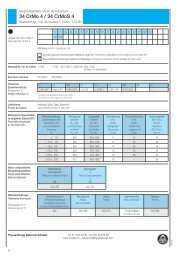
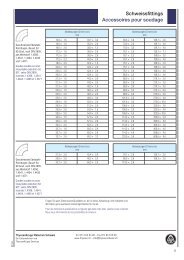
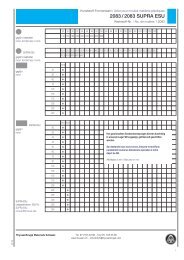
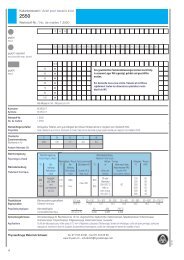
Engineering
Engineering
Engineering
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3.6 Consolidated financial statements Notes to the consolidated financial statements<br />
interest level this approach is also maintained for the current analysis.<br />
The analysis results in the opportunities (positive values) and risks<br />
(negative values) shown in the following table:<br />
million €<br />
Changes in all yield curves<br />
as of Sept. 30, 2011 by<br />
+ 100 basis<br />
points<br />
(20) basis<br />
points<br />
Cash flow risk 26 (5)<br />
Opportunity effects<br />
Interest rate risks resulting from interest rate<br />
164 (34)<br />
derivatives affecting balance sheet<br />
Interest rate risks resulting from interest rate<br />
(1) 0<br />
derivatives affecting earnings 0 0<br />
In the previous year the analysis resulted in the opportunities (positive<br />
values) and risks (negative values) shown in the following table:<br />
million €<br />
Changes in all yield curves<br />
as of Sept. 30, 2010 by<br />
+ 100 basis<br />
points<br />
(20) basis<br />
points<br />
Cash flow risk 27 (5)<br />
Opportunity effects<br />
Interest rate risks resulting from interest rate<br />
203 (42)<br />
derivatives affecting balance sheet<br />
Interest rate risks resulting from interest rate<br />
2 0<br />
derivatives affecting earnings 0 0<br />
If, as of September 30, 2011, all yield curves combined had been 100<br />
basis points higher, the hedge reserve in equity and fair value of the<br />
relevant interest derivatives would have been €1 million lower (2010:<br />
€2 million higher) and earnings resulting from the measurement as of<br />
the balance sheet date €26 million (2009/2010: €27 million) higher. If,<br />
as of September 30, 2011, all yield curves combined had been 20<br />
basis points lower, the hedge reserve in equity and fair value of the<br />
relevant interest derivatives would have been unchanged as in the<br />
previous year and earnings resulting from the measurement as of the<br />
balance sheet date €5 million (2009/2010: €5 million) lower.<br />
Commodity price risks<br />
The Group uses various nonferrous metals, especially nickel, as well as<br />
commodities such as ore, coal, coke and energy, for different<br />
production processes. Purchase prices for commodities and energy<br />
can vary significantly depending on market conditions.<br />
Consolidated financial statements<br />
184 | 185<br />
This causes commodity price risks which can affect income, equity and<br />
cash flow. We react with adjusted selling prices and alternative<br />
purchasing resources to ensure our competitiveness. To minimize risks<br />
arising from commodity price volatilities, the Group also uses<br />
derivatives, especially for nickel and copper. The contracting of such<br />
financial derivatives is subject to strict guidelines which are checked for<br />
compliance by internal auditing. The nonferrous metals are generally<br />
hedged by a central system. Only marketable instruments are used, as<br />
there are mainly commodity forward contracts. Commodity forward<br />
contracts are measured at fair value. Fluctuations in fair value are<br />
recognized predominately in profit or loss under sales revenue or cost<br />
of sales. Sometimes cash flow hedge accounting is used when<br />
commodity derivatives are immediately and directly allocated to a<br />
particular firm commitment. In some cases, fair value hedges are used<br />
to hedge the exposure to changes in fair value of a firm commitment<br />
and exposure to inventory price risks.<br />
Risks resulting from rising energy prices are limited by structuring<br />
procurement on the electricity market and concluding or extending<br />
long-term natural gas contracts. These contracts are subject to the socalled<br />
“own use exemption” and therefore not carried as derivatives.<br />
Only hypothetical changes in market prices for derivatives are included<br />
in scenario analysis, required for financial instruments under IFRS 7.<br />
Offsetting effects from underlying transactions are not taken into<br />
account and would reduce their effect significantly.<br />
As of September 30, 2011 a +20/(20)% shift in market prices for<br />
commodities is assumed. The prior year assumptions of market prices<br />
at production cost level of important manufacturers respectively<br />
historical peak market prices have been replaced by this shift in market<br />
prices which seems to be more probable. If an increase of 20%<br />
(2009/2010: 142%) in market prices for said commodities is assumed,<br />
the estimated hypothetical impact on profit or loss resulting from the<br />
measurement as of the balance sheet date is 0 (2009/2010: €(200)<br />
million), and on equity €(9) million (2010: €113 million). If a decrease<br />
of 20% (2009/2010: 78%) in market prices for said commodities is<br />
assumed, the estimated hypothetical impact on profit or loss resulting<br />
from the measurement as of the balance sheet date is €65 million<br />
(2009/2010: €142 million), and on equity €(46) million (2010: €(50)<br />
million).