- Page 1 and 2:
PRODUÇÃO DE MICROPARTÍCULAS E NA
- Page 3 and 4:
Oliveira, Marco Antonio Monteiro de
- Page 5 and 6:
Agradecimentos Aos Mestres, familia
- Page 7 and 8:
Abstract of Thesis presented to COP
- Page 9 and 10:
Síntese de nanogel biodegradável
- Page 11 and 12:
1.1 Introdução Polímeros são ma
- Page 13 and 14:
Independentemente do mecanismo resp
- Page 15 and 16:
nos mais variados tipos de aplicaç
- Page 17 and 18:
obtidas com auxílio de reações d
- Page 19 and 20:
2.1 Introdução 2.1.1 A embolizaç
- Page 21 and 22:
O tratamento de tumores sempre requ
- Page 23 and 24:
fibroma necessitam de um tratamento
- Page 25 and 26:
importante a ser considerado é que
- Page 27 and 28:
Embora o PVA seja largamente utiliz
- Page 29 and 30:
concentração e o tipo de agente d
- Page 31 and 32:
Identificação - devido às altas
- Page 33 and 34:
eações de polimerização, variá
- Page 35 and 36:
O O O O n n n n O O O O + n ROH ác
- Page 37 and 38:
insolúveis no álcool usado nas re
- Page 39 and 40:
partículas, o que é muito positiv
- Page 41 and 42:
algumas propriedades adicionais sã
- Page 43 and 44:
formadas, o potencial zeta, a capac
- Page 45 and 46:
possível a incorporação de fárm
- Page 47 and 48:
Química Fina), lauril sulfato de s
- Page 49 and 50:
utilizando-se água destilada para
- Page 51 and 52:
y normalizado = y i y máximo Calor
- Page 53 and 54:
HO 4' 3' 5' 2' 1' 6' 10 NH 2 Fi
- Page 55 and 56:
2.4 Resultados & Discussão 2.4.1 E
- Page 57 and 58:
concentração de fármaco também
- Page 59 and 60:
manuseio das amostras ficou comprom
- Page 61 and 62:
a) b) w(log M) (a.u.) w(log M) (a.u
- Page 63 and 64:
Os espectros anteriormente apresent
- Page 65 and 66:
2.21 e 2.22 apresentam as micrograf
- Page 67 and 68:
Figura 2.24 - Detalhe da superfíci
- Page 69 and 70:
Figura 2.26 - Detalhe da superfíci
- Page 71 and 72:
A Tabela 2.8 contém os resultados
- Page 73 and 74:
A Tabela 2.9 mostra os resultado da
- Page 75 and 76:
Para tentar elucidar a hipótese de
- Page 77 and 78:
Table 2.10 - Composição dos copol
- Page 79 and 80:
para fins de cálculo. A Tabela 2.1
- Page 81 and 82:
amoxicilina nas matrizes poliméric
- Page 83 and 84:
nos valores de massa molar e temper
- Page 85 and 86:
3.1 Introdução 3.1.1 Cinética da
- Page 87 and 88:
determinado iniciador químico, sen
- Page 89 and 90:
R i = R t = k t [P•] 2 (3.10) Reo
- Page 91 and 92:
propagação e terminação. Entret
- Page 93 and 94:
efeito terapêutico da infusão des
- Page 95 and 96:
Penicilina Observada pela primeira
- Page 97 and 98:
A amoxicilina e a ampicilina (fárm
- Page 99 and 100:
incluem principalmente o tratamento
- Page 101 and 102:
adquirida. [112] Em pacientes com c
- Page 103 and 104:
O mecanismo de ação da doxorrubic
- Page 105 and 106:
vinílico) (PVA, 88% de hidrólise
- Page 107 and 108:
Polimerização em suspensão As re
- Page 109 and 110:
No procedimento adotado, em um sist
- Page 111 and 112:
Tamanho de partículas A distribui
- Page 113 and 114:
Nas Figuras 3.7 e 3.8 são ilustrad
- Page 115 and 116:
de atividade superficial, além de
- Page 117 and 118: a) b) Tensão interfacial (mN/m) Te
- Page 119 and 120: de fármaco no meio reacional e ao
- Page 121 and 122: nas vizinhanças da superfície das
- Page 123 and 124: Com auxílio de cálculos de integr
- Page 125 and 126: análises de tamanho de partícula
- Page 127 and 128: sido ocasionado pelo consumo das pa
- Page 129 and 130: Conversão (%) Figura 3.17 - Evolu
- Page 131 and 132: a) b) c) Conversão (%) Conversão
- Page 133 and 134: w(log M) (a.u.) 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4
- Page 135 and 136: a) b) c) w(log M) (a.u.) w(log M) (
- Page 137 and 138: a) b) M w x 10 -3 (g/mol) M w x 10
- Page 139 and 140: 3.4.2 Efeitos da incorporação in
- Page 141 and 142: Figura 3.25 - Micrografia de partí
- Page 143 and 144: superiores pode estar relacionado
