Annual Energy Outlook 2006 with Projections to 2030 - Usinfo.org
Annual Energy Outlook 2006 with Projections to 2030 - Usinfo.org
Annual Energy Outlook 2006 with Projections to 2030 - Usinfo.org
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
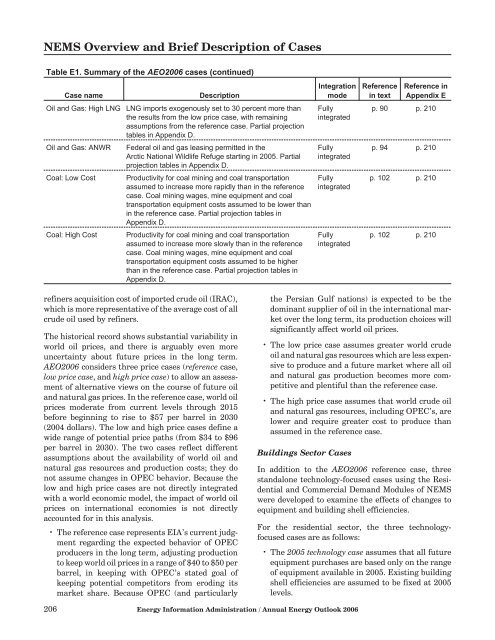
NEMS Overview and Brief Description of CasesTable E1. Summary of the AEO<strong>2006</strong> cases (continued)Case nameOil and Gas: High LNGDescriptionLNG imports exogenously set <strong>to</strong> 30 percent more thanthe results from the low price case, <strong>with</strong> remainingassumptions from the reference case. Partial projectiontables in Appendix D.IntegrationmodeReferencein textReference inAppendix EFullyintegratedp. 90 p. 210Oil and Gas: ANWRFederal oil and gas leasing permitted in theArctic National Wildlife Refuge starting in 2005. Partialprojection tables in Appendix D.Fullyintegratedp. 94 p. 210Coal: Low CostProductivity for coal mining and coal transportationassumed <strong>to</strong> increase more rapidly than in the referencecase. Coal mining wages, mine equipment and coaltransportation equipment costs assumed <strong>to</strong> be lower thanin the reference case. Partial projection tables inAppendix D.Fullyintegratedp. 102 p. 210Coal: High CostProductivity for coal mining and coal transportationassumed <strong>to</strong> increase more slowly than in the referencecase. Coal mining wages, mine equipment and coaltransportation equipment costs assumed <strong>to</strong> be higherthan in the reference case. Partial projection tables inAppendix D.Fullyintegratedp. 102 p. 210refiners acquisition cost of imported crude oil (IRAC),which is more representative of the average cost of allcrude oil used by refiners.The his<strong>to</strong>rical record shows substantial variability inworld oil prices, and there is arguably even moreuncertainty about future prices in the long term.AEO<strong>2006</strong> considers three price cases (reference case,low price case, and high price case) <strong>to</strong> allow an assessmen<strong>to</strong>f alternative views on the course of future oiland natural gas prices. In the reference case, world oilprices moderate from current levels through 2015before beginning <strong>to</strong> rise <strong>to</strong> $57 per barrel in <strong>2030</strong>(2004 dollars). The low and high price cases define awide range of potential price paths (from $34 <strong>to</strong> $96per barrel in <strong>2030</strong>). The two cases reflect differentassumptions about the availability of world oil andnatural gas resources and production costs; they donot assume changes in OPEC behavior. Because thelow and high price cases are not directly integrated<strong>with</strong> a world economic model, the impact of world oilprices on international economies is not directlyaccounted for in this analysis.• The reference case represents EIA’s current judgmentregarding the expected behavior of OPECproducers in the long term, adjusting production<strong>to</strong> keep world oil prices in a range of $40 <strong>to</strong> $50 perbarrel, in keeping <strong>with</strong> OPEC’s stated goal ofkeeping potential competi<strong>to</strong>rs from eroding itsmarket share. Because OPEC (and particularlythe Persian Gulf nations) is expected <strong>to</strong> be thedominant supplier of oil in the international marke<strong>to</strong>ver the long term, its production choices willsignificantly affect world oil prices.• The low price case assumes greater world crudeoil and natural gas resources which are less expensive<strong>to</strong> produce and a future market where all oiland natural gas production becomes more competitiveand plentiful than the reference case.• The high price case assumes that world crude oiland natural gas resources, including OPEC’s, arelower and require greater cost <strong>to</strong> produce thanassumed in the reference case.Buildings Sec<strong>to</strong>r CasesIn addition <strong>to</strong> the AEO<strong>2006</strong> reference case, threestandalone technology-focused cases using the Residentialand Commercial Demand Modules of NEMSwere developed <strong>to</strong> examine the effects of changes <strong>to</strong>equipment and building shell efficiencies.For the residential sec<strong>to</strong>r, the three technologyfocusedcases are as follows:• The 2005 technology case assumes that all futureequipment purchases are based only on the rangeof equipment available in 2005. Existing buildingshell efficiencies are assumed <strong>to</strong> be fixed at 2005levels.206 <strong>Energy</strong> Information Administration / <strong>Annual</strong> <strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Outlook</strong> <strong>2006</strong>