00475 for Miyamoto <strong>and</strong><br />
children 2–6 Kotake (2006)<br />
years 0.00195 for<br />
adults<br />
a<br />
The study authors acknowledged <strong>the</strong> use of aggressive migrati<strong>on</strong> testing c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s <strong>and</strong> c<strong>on</strong>servative assumpti<strong>on</strong>s in calculati<strong>on</strong>s, thus<br />
leading to overestimated infant exposures.<br />
chopped into granules <strong>and</strong> bagged, <strong>and</strong> it is during that possible. A residual bisphenol A c<strong>on</strong>centrati<strong>on</strong> of<br />
stage that exposure to residual bisphenol A (reported at 300 ppm was reported for epoxy resins, but it was noted<br />
r100 ppm) through dust is possible. However, it is noted that most bisphenol A was trapped within <strong>the</strong> resin<br />
that polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate is stable <strong>and</strong> that residual bisphenol matrix. Exposure to bisphenol A during producti<strong>on</strong> of<br />
A is c<strong>on</strong>tained within <strong>the</strong> polymer matrix. The European epoxy paints is reported to be negligible. In <strong>the</strong><br />
Uni<strong>on</strong> stated that exposure to bisphenol A during <strong>the</strong> manufacture of powder epoxy coatings, exposure is<br />
manufacture of polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate items is not likely to thought possible during weighing <strong>and</strong> milling. Exposure<br />
exceed values observed during <strong>the</strong> manufacture of to bisphenol A during <strong>the</strong> use of powder paints has been<br />
polycarb<strong>on</strong>ate. In <strong>the</strong> producti<strong>on</strong> of epoxy resin, bi- documented.<br />
sphenol A exposure is most likely during reactor There are no known regulatory limits for occupati<strong>on</strong>al<br />
charging, but exposure during maintenance is also exposure to bisphenol A in <strong>the</strong> U.S. In 2004, <strong>the</strong><br />
Birth Defects Research (Part B) 83:157–395, 2008