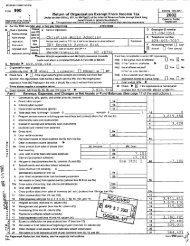
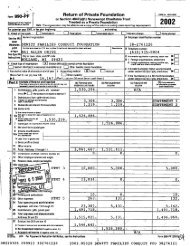
- Page 1 and 2:
Fourth National Incidence Studyof C
- Page 3 and 4:
Fourth National Incidence Studyof C
- Page 5 and 6:
TABLE OF CONTENTSChapterPageEXECUTI
- Page 7 and 8:
ChapterPage5.1.2 Differences in Mal
- Page 9 and 10:
LIST OF TABLESTablePage2-1 NIS-4 60
- Page 11 and 12:
LIST OF FIGURESFigurePage2-1 Levels
- Page 13 and 14:
Figure5-265-275-286-16-26-36-46-56-
- Page 15 and 16:
EXECUTIVE SUMMARYThis executive sum
- Page 17 and 18:
In the NIS classifications, maltrea
- Page 19 and 20:
3. The National Incidence of Child
- Page 21 and 22:
(36%, or 302,600 children) were emo
- Page 23 and 24:
maltreatment outcomes—rates of ch
- Page 25 and 26:
details that would exclude legitima
- Page 27 and 28:
Grandparents as caregivers. The NIS
- Page 29 and 30:
males more often were abusers (62%
- Page 31 and 32:
maltreated children to enter CPS in
- Page 33 and 34:
with Harm Standard maltreatment and
- Page 35 and 36:
differences in maltreatment rates r
- Page 37 and 38:
1. INTRODUCTIONThis report presents
- Page 39 and 40:
Incorporating the TAG input, DHHS d
- Page 41 and 42:
• The NIS-4 Data Collection Repor
- Page 43:
these with the percentages that rec
- Page 46 and 47: Rationale. Although CPS investigate
- Page 48 and 49: eveal the maltreatment to persons i
- Page 50 and 51: Figure 2-3.Schematic Summary of the
- Page 52 and 53: CPS recruitment. In order to undupl
- Page 54 and 55: format: the Sentinel data form desc
- Page 56 and 57: 3. Purposive and Avoidable Acts/Omi
- Page 58 and 59: each child substantiated by CPS or
- Page 60 and 61: 2.6 Weighting and Estimation 14The
- Page 62 and 63: the population. The estimated total
- Page 64 and 65: 2.8 Supplementary StudiesThe NIS pr
- Page 67 and 68: 3. INCIDENCE OF CHILD ABUSE AND NEG
- Page 69 and 70: 3.1.1 Overall Incidence of Harm Sta
- Page 71 and 72: 3.1.2 Incidence of Harm Standard Ab
- Page 73 and 74: children represent 58% of all child
- Page 75 and 76: From inadequate supervision to the
- Page 77 and 78: 3.1.5 Severity of Outcomes from Har
- Page 79 and 80: interpreted as less serious than mo
- Page 81 and 82: considered to be endangered by thei
- Page 83 and 84: totals represent national incidence
- Page 85 and 86: Changes since 1986 in the incidence
- Page 87 and 88: The NIS-3 found significant increas
- Page 89 and 90: Moderate harm. Moderate harm due to
- Page 91 and 92: 4. DISTRIBUTION OF ABUSE AND NEGLEC
- Page 93 and 94: Sexual Abuse. Girls experienced Har
- Page 95: Table 4-2. Sex Differences in Incid
- Page 99 and 100: Figure 4-4.Age Differences in Incid
- Page 101 and 102: graph shows, the incidence rate for
- Page 103 and 104: 4.2.2 Age Differences in Endangerme
- Page 105 and 106: Physical abuse. The incidence of En
- Page 107 and 108: Figure 4-11.Age Differences in the
- Page 109 and 110: Figure 4-12.Percent Changes since t
- Page 111 and 112: Endangered. Chapter 3 reported that
- Page 113 and 114: significantly higher than that for
- Page 115 and 116: Changes since the NIS-3 in Rates of
- Page 117 and 118: Overall Endangerment Standard Maltr
- Page 119 and 120: Changes since the NIS-3 in Rates of
- Page 121 and 122: 4.4.1 Differences in Harm Standard
- Page 123 and 124: Table 4-6. Differences Related to C
- Page 125 and 126: Thus, the incidence rate for childr
- Page 127 and 128: Overall Harm Standard MaltreatmentS
- Page 129 and 130: Table 4-8. Differences Related to C
- Page 131: Endangerment Standard maltreatment,
- Page 134 and 135: 5.1 Differences in the Incidence of
- Page 136 and 137: more than 2 times the rate for chil
- Page 138 and 139: inferring that they were harmed. Th
- Page 140 and 141: Specific Categories of Endangerment
