The Status of Nepal's Mammals: The National Red List Series - IUCN
The Status of Nepal's Mammals: The National Red List Series - IUCN
The Status of Nepal's Mammals: The National Red List Series - IUCN
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
13) Boselaphus tragocamelus<br />
(Pallas, 1766)<br />
Common Names<br />
Nilgai (English); Nilgai (Nepali)<br />
Species Description<br />
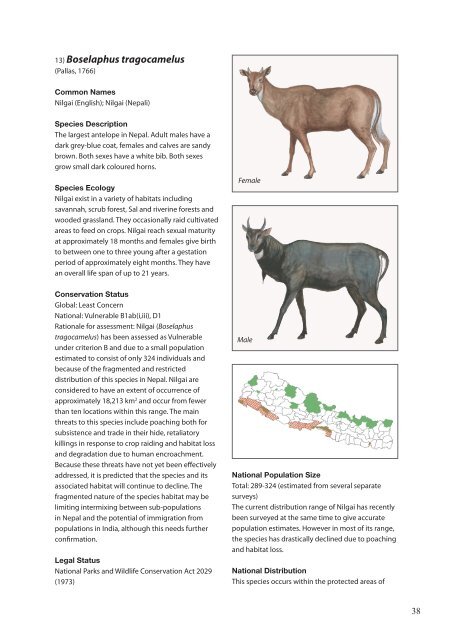
<strong>The</strong> largest antelope in Nepal. Adult males have a<br />
dark grey-blue coat, females and calves are sandy<br />
brown. Both sexes have a white bib. Both sexes<br />
grow small dark coloured horns.<br />
Species Ecology<br />
Nilgai exist in a variety <strong>of</strong> habitats including<br />
savannah, scrub forest, Sal and riverine forests and<br />
wooded grassland. <strong>The</strong>y occasionally raid cultivated<br />
areas to feed on crops. Nilgai reach sexual maturity<br />
at approximately 18 months and females give birth<br />
to between one to three young after a gestation<br />
period <strong>of</strong> approximately eight months. <strong>The</strong>y have<br />
an overall life span <strong>of</strong> up to 21 years.<br />
Conservation <strong>Status</strong><br />
Global: Least Concern<br />
<strong>National</strong>: Vulnerable B1ab(i,iii), D1<br />
Rationale for assessment: Nilgai (Boselaphus<br />
tragocamelus) has been assessed as Vulnerable<br />
under criterion B and due to a small population<br />
estimated to consist <strong>of</strong> only 324 individuals and<br />
because <strong>of</strong> the fragmented and restricted<br />
distribution <strong>of</strong> this species in Nepal. Nilgai are<br />
considered to have an extent <strong>of</strong> occurrence <strong>of</strong><br />
approximately 18,213 km 2 and occur from fewer<br />
than ten locations within this range. <strong>The</strong> main<br />
threats to this species include poaching both for<br />
subsistence and trade in their hide, retaliatory<br />
killings in response to crop raiding and habitat loss<br />
and degradation due to human encroachment.<br />
Because these threats have not yet been effectively<br />
addressed, it is predicted that the species and its<br />
associated habitat will continue to decline. <strong>The</strong><br />
fragmented nature <strong>of</strong> the species habitat may be<br />
limiting intermixing between sub-populations<br />
in Nepal and the potential <strong>of</strong> immigration from<br />
populations in India, although this needs further<br />
confirmation.<br />
Legal <strong>Status</strong><br />
<strong>National</strong> Parks and Wildlife Conservation Act 2029<br />
(1973)<br />
Female<br />
Male<br />
<strong>National</strong> Population Size<br />
Total: 289-324 (estimated from several separate<br />
surveys)<br />
<strong>The</strong> current distribution range <strong>of</strong> Nilgai has recently<br />
been surveyed at the same time to give accurate<br />
population estimates. However in most <strong>of</strong> its range,<br />
the species has drastically declined due to poaching<br />
and habitat loss.<br />
<strong>National</strong> Distribution<br />
This species occurs within the protected areas <strong>of</strong><br />
38