Indice - Giornale Italiano di Medicina del Lavoro ed Ergonomia ...
Indice - Giornale Italiano di Medicina del Lavoro ed Ergonomia ...
Indice - Giornale Italiano di Medicina del Lavoro ed Ergonomia ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
G Ital M<strong>ed</strong> Lav Erg 2006; 28:3, Suppl 91<br />
www.gimle.fsm.it<br />
PHOSPHATIDYLSERINE METABOLISM DURING CHROMIUM<br />
(VI)-INDUCED APOPTOSIS IN HUMAN LYMPHOBLASTIC<br />
CELLS<br />
Key words: chromium VI, phosphatidylserine, apoptosis.<br />
ABSTRACT. Hexavalent Chromium (Cr VI) compounds, which are<br />
recogniz<strong>ed</strong> human carcinogens, induce apoptosis with mechanisms that<br />
have not been completely clarifi<strong>ed</strong>.<br />
Phosphatidylserine (PS) exposure toward the external surface of the<br />
membrane is a well-establish<strong>ed</strong> event of programm<strong>ed</strong> cell death; in<br />
ad<strong>di</strong>tion, apoptotic stimuli mo<strong>di</strong>fy PS metabolism in several cell types.<br />
Cr (VI) induces apoptosis in a human lymphoblastic cell line (MOLT-4).<br />
In this study we evaluat<strong>ed</strong> whether PS metabolism is mo<strong>di</strong>fi<strong>ed</strong> during<br />
Cr (VI)-induc<strong>ed</strong> apoptosis in MOLT-4 cells, measuring the<br />
incorporation of [ 3 H]serine into PS and the conversion of newly<br />
synthesis<strong>ed</strong> PS into metabolically relat<strong>ed</strong> glycerophospholipids. The<br />
apoptosis level and PS exposure were measur<strong>ed</strong> in parallel samples<br />
using propi<strong>di</strong>um io<strong>di</strong>de solution and annexin V bin<strong>di</strong>ng, respectively.<br />
Cell treatment with 200 µM Cr (VI) decreas<strong>ed</strong> the incorporation of<br />
[ 3 H]serine into PS before DNA fragmentation and PS exposure. Newly<br />
synthesiz<strong>ed</strong> PS was decarboxylat<strong>ed</strong> to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE);<br />
ra<strong>di</strong>oactive PE/ PS ratio was decreas<strong>ed</strong> 6 and 12 hours after Cr (VI)<br />
treatment causing apoptosis.<br />
In conclusion, this study demonstrates that Cr (VI) treatment increases<br />
PS exposure and mo<strong>di</strong>fies PS metabolism in MOLT-4 cells. These events<br />
appear correlat<strong>ed</strong> with Cr (VI)-induc<strong>ed</strong> apoptosis. These fin<strong>di</strong>ngs could<br />
be relevant in elucidating the mechanism underlying Cr (VI)-induc<strong>ed</strong><br />
apoptosis in MOLT-4 cells.<br />
INTRODUZIONE<br />
Il cromo è un metallo <strong>di</strong> transizione la cui evidenza <strong>di</strong> cancerogenicità<br />
è per la IARC “inadeguata per cromo metallico e composti <strong>del</strong> cromo<br />
trivalente per l’uomo”, “sufficiente per i composti <strong>del</strong> cromo esavalente”quin<strong>di</strong><br />
classificati nel gruppo 1 (1). L’impiego <strong>del</strong> Cromo (Cr) è <strong>di</strong>ffuso<br />
