Yoshida - 1981 - Fundamentals of Rice Crop Science
Yoshida - 1981 - Fundamentals of Rice Crop Science
Yoshida - 1981 - Fundamentals of Rice Crop Science
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
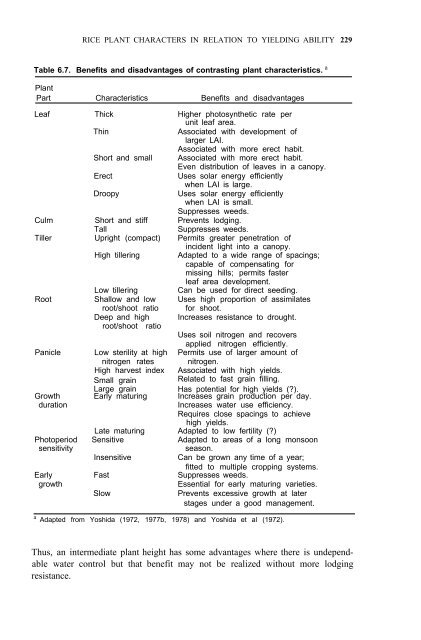
RICE PLANT CHARACTERS IN RELATION TO YIELDING ABILITY 229<br />
Table 6.7. Benefits and disadvantages <strong>of</strong> contrasting plant characteristics. a<br />
Plant<br />
Part Characteristics Benefits and disadvantages<br />
Leaf Thick<br />
Thin<br />
Higher photosynthetic rate per<br />
unit leaf area.<br />
Associated with development <strong>of</strong><br />
larger LAI.<br />
Associated with more erect habit.<br />
Short and small Associated with more erect habit.<br />
Even distribution <strong>of</strong> leaves in a canopy.<br />
Erect<br />
Uses solar energy efficiently<br />
Droopy<br />
when LAI is large.<br />
Uses solar energy efficiently<br />
when LAI is small.<br />
Suppresses weeds.<br />
Culm Short and stiff Prevents lodging.<br />
Tall<br />
Suppresses weeds.<br />
Tiller Upright (compact)<br />
High tillering<br />
Permits greater penetration <strong>of</strong><br />
incident light into a canopy.<br />
Adapted to a wide range <strong>of</strong> spacings;<br />
capable <strong>of</strong> compensating for<br />
missing hills; permits faster<br />
leaf area development.<br />
Low tillering<br />
Can be used for direct seeding.<br />
Root Shallow and low Uses high proportion <strong>of</strong> assimilates<br />
root/shoot ratio for shoot.<br />
Deep and high Increases resistance to drought.<br />
root/shoot ratio<br />
Uses soil nitrogen and recovers<br />
applied nitrogen efficiently.<br />
Panicle Low sterility at high Permits use <strong>of</strong> larger amount <strong>of</strong><br />
nitrogen rates nitrogen.<br />
High harvest index Associated with high yields.<br />
Small grain<br />
Related to fast grain filling.<br />
Growth<br />
Large grain<br />
Early maturing<br />
Has potential for high yields (?).<br />
Increases grain production per day.<br />
duration<br />
Increases water use efficiency.<br />
Requires close spacings to achieve<br />
high yields.<br />
Late maturing Adapted to low fertility (?)<br />
Photoperiod Sensitive Adapted to areas <strong>of</strong> a long monsoon<br />
sensitivity<br />
season.<br />
Insensitive<br />
Can be grown any time <strong>of</strong> a year;<br />
fitted to multiple cropping systems.<br />
Early Fast Suppresses weeds.<br />
growth<br />
Slow<br />
Essential for early maturing varieties.<br />
Prevents excessive growth at later<br />
stages under a good management.<br />
a Adapted from <strong>Yoshida</strong> (1972, 1977b, 1978) and <strong>Yoshida</strong> et al (1972).<br />
Thus, an intermediate plant height has some advantages where there is undependable<br />
water control but that benefit may not be realized without more lodging<br />
resistance.