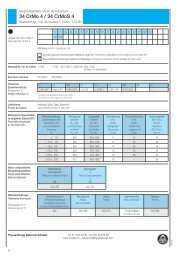
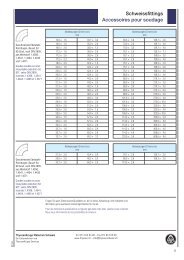
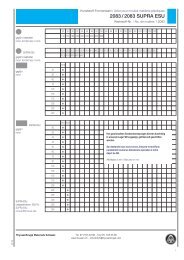
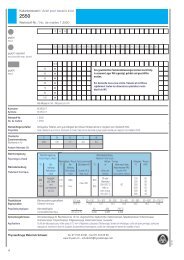
Engineering
Engineering
Engineering
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3.6 Consolidated financial statements Notes to the consolidated financial statements<br />
3.6 Consolidated financial statements Notes to the consolidated financial statements<br />
Impairments in the form of individual allowances for doubtful accounts<br />
adequately consider default risk. When there is objective evidence of<br />
default, the receivable concerned is derecognized. Receivables that are<br />
immaterial, and receivables of similar default risk, are grouped<br />
together and tested collectively for impairment based on past<br />
experience. Partially, impairments are accounted for using separate<br />
allowance accounts. Whether default risk is recognized by means of an<br />
allowance account or a direct derecognition of the receivable depends<br />
on the probability of default and the reliability of its estimation.<br />
Receivables that do not bear interest or bear below market interest<br />
rates and have an expected term of more than one year are discounted<br />
with the discount subsequently amortized to interest income over the<br />
term of the receivable.<br />
The Group sells undivided interests in certain trade accounts and notes<br />
receivable both on an ongoing and one-time basis to special purpose<br />
entities, which are not required to be consolidated, or to other lending<br />
institutions. Financial assets sold under these arrangements are<br />
excluded from accounts receivable in the Group’s balance sheet at the<br />
time of sale if it is assured that the cash flows related to those<br />
receivables will be passed through to the acquirer and substantially all<br />
risks and rewards have been transferred. If substantially all risks and<br />
rewards have neither been transferred nor retained, financial assets<br />
are excluded from the books at the time of the sale if it is assured that<br />
the cash flows of the receivables will be passed through to the acquirer<br />
and the acquirer has gained control over the receivables. If<br />
substantially all risks and rewards have been retained financial assets<br />
remain in the Group’s balance sheet as collateral for borrowings.<br />
Cash and cash equivalents<br />
Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand and demand deposits<br />
as well as financial assets that are readily convertible to cash and<br />
which are only subject to an insignificant risk of change in value, they<br />
are measured at amortized cost.<br />
Financial assets held for trading<br />
Derivatives that are not part of an effective hedge accounting in<br />
accordance with IAS 39 must be assigned to this category when the<br />
fair value is positive as of measurement date. Gains or losses resulting<br />
from changes in fair value are recognized in profit or loss.<br />
Available-for-sale financial assets<br />
Available-for-sale financial assets are those non-derivative financial<br />
assets not assigned to any of the above categories (trade accounts<br />
receivable and other current receivables, cash and cash equivalents,<br />
and financial assets held for trading). This category includes primarily<br />
equity and debt instruments which are in general measured at fair<br />
value. Gains or losses resulting from the measurement of available-forsale<br />
financial assets are recognized directly in equity, with the<br />
exception of impairment losses and foreign currency conversion<br />
effects. On disposal of these financial assets, a cumulative gain or loss<br />
recognized directly in equity until then is recognized in profit or loss of<br />
the respective period. When the fair value of unlisted equity<br />
instruments cannot be reliably measured, they are measured at cost.<br />
Financial assets measured at fair value through profit or loss<br />
The Group does not use the option to categorize financial assets at fair<br />
value through profit or loss when initially recognized.<br />
Impairment of financial assets<br />
At each balance sheet date, an assessment is made of whether there<br />
is any objective evidence that the carrying amounts of financial assets<br />
not carried at fair value through profit or loss are impaired. Objective<br />
evidence includes, for example, considerable financial difficulty of the<br />
debtor obligor, disappearance of an active market, and significant<br />
changes in the technological, market, economic or legal environment.<br />
A significant or prolonged decline in the fair value of an equity<br />
instrument is an objective evidence of impairment.<br />
The impairment loss on a financial asset carried at amortized cost is<br />
measured as the difference between the asset’s carrying amount and<br />
the present value of estimated future cash flows discounted at the<br />
financial asset’s original effective interest rate. An impairment loss is<br />
recognized in profit or loss.<br />
138