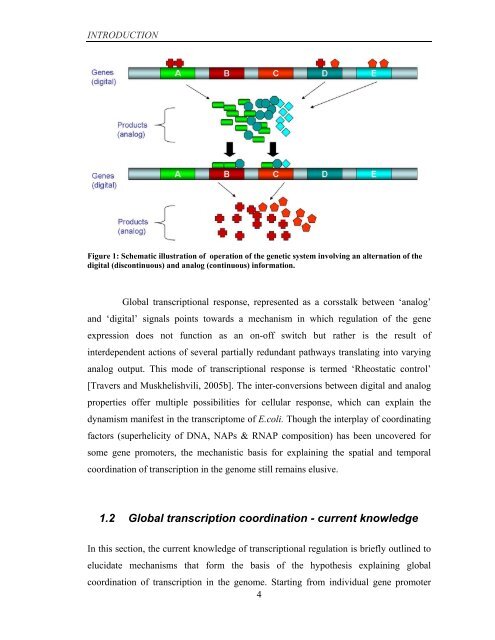
- Page 1 and 2: Coordinated regulation of gene expr
- Page 3 and 4: Parts of this work has been publish
- Page 5 and 6: ABSTRACT promoter region determines
- Page 7 and 8: ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS first impression o
- Page 9 and 10: TABLE OF CONTENTS 2.2.5 Preparation
- Page 11 and 12: LIST OF TABLES List of tables Table
- Page 13 and 14: LIST OF FIGURES List of Figures Fig
- Page 15 and 16: ABBREVIATIONS Abbreviations ∆61
- Page 17 and 18: ABBREVIATIONS TBE Tris TS tyrT35U t
- Page 19: INTRODUCTION Salmonella: “In more
- Page 23 and 24: INTRODUCTION UP element -35 -10 Spa
- Page 25 and 26: INTRODUCTION can also influence elo
- Page 27 and 28: INTRODUCTION have more base-pairs t
- Page 29 and 30: INTRODUCTION Figure 6: Graphical re
- Page 31 and 32: INTRODUCTION shown that H-NS reache
- Page 33 and 34: INTRODUCTION formed as a repercussi
- Page 35 and 36: MATERIALS AND METHODS 2 Materials a
- Page 37 and 38: MATERIALS AND METHODS NaCl 10 gm YT
- Page 39 and 40: MATERIALS AND METHODS LZ41 3 pyrF28
- Page 41 and 42: MATERIALS AND METHODS 2.2 Methods 2
- Page 43 and 44: MATERIALS AND METHODS given using a
- Page 45 and 46: MATERIALS AND METHODS phenol: chlor
- Page 47 and 48: MATERIALS AND METHODS Filtered (by
- Page 49 and 50: MATERIALS AND METHODS free water (A
- Page 51 and 52: RESULTS 3 Results Growth phase-depe
- Page 53 and 54: RESULTS Neither the fis nor the hns
- Page 55 and 56: RESULTS these identified genes (by
- Page 57 and 58: RESULTS furthermore the colour of t
- Page 59 and 60: RESULTS During the entire growth cy
- Page 61 and 62: RESULTS transcripts of a growth pha
- Page 63 and 64: RESULTS phosphorylation, are associ
- Page 65 and 66: RESULTS Table 4: RT-PCR analysis of
- Page 67 and 68: RESULTS Figure 16: Schematic repres
- Page 69 and 70: RESULTS parC) which allows the supe
- Page 71 and 72:
RESULTS Figure 19: In vitro transcr
- Page 73 and 74:
RESULTS contrast the tyrTD promoter
- Page 75 and 76:
DISCUSSION 4 Discussion The idea of
- Page 77 and 78:
DISCUSSION In a study by Balke & Gr
- Page 79 and 80:
DISCUSSION cells maintain viability
- Page 81 and 82:
DISCUSSION writhe in the UAS by FIS
- Page 83 and 84:
DISCUSSION 4.3.2 Mechanism of trans
- Page 85 and 86:
CONCLUSION 5 Conclusion Regulation
- Page 87 and 88:
REFERENCES Bordes, P., Conter, A.,
- Page 89 and 90:
REFERENCES Gruber, T.M., and Gross,
- Page 91 and 92:
REFERENCES molecular basis for sele
- Page 93 and 94:
REFERENCES Pan, C.Q., Finkel, S.E.,
- Page 95 and 96:
REFERENCES Schroder, O., and Wagner
- Page 97 and 98:
REFERENCES Willenbrock, H., and Uss
- Page 99 and 100:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 101 and 102:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 103 and 104:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 105 and 106:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 107 and 108:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 109 and 110:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 111 and 112:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 113 and 114:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 115 and 116:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 117 and 118:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 119 and 120:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 121 and 122:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 123 and 124:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 125 and 126:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 127 and 128:
APPENDIX I Supplementary table - VI
- Page 129 and 130:
APPENDIX I fabB b2323 0.6336 0.0043
- Page 131 and 132:
APPENDIX I ibpA b3687 2.4960 0.0181
- Page 133 and 134:
APPENDIX I pepP b2908 1.2182 0.0368
- Page 135 and 136:
APPENDIX I speG b1584 0.4151 0.0001
- Page 137 and 138:
APPENDIX I ycjX b1321 4.0841 0.0141
- Page 139 and 140:
APPENDIX I yhfY b3382 1.4063 0.0453
- Page 141 and 142:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 143 and 144:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 145 and 146:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 147 and 148:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 149 and 150:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 151 and 152:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 153 and 154:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 155 and 156:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 157 and 158:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio A/B
- Page 159 and 160:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 161 and 162:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 163 and 164:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 165 and 166:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 167 and 168:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 169 and 170:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio A/B
- Page 171 and 172:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio A/B
- Page 173 and 174:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio A/B
- Page 175 and 176:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio A/B
- Page 177 and 178:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio A/B
- Page 179 and 180:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 181 and 182:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 183 and 184:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 185 and 186:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 187 and 188:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 189 and 190:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 191 and 192:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 193 and 194:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 195 and 196:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 197 and 198:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 199 and 200:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio A/B
- Page 201 and 202:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 203 and 204:
APPENDIX I gene blattner ratio p-va
- Page 205 and 206:
Statement of sources Declaration I
- Page 207:
190