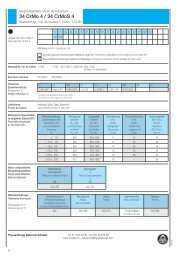
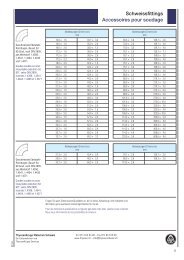
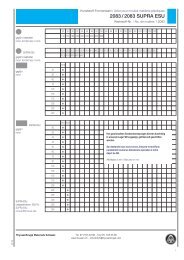
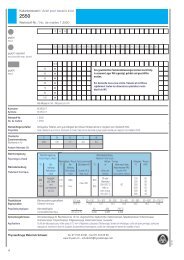
Engineering
Engineering
Engineering
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3.6 Consolidated financial statements Notes to the consolidated financial statements<br />
3.6 Consolidated financial statements Notes to the consolidated financial statements<br />
Derivates that do not qualify for hedge accounting<br />
If a hedging relationship does not meet the requirements for hedge<br />
accounting in accordance with the conditions under IAS 39, the<br />
derivative financial instrument is recognized as a derivative that does<br />
not qualify for hedge accounting. The resulting impact on profit or loss<br />
is shown in the table on net gains and losses from financial<br />
instruments by measurement categories. This item also includes<br />
embedded derivatives. They exist in the ThyssenKrupp Group in the<br />
way that regular supply and service transactions with suppliers and<br />
customers abroad are not concluded in the functional currency (local<br />
currency) of either contracting parties.<br />
Financial risks<br />
The management of ThyssenKrupp AG has implemented a risk<br />
management system that is monitored by the Supervisory Board. The<br />
general conditions for compliance with the requirements for proper and<br />
future-oriented risk management within the ThyssenKrupp Group are<br />
set out in the risk management principles. These principles aim at<br />
encouraging all Group members of staff to responsibly deal with risks<br />
as well as supporting a sustained process to improve risk awareness.<br />
The Group guideline on risk management and other Group guidelines<br />
specify risk management processes, compulsory limitations, and the<br />
application of financial instruments. The risk management system aims<br />
at identifying, analyzing, managing, controlling and communicating<br />
risks promptly throughout the Group. ThyssenKrupp Group’s risk<br />
environment is updated at least twice a year by carrying out a risk<br />
inventory in all Group companies. The results of the risk inventory<br />
process are communicated to both ThyssenKrupp AG’s Executive<br />
Board and the Supervisory Board's audit committee. Risk management<br />
reporting is a continuous process and part of regular Group reporting.<br />
Group guidelines and information systems are checked regularly and<br />
adapted to current developments. In addition, the internal auditing<br />
department regularly checks whether Group companies comply with<br />
risk management system requirements.<br />
Being a global Group, ThyssenKrupp is exposed to credit, liquidity and<br />
market risks (foreign currency, interest rate and commodity price risks)<br />
during the course of ordinary activities. The aim of risk management is<br />
to limit the risks arising from operating activities and associated<br />
financing requirements by applying selected derivate and nonderivative<br />
hedging instruments.<br />
Credit risk (counterparty default risk)<br />
To the Group, financial instruments bear default risk resulting from one<br />
party’s possible failure to meet its payment obligations, with the<br />
maximum default risk being equal to the positive fair value of the<br />
respective financial instrument. During crises, default risks take on<br />
greater significance; we are managing them very carefully by our<br />
business policy. In order to minimize default risk, the ThyssenKrupp<br />
Group only enters into financial instruments for financing purposes<br />
with contracting parties that have a very good credit standing or are<br />
members of a deposit protection fund. For further risk minimizing<br />
transactions are concluded in compliance with specified risk limits. In<br />
the operative area, receivables and default risks are monitored by<br />
Group companies on an ongoing basis and partially covered by<br />
merchandise credit insurance. Risks arising from the delivery of goods<br />
to major customers are subject to a special credit watch. In addition,<br />
letters of credit and indemnity bonds are used to hedge receivables<br />
from major customers. However, receivables from these contracting<br />
parties do not reach levels that would result in extraordinary risk<br />
concentrations. Default risk is taken into account by valuation<br />
allowances.<br />
Liquidity risk<br />
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Group is unable to meet its existing or<br />
future obligations due to insufficient availability of cash or cash<br />
equivalents. Managing liquidity risk, and therefore allocating resources<br />
and hedging the Group’s financial independence, are some of the<br />
central tasks of ThyssenKrupp AG. In order to be able to ensure the<br />
Group’s solvency and financial flexibility at all times, long-term credit<br />
limits and cash and cash equivalents are reserved on the basis of<br />
perennial financial planning and monthly rolling liquidity planning.<br />
Cash pooling and external financing focus primarily on ThyssenKrupp<br />
AG and specific financing companies. Despite the partially still difficult<br />
market environment as a consequence of the financial crisis and the<br />
current debt crisis of some countries, our financing is also secured for<br />
the next fiscal year.<br />
Cash pooling and external financing focus primarily on ThyssenKrupp<br />
AG and specific financing companies. Funds are provided internally to<br />
Group companies according to need.<br />
182