- Page 142 and 143: Endangered. The estimated incidence
- Page 144 and 145: families. The incidence rate for ch
- Page 146 and 147:
Educational neglect. Children in fa
- Page 148 and 149:
The incidence rate of Endangerment
- Page 150 and 151:
Endangered. Children in families of
- Page 152 and 153:
Figure 5-1.Incidence of Harm Standa
- Page 154 and 155:
Figure 5-2.Incidence of Harm Standa
- Page 156 and 157:
higher, the rate for children whose
- Page 158 and 159:
maltreatment at a reliably higher r
- Page 160 and 161:
Figure 5-6.Percent Changes since NI
- Page 162 and 163:
5.3.2 Differences in the Incidence
- Page 164 and 165:
Specific Categories of Endangerment
- Page 166 and 167:
Figure 5-11.Incidence of Endangerme
- Page 168 and 169:
living with a single parent who had
- Page 170 and 171:
oth parents showed much smaller cha
- Page 172 and 173:
child’s primary caregiver, when t
- Page 174 and 175:
Table 5-6. Differences in Incidence
- Page 176 and 177:
in households with two children), a
- Page 178 and 179:
per 1,000). Also, the rate of moder
- Page 180 and 181:
two children, 1.7 times the rate fo
- Page 182 and 183:
Emotional abuse. The incidence of E
- Page 184 and 185:
Endangered. The estimated incidence
- Page 186 and 187:
Figure 5-23.Incidence of Harm Stand
- Page 188 and 189:
5.6.2 Differences in Endangerment S
- Page 190 and 191:
were 1.5 times more likely to be ph
- Page 192 and 193:
Moderate harm. Children residing in
- Page 194 and 195:
Second, because multiple persons so
- Page 196 and 197:
hierarchy comprises other adults kn
- Page 198 and 199:
Table 6-2 also reveals a marked dif
- Page 200 and 201:
with the fact that mothers tend to
- Page 202 and 203:
Table 6-4. Perpetrator's Sex by Sev
- Page 204 and 205:
perpetrator relationship, with the
- Page 206 and 207:
earlier (Chapter 4) and did not var
- Page 208 and 209:
perpetrator’s alcohol use was a f
- Page 210 and 211:
More of the moderately harmed child
- Page 213 and 214:
7. RECOGNIZING ABUSED AND NEGLECTED
- Page 215 and 216:
classification hierarchy. If more t
- Page 217 and 218:
neglected. That is, when school sen
- Page 219 and 220:
NIS-4 estimates and rates per 1,000
- Page 221 and 222:
largest contributor in this sector,
- Page 223 and 224:
schools and social services agencie
- Page 225 and 226:
maltreatment situations only to CPS
- Page 227:
that influence sentinels’ respons
- Page 230 and 231:
8.1 CPS Investigation of Abused and
- Page 232 and 233:
Figure 8-1.Changes in Rates of CPS
- Page 234 and 235:
Figure 8-2.CPS Investigation of Mal
- Page 236 and 237:
CPS investigated more than one-half
- Page 238 and 239:
Figure 8-6. CPS Investigation of Ch
- Page 240 and 241:
children recognized at shelters, al
- Page 242 and 243:
Figure 8-8.Changes in Rates of CPS
- Page 244 and 245:
Just as in the Harm Standard, the i
- Page 246 and 247:
Figure 8-11.Changes in Investigatio
- Page 248 and 249:
Figure 8-13.CPS Investigation of Ch
- Page 250 and 251:
maltreated children. With these chi
- Page 252 and 253:
during the extra month but were alr
- Page 254 and 255:
Figure 8-15.Uninvestigated Maltreat
- Page 256 and 257:
columns, providing the presumptive
- Page 258 and 259:
determining whether the child would
- Page 260 and 261:
Table 8-2 shows the actual and pres
- Page 262 and 263:
8.4 Relationship between CPS Invest
- Page 264 and 265:
investigation rates were lower for
- Page 266 and 267:
Prioritizing recommended responses
- Page 268 and 269:
maltreatment directly to CPS. Among
- Page 270 and 271:
columns, the educational neglect pe
- Page 273 and 274:
9. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONSThe
- Page 275 and 276:
sliding scales for the poorer child
- Page 277 and 278:
REFERENCESAhlbom, A., & Norell, S.
