Through the Eras
Edward Bleiberg ed., Ancient Egypt (2675-332 ... - The Fellowship
Edward Bleiberg ed., Ancient Egypt (2675-332 ... - The Fellowship
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
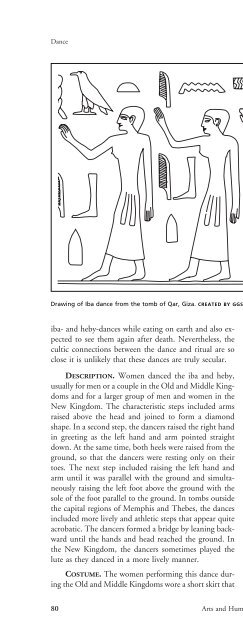
DanceDrawing of Iba dance from <strong>the</strong> tomb of Qar, Giza. CREATED BY GGS INFORMATION SERVICES. GALE.iba- and heby-dances while eating on earth and also expectedto see <strong>the</strong>m again after death. Never<strong>the</strong>less, <strong>the</strong>cultic connections between <strong>the</strong> dance and ritual are soclose it is unlikely that <strong>the</strong>se dances are truly secular.DESCRIPTION. Women danced <strong>the</strong> iba and heby,usually for men or a couple in <strong>the</strong> Old and Middle Kingdomsand for a larger group of men and women in <strong>the</strong>New Kingdom. The characteristic steps included armsraised above <strong>the</strong> head and joined to form a diamondshape. In a second step, <strong>the</strong> dancers raised <strong>the</strong> right handin greeting as <strong>the</strong> left hand and arm pointed straightdown. At <strong>the</strong> same time, both heels were raised from <strong>the</strong>ground, so that <strong>the</strong> dancers were resting only on <strong>the</strong>irtoes. The next step included raising <strong>the</strong> left hand andarm until it was parallel with <strong>the</strong> ground and simultaneouslyraising <strong>the</strong> left foot above <strong>the</strong> ground with <strong>the</strong>sole of <strong>the</strong> foot parallel to <strong>the</strong> ground. In tombs outside<strong>the</strong> capital regions of Memphis and Thebes, <strong>the</strong> dancesincluded more lively and athletic steps that appear quiteacrobatic. The dancers formed a bridge by leaning backwarduntil <strong>the</strong> hands and head reached <strong>the</strong> ground. In<strong>the</strong> New Kingdom, <strong>the</strong> dancers sometimes played <strong>the</strong>lute as <strong>the</strong>y danced in a more lively manner.COSTUME. The women performing this dance during<strong>the</strong> Old and Middle Kingdoms wore a short skirt thatended just above <strong>the</strong> knees. They sometimes wore a bandof cloth that encircled <strong>the</strong> neck and crossed between <strong>the</strong>breasts and over <strong>the</strong> back. Sometimes <strong>the</strong> women wore aheaddress of lotus flowers. This costume was certainly lessmodest than <strong>the</strong> typical Old Kingdom dress for women.Women of all classes normally wore tight-fitting longdresses with straps over <strong>the</strong> shoulders and a V-neck; <strong>the</strong>singers and clappers are distinguished from <strong>the</strong> dancersby <strong>the</strong>ir wearing of this more traditional clothing. Theshort skirt clearly allowed <strong>the</strong> dancers to move more freelythan <strong>the</strong>y would while wearing <strong>the</strong> typical street clo<strong>the</strong>s.Some scholars have suggested that this costume indicates<strong>the</strong> dancers were foreigners. Though foreigners could bemembers of <strong>the</strong> dance troupe, <strong>the</strong>re is no evidence to support<strong>the</strong> belief that foreigners or foreign dress dominatedEgyptian dance.IN PROCESSION. In at least one case during <strong>the</strong> OldKingdom, a tomb displays dancers doing <strong>the</strong> iba dancein a funeral procession ra<strong>the</strong>r than during a meal. Thewomen dancing in <strong>the</strong> tomb of Akhethotep raise <strong>the</strong>irarms to form a diamond shape with <strong>the</strong> hands apart. Perhapsthis scene is a clue that <strong>the</strong> iba actually was a partof <strong>the</strong> tjeref funeral dance. The nature of <strong>the</strong> evidencemakes it difficult to know exactly how <strong>the</strong>se dances fittoge<strong>the</strong>r.80 Arts and Humanities <strong>Through</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Eras</strong>: Ancient Egypt (2675 B.C.E.–332 B.C.E.)