in molti processi industriali. Numerosi stu<strong>di</strong> hanno <strong>di</strong>mostrato che a<br />
livello cellulare il Cr innesca processi ossidativi (2, 3) che danneggiano il<br />
DNA inducendo l’arresto <strong>del</strong> ciclo cellulare, l’apoptosi o la trasformazione<br />
neoplastica. Il meccanismo citotossico alla base <strong>di</strong> tali meccanismi<br />
non è tuttavia completamente chiarito.<br />
È generalmente accettato che le cellule apoptotiche espongono sulla<br />
superficie cellulare la fosfati<strong>di</strong>lserina (PS), normalmente presente sul lato<br />
citosolico <strong>del</strong>la membrana, e che questo evento determini il loro riconoscimento<br />
<strong>ed</strong> eliminazione da parte dei macrofagi. Il meccanismo molecolare<br />
alla base <strong>del</strong>l’esposizione <strong>del</strong>la PS non è ancora definito e potrebbe,<br />
almeno in parte, <strong>di</strong>pendere dal tipo cellulare. In alcune cellule, stimoli<br />
apoptotici causano aumento <strong>del</strong>la sintesi <strong>di</strong> PS (4, 5, 6), che potrebbe contribuire<br />
alla sua esposizione. Il fenomeno non può però essere generalizzato,<br />
in quanto macrofagi indotti all’apoptosi da infezione con streptococco<br />
<strong>di</strong> gruppo B (GBS) espongono la PS pur avendo una <strong>di</strong>minuita sintesi<br />
<strong>del</strong> fosfolipide (7).<br />
Le variazioni nella sintesi <strong>di</strong> PS sopra menzionate potrebbero avere<br />
un ruolo rilevante nell’in<strong>di</strong>rizzare la cellula verso la morte programmata,<br />
in quanto è nota la capacità <strong>del</strong> fosfolipide <strong>di</strong> modulare l’attività <strong>di</strong> numerose<br />
proteine implicate nella trasduzione dei segnali.<br />
Cellule linfocitarie umane (MOLT-4) sono indotte all’apoptosi in<br />
modo dose e tempo-<strong>di</strong>pendente dall’esposizione al Cr VI (8). In questo<br />
stu<strong>di</strong>o, abbiamo verificato se il metabolismo <strong>del</strong>la PS fosse mo<strong>di</strong>ficato,<br />
durante l’apoptosi indotta dal Cr VI, in cellule MOLT-4, misurando l’incorporazione<br />
<strong>del</strong>la [ 3 H]serina nella PS e la conversione <strong>del</strong>la PS <strong>di</strong> nuova<br />
sintesi nei fosfolipi<strong>di</strong> ad essa correlati. Esperimenti paralleli sono stati<br />
condotti per verificare se anche in tale mo<strong>del</strong>lo <strong>di</strong> apoptosi venisse esposta<br />
la PS.<br />
MATERIALI E METODI<br />
Cellule MOLT-4 (ATCC N. CRL-1582) (5x10 5 cellule/pozzetto)<br />
erano poste, in doppio, in 2 ml RPMI-1640 supplementato con 20% FBS,<br />
glutamina (2 mM) e gentamicina (80 mg/l) (me<strong>di</strong>um) e mantenute in atmosfera<br />
al 5% <strong>di</strong> CO 2 a 37°C.<br />
L’effetto <strong>del</strong> Cr VI sul metabolismo <strong>del</strong>la PS è stato stu<strong>di</strong>ato incubando<br />