- Page 279 and 280:
Youth and Families, Administration
- Page 281 and 282:
U.S. Census Bureau. (2004). Current
- Page 283 and 284:
Appendix A Design and Methods Summa
- Page 285 and 286:
weighted the records (so the sample
- Page 287 and 288:
design. The measure of size was the
- Page 289 and 290:
optimal sample sizes from law enfor
- Page 291 and 292:
CPS RECRUITMENT In order to develop
- Page 293 and 294:
SENTINEL AGENCY RECRUITMENT The sen
- Page 295 and 296:
Table A-2.NIS-4 Agency Participatio
- Page 297 and 298:
DATA COLLECTIONThe goals of the NIS
- Page 299 and 300:
Table A-5. Participating Sentinel A
- Page 301 and 302:
• The nature of harm (injuries to
- Page 303 and 304:
The evaluative coders recorded thes
- Page 305 and 306:
Table A-9. Agreement Rates for Over
- Page 307 and 308:
probability-based matching software
- Page 309 and 310:
WEIGHTING Sampling weights were dev
- Page 311 and 312:
eport the child to CPS, which in tu
- Page 313 and 314:
Table A-12. Topics Covered in the 4
- Page 315 and 316:
CPS SCREENING POLICIES STUDY (SPS)
- Page 317 and 318:
• 52 agencies provided their own
- Page 319 and 320:
SENTINEL DEFINITIONS SURVEY (SDS) T
- Page 321 and 322:
The first surveys were mailed in Ma
- Page 323 and 324:
TABLE B-1.CATEGORIES OF MALTREATMEN
- Page 325 and 326:
TABLE B-4.AGE BY CATEGORIES OF MALT
- Page 327 and 328:
TABLE B-4. (Continued)AGE CLASS = 1
- Page 329 and 330:
TABLE B-5. (Continued)RACE/ETHNICIT
- Page 331 and 332:
TABLE B-6. (Continued) NCHILDR = 4
- Page 333 and 334:
TABLE B-8.CHILDREN COUNTABLE UNDER
- Page 335 and 336:
TABLE B-8. (Continued)CLASS = NOT I
- Page 337 and 338:
TABLE B-10.FAMILY STRUCTURE AND PAR
- Page 339 and 340:
TABLE B-10. (Continued)FAMILY STRUC
- Page 341 and 342:
TABLE B-11. (Continued)FAMILY STRUC
- Page 343 and 344:
TABLE B-13. (Continued)PARENTS' EMP
- Page 345 and 346:
Appendix C Endangerment Standard Es
- Page 347 and 348:
TABLE C-3.SEX BY CATEGORIES OF MALT
- Page 349 and 350:
TABLE C-4. (Continued)AGE CLASS = 6
- Page 351 and 352:
TABLE C-5.RACE/ETHNICITY BY CATEGOR
- Page 353 and 354:
TABLE C-6. (Continued)NCHILDR = 2 C
- Page 355 and 356:
TABLE C-7. (Continued)METROSTATUS =
- Page 357 and 358:
TABLE C-8. (Continued)CLASS = INVES
- Page 359 and 360:
TABLE C-9.PROPORTION OF ENDANGERMEN
- Page 361 and 362:
TABLE C-10. (Continued)FAMILY STRUC
- Page 363 and 364:
TABLE C-11.FAMILY STRUCTURE BY CATE
- Page 365 and 366:
TABLE C-12. (Continued)SOCIOECONOMI
- Page 367 and 368:
