Coordinated regulation of gene expression by E ... - Jacobs University
Coordinated regulation of gene expression by E ... - Jacobs University
Coordinated regulation of gene expression by E ... - Jacobs University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
RESULTS<br />
parC) which allows the supercoiling in this strain to be maintained after norfloxacin<br />
treatment at near physiological levels (σ = - 0.073) [Zechiedrich et al., 1997]. In<br />
contrast, the same treatment induces DNA relaxation in LZ41 and hypernegative<br />
supercoiling in LZ54 (Figure 12A). Under these conditions the response <strong>of</strong> the rrnA P1<br />
promoter is dependent on the fis genotype, implying that there are no significant<br />
variations in FIS levels during the norfloxacin treatment [Rochman et al., 2002]. All the<br />
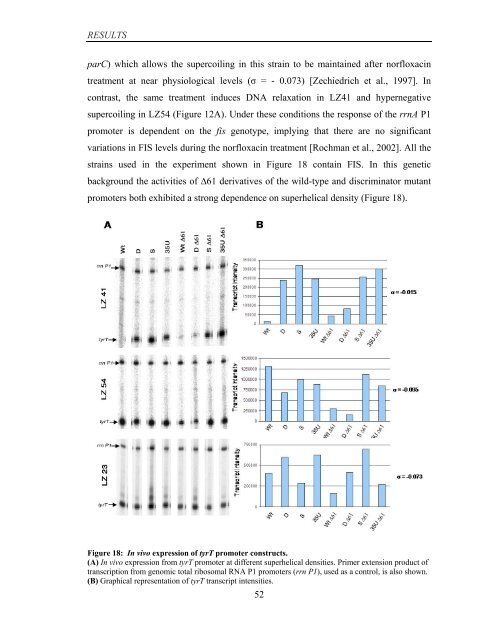
strains used in the experiment shown in Figure 18 contain FIS. In this <strong>gene</strong>tic<br />
background the activities <strong>of</strong> ∆61 derivatives <strong>of</strong> the wild-type and discriminator mutant<br />
promoters both exhibited a strong dependence on superhelical density (Figure 18).<br />
Figure 18: In vivo <strong>expression</strong> <strong>of</strong> tyrT promoter constructs.<br />
(A) In vivo <strong>expression</strong> from tyrT promoter at different superhelical densities. Primer extension product <strong>of</strong><br />
transcription from genomic total ribosomal RNA P1 promoters (rrn P1), used as a control, is also shown.<br />
(B) Graphical representation <strong>of</strong> tyrT transcript intensities.<br />
52