- Page 145 and 146: semelhança ao de inibidores quími
- Page 147 and 148: Na Figura 3.31 são apresentados os
- Page 149 and 150: a) b) w(log M) (a.u.) w(log M) (a.u
- Page 151 and 152: Neste Capítulo também foi estudad
- Page 153 and 154: 4.1 Introdução 4.1.1 Polimerizaç
- Page 155 and 156: outras tecnologias disponíveis. Po
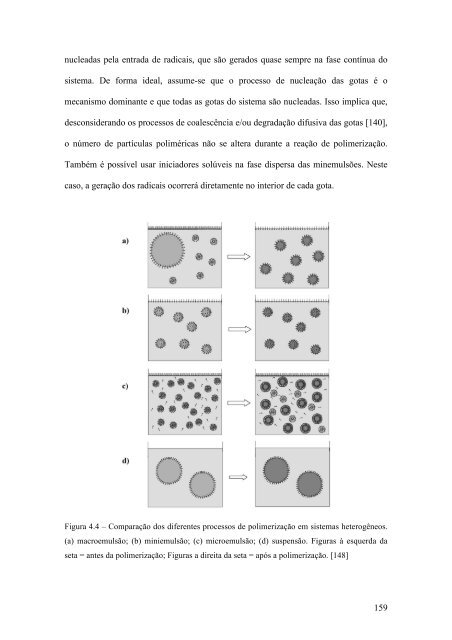
- Page 157 and 158: O leitor deve tomar alguns cuidados
- Page 159 and 160: ! !(!"ó!"#$) ≈ [!]!![!]! !" (4.6
- Page 161 and 162: ! "# $ $ % Terminação: ! & ! " $
- Page 163 and 164: Embora a técnica de polimerizaçã
- Page 165 and 166: O efeito Ostwald ripening (degrada
- Page 167: As microemulsões são sistemas ger
- Page 171 and 172: aplicações de liberação control
- Page 173 and 174: 4.3 Metodologia experimental 4.3.1
- Page 175 and 176: adicionou-se uma solução de ferri
- Page 177 and 178: filtrações a vácuo e o solvente
- Page 179 and 180: A massa molar numérica média teó
- Page 181 and 182: aquoso (pH =12). O potencial zeta d
- Page 183 and 184: sendo que a confirmação da obten
- Page 185 and 186: sal, além de um aspecto ligeiramen
- Page 187 and 188: permanecesse predominantemente na f
- Page 189 and 190: Os testes foram realizados utilizan
- Page 191 and 192: (dimetilamino) metacrilade de etila
- Page 193 and 194: A polimerização convencional em m
- Page 195 and 196: As emulsões, antes e após o proce
- Page 197 and 198: apresentado na Tabela 4.1, a difere
- Page 199 and 200: A solução encontrada para aumenta
- Page 201 and 202: Tabela 4.3 - Características dos m
- Page 203 and 204: Conversão (%) Figura 4.31 - Gráfi
- Page 205 and 206: polimerização convencional e RAFT
- Page 207 and 208: estabilidade coloidal em um sistema
- Page 209 and 210: HO O j NC i O Figura 4.37 - Espect
- Page 211 and 212: conforme descrito na Tabela 4.1, a
- Page 213 and 214: Os menores tamanhos médios provave
- Page 215 and 216: do agente macro-RAFT, conforme hip
- Page 217 and 218: 4.5 Conclusões Neste Capítulo foi
- Page 219 and 220:
Em um segundo momento, foi descrita
- Page 221 and 222:
Referências bibliográficas 1. STE
- Page 223 and 224:
21. MENDES, W.D.S., CHAGAS, V.L.A.,
- Page 225 and 226:
one Neoplasms", CardioVascular and
- Page 227 and 228:
shell-and-nucleus structure and its
- Page 229 and 230:
67. ITO, F., FUJIMORI, H., HONNAMI,
- Page 231 and 232:
81. ZUCCARI, G., CAROSIO, R., FINI,
- Page 233 and 234:
98. KATO, T., NEMOTO, R., MORI, H.
- Page 235 and 236:
113. PEREIRA, J., PHAN, T., 2004, "
- Page 237 and 238:
polymerization: Renaissance of a ke
- Page 239 and 240:
147. LEAL-CALERON, F., SCHMITT, V.,
- Page 241 and 242:
164. HOARE, T.R., KOHANE, D.S., 200
- Page 243 and 244:
181. LIN, S., DU, F., WANG, Y. et a
- Page 245 and 246:
ased on tertiary amine methaceylate
- Page 247 and 248:
Anexo Teste de atividade farmacoló
- Page 249 and 250:
A Tabela A1 resume os resultados ob
- Page 251 and 252:
Resultados Com base nos resultados
- Page 253 and 254:
Pelos resultados preliminares de li
- Page 255 and 256:
1% (fase orgânica), com 180 µg/mL
- Page 257 and 258:
Os multicromatogramas são gráfico
- Page 259 and 260:
Teste de liberação prolongada de
- Page 261 and 262:
7) Assim que a bomba for acionada,
- Page 263 and 264:
Curvas de DSC A seguir são apresen
- Page 265 and 266:
Filename: C:\Program Files\Pyr...\a
- Page 267 and 268:
Filename: C:\Program Files\Pyr...\a
- Page 269 and 270:
Filename: C:\Program Files\Py...\am
- Page 271 and 272:
Filename: C:\Program Files\Py...\am
- Page 273 and 274:
Filename: C:\Program Files\Py...\am
- Page 275 and 276:
Filename: C:\Program Fil...\amostra
- Page 277 and 278:
Filename: C:\Program Files\Pyr...\a
- Page 279 and 280:
Figura A20 - Espectro de 13 C-RMN d
- Page 281 and 282:
Figura A24 - Espectro de 13 C-RMN d
- Page 283 and 284:
Figura A28 - Espectro de 13 C-RMN d
- Page 285 and 286:
Figura A32 - Espectro de 1 H-RMN do