TABLE C-14.GRANDPARENTS AS CAREGIVE
- Page 369 and 370:
APPENDIX DWITHIN STUDY ANALYSES Thi
- Page 371 and 372:
Table D-3. T-statistics for age dif
- Page 373 and 374:
Table D-3. ContinuedAge 6-8 vs 9-11
- Page 375 and 376:
Table D-4. ContinuedAge 0-2 vs 12-1
- Page 377 and 378:
Table D-4 ContinuedAge 9-11 vs 12-1
- Page 379 and 380:
Table D-6. T-statistics for racial/
- Page 381 and 382:
Table D-8. T-statistics for parent'
- Page 383 and 384:
Table D-11. T-statistics for family
- Page 385 and 386:
Table D-11. ContinuedUnmarried Pare
- Page 387 and 388:
Table D-12. ContinuedMarried Parent
- Page 389 and 390:
Table D-12. ContinuedSingle ParentW
- Page 391 and 392:
Table D-15. T-statistics for family
- Page 393 and 394:
Table D-16. T-statistics for family
- Page 395 and 396:
Table D-17. T-statistics for metros
- Page 397 and 398:
Table D-19. Chi-squared Results for
- Page 399 and 400:
Table D-21. Chi-squared Results for
- Page 401 and 402:
Table D-23. Chi-squared Results for
- Page 403 and 404:
Table D-25. Chi-squared Results for
- Page 405 and 406:
APPENDIX E BETWEEN-STUDY ANALYSES T
- Page 407 and 408:
Table E-1a. T-statistics for compar
- Page 409 and 410:
Table E-3. Chi-squared tables for s
- Page 411 and 412:
Table E-3. (Continued)Emotional Neg
- Page 413 and 414:
Table E-4. (Continued)Sexual Abuse0
- Page 415 and 416:
Table E-4. (Continued)Severity, Mod
- Page 417 and 418:
Table E-5. (Continued)Physical Negl
- Page 419 and 420:
Table E-6. Chi-squared tables for p
- Page 421 and 422:
Table E-6. (Continued)Educational N
- Page 423 and 424:
Table E-7. Chi-squared tables for f
- Page 425 and 426:
Table E-7. (Continued)Emotional Neg
- Page 427 and 428:
Table E-8. (Continued)Sexual AbuseL
- Page 429 and 430:
Table E-8. (Continued)Severity, Mod
- Page 431 and 432:
Table E-9. (Continued)Emotional Abu
- Page 433 and 434:
Table E.9. (Continued)Severity, Inf
- Page 435 and 436:
Table E-10. (Continued)Emotional Ab
- Page 437 and 438:
Table E-10. (Continued)Severity, In
- Page 439 and 440:
Table E-11. (Continued)Emotional Ab
- Page 441 and 442:
Table E-11. (Continued)Severity, In
- Page 443 and 444:
Table E-12. (Continued)Emotional Ab
- Page 445 and 446:
Table E-12. (Continued)Severity, In
- Page 447 and 448:
Table E-13. (Continued)Emotional Ab
- Page 449 and 450:
Table E-13. (Continued)Severity, In
- Page 451 and 452:
Table E-14. (Continued)Emotional Ab
- Page 453 and 454:
Table E-14. (Continued)Severity, In
- Page 455:
Table E-17. T-statistics for Source