KARNEVAL I KLASSRUM âKUNSKAP PÃ HJUL
KARNEVAL I KLASSRUM âKUNSKAP PÃ HJUL
KARNEVAL I KLASSRUM âKUNSKAP PÃ HJUL
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Young teenagers comprise my research group. They exist in a tumultuous phase<br />
of life with one foot in childhood and the other in the adult world. Teenagers’<br />
heads are occupied with many thoughts and emotions. They are intensively<br />
engaged in fitting in yet simultaneously have a need to clearly articulate their<br />
independence. An individual’s youth and identity are connected, addressed in<br />
the dissertation’s introduction through reference to Anthony Giddens, Knud<br />
Illeris, and Thomas Ziehe. I make a connection to, among others, Märta Sandvik<br />
(2009) who, emanating from Heinz Kohut’s theories on the self, has developed a<br />
model that describes the three-dimensional self: the grandiose self, the idealized<br />
self, and the twin-seeking self.<br />
The classroom is a place for meetings where teaching is focused on. The goal is<br />
the procurement of knowledge. Aristotle’s manner of dividing knowledge into<br />
epistêmê, technê, and phronêsis creates the starting point for the description of<br />
the pupils’ learning during work with clown figures. Art can be accommodated<br />
in practical knowledge (technê) but also in that which provides something more,<br />
experience and in depth knowledge (phronêsis). Jørgensen (2008: 22) writes that<br />
the task of school should consist of offering both scientific knowledge and<br />
personal development and that these two units inspire one another by developing<br />
pupils’ ability to think. Philosophical thinking is simply the schooling of human<br />
beings’ “thinking about one’s own thinking”. Holistic thinking is needed in<br />
order to create context.<br />
Gardner (2009) points to five manners of thinking that he maintains are<br />
important for the future. These are: the disciplined mind, the synthesizing mind,<br />
the creative mind, the respectful mind, and the ethical mind. This is a holistic<br />
view with both breadth and depth while also accommodating room for change.<br />
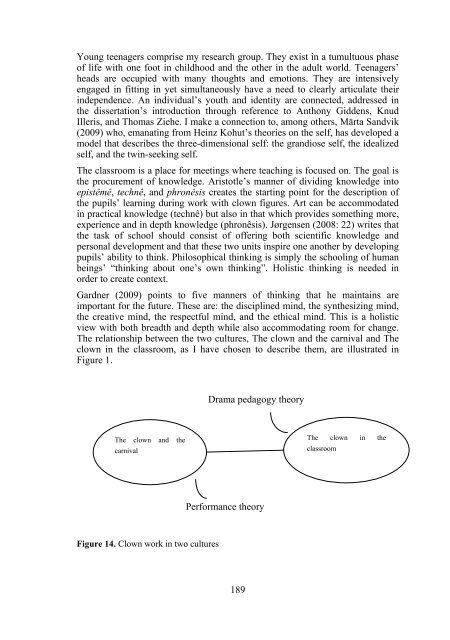
The relationship between the two cultures, The clown and the carnival and The<br />
clown in the classroom, as I have chosen to describe them, are illustrated in<br />
Figure 1.<br />
Drama pedagogy theory<br />
The clown and the<br />
carnival<br />
The clown in the<br />
classroom<br />
Performance theory<br />
Figure 14. Clown work in two cultures<br />
189