le cellule per <strong>di</strong>versi tempi (1, 2, 4, 6, 12 ore) nel me<strong>di</strong>um contenente<br />
30 µCi L-[ 3 H(G)]serina (S.R. 25.8 mCi/mmol,; Perkin Elmer, Boston,<br />
USA), in presenza o assenza <strong>di</strong> Cr VI, utilizzato a 2 concentrazioni<br />
(9 e 200 µM). Al termine <strong>del</strong>l’incubazione, le cellule erano centrifugate a<br />
200xg per 10 minuti <strong>ed</strong> era valutata la ra<strong>di</strong>oattività nella PS. L’estrazione<br />
lipi<strong>di</strong>ca, la separazione dei fosfolipi<strong>di</strong> me<strong>di</strong>ante cromatografia bi<strong>di</strong>mensionale<br />
su strato sottile e la misura <strong>del</strong>la ra<strong>di</strong>oattività nella PS, nella fosfati<strong>di</strong>letanolammina<br />
(PE) e nella fosfati<strong>di</strong>lcolina (PC) erano condotte<br />
come prec<strong>ed</strong>entemente riportato (7).<br />
In cellule incubate nelle stesse con<strong>di</strong>zioni ma in assenza <strong>di</strong> serina ra<strong>di</strong>oattiva<br />
veniva valutata l’apoptosi, me<strong>di</strong>ante metodo <strong>del</strong> propi<strong>di</strong>o ioduro<br />
(8), e l’esposizione <strong>del</strong>la PS utilizzando il test per l’annessina V (Vybrant<br />
Apoptosis Assay, Invitrogen).<br />
RISULTATI<br />
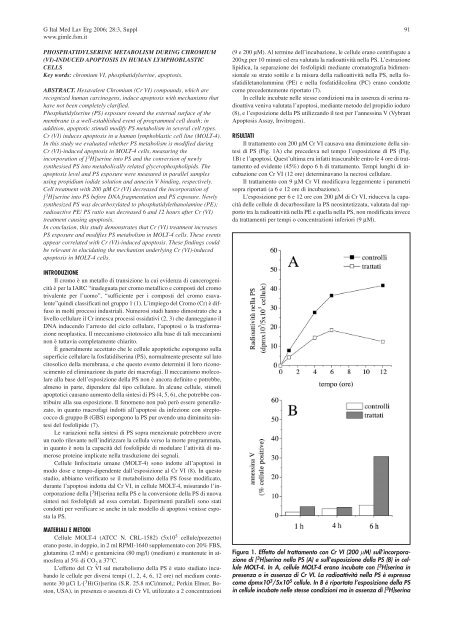
Il trattamento con 200 µM Cr VI causava una <strong>di</strong>minuzione <strong>del</strong>la sintesi<br />
<strong>di</strong> PS (Fig. 1A) che prec<strong>ed</strong>eva nel tempo l’esposizione <strong>di</strong> PS (Fig.<br />
1B) e l’apoptosi. Quest’ultima era infatti trascurabile entro le 4 ore <strong>di</strong> trattamento<br />
<strong>ed</strong> evidente (45%) dopo 6 h <strong>di</strong> trattamento. Tempi lunghi <strong>di</strong> incubazione<br />
con Cr VI (12 ore) determinavano la necrosi cellulare.<br />
Il trattamento con 9 µM Cr VI mo<strong>di</strong>ficava leggermente i parametri<br />
sopra riportati (a 6 e 12 ore <strong>di</strong> incubazione).<br />
L’esposizione per 6 e 12 ore con 200 µM <strong>di</strong> Cr VI, riduceva la capacità<br />
<strong>del</strong>le cellule <strong>di</strong> decarbossilare la PS neosintetizzata, valutata dal rapporto<br />
tra la ra<strong>di</strong>oattività nella PE e quella nella PS, non mo<strong>di</strong>ficata invece<br />
da trattamenti per tempi o concentrazioni inferiori (9 µM).<br />
Figura 1. Effetto <strong>del</strong> trattamento con Cr VI (200 µM) sull’incorporazione<br />
<strong>di</strong> [ 3 H]serina nella PS (A) e sull’esposizione <strong>del</strong>la PS (B) in cellule<br />
MOLT-4. In A, cellule MOLT-4 erano incubate con [ 3 H]serina in<br />
presenza o in assenza <strong>di</strong> Cr VI. La ra<strong>di</strong>oattività nella PS è espressa<br />
come dpmx10 3 /5x10 5 cellule. In B è riportata l’esposizione <strong>del</strong>la PS<br />
in cellule incubate nelle stesse con<strong>di</strong>zioni ma in assenza <strong>di</strong> [ 3 H]serina