- Page 1:
United Nations Environment Programm
- Page 4 and 5:
IPEA Instituto de Pesquisas Econôm
- Page 6 and 7:
GEO Brazil 2002- Brazil Environment
- Page 8 and 9:
presentation of the Minister of Sta
- Page 10 and 11:
UNEP Presentation Introduction to E
- Page 12 and 13:
These are aspects that provide moti
- Page 14 and 15:
Chapter 2 .........................
- Page 16 and 17:
8.9 Habitat Loss and Biodiversity -
- Page 18 and 19:
2.1 Precedents: Rio 92 and Agenda 2
- Page 20 and 21:
Overview ..........................
- Page 22 and 23:
list of pictures Chapter 1 Introduc
- Page 24 and 25:
The state of forests Table 1 Natura
- Page 26 and 27:
Table 8 Annual average growth rate
- Page 28 and 29:
Figure 6 Indigenous lands likely to
- Page 31 and 32:
introduction 1. IDENTITY AND TERRIT
- Page 33 and 34:
The underlying principle guiding th
- Page 35 and 36:
1.4. Report’s Structure and Conte
- Page 37 and 38:
The ANNEXES in the end of this repo
- Page 39 and 40:
2. Current Status and Perspectives
- Page 41 and 42:
An interesting system to define pos
- Page 43 and 44:
Some relevant aspects rise in the i
- Page 45 and 46:
What has been proposed as a mechani
- Page 47 and 48:
The second reason is the short term
- Page 49 and 50:
A redesign of the institutional str
- Page 51 and 52:
chapter 2 the state of the the stat
- Page 53 and 54:
territorial dynamics and the enviro
- Page 55 and 56:
cycle, which at its time was the mo
- Page 57 and 58:
200 - 500 inhabitants - which in 19
- Page 59 and 60:
This new environmental division of
- Page 61 and 62:
Superior plants, despite betterclas
- Page 63:
Figure 1-Proportion of taxons of or
- Page 66 and 67:
the state of biodiversity the state
- Page 68 and 69:
the state of biodiversity the state
- Page 70 and 71:
the state of biodiversity the state
- Page 72 and 73:
the state of biodiversity the state
- Page 74 and 75:
the state of biodiversity the state
- Page 76 and 77:
soil conditions the state of the en
- Page 78 and 79:
soil conditions 12 Land potential u
- Page 80:
soil conditions the state of the en
- Page 83 and 84:
the Northeast In 1998, average farm
- Page 85 and 86:
In ha Figure 4 - A verage area of h
- Page 87 and 88:
A distance concept (in metres L 1 )
- Page 89 and 90:
that, it may be a possible solution
- Page 91 and 92:
m 3 in agricultural lands and 448 b
- Page 93 and 94:
environmental availability (shallow
- Page 95 and 96:
All and any human activity leads to
- Page 97 and 98:
Figure 1 - Geologic units that are
- Page 99 and 100:
Table 1 - Environmental Impacts on
- Page 101 and 102:
Figure 3 - Impact of gold prospecti
- Page 103 and 104:
23 Environmental Impacts resulting
- Page 105 and 106:
the state of environment in Brazil
- Page 107 and 108:
shortage in the Northeastern region
- Page 109 and 110:
Chart 2 - P opulation s erved w ith
- Page 111 and 112:
carried out as far as requests for
- Page 113 and 114:
generation Hydro-electric generatio
- Page 115 and 116:
the use of the soil do not exacerba
- Page 117 and 118:
of water levels in water wells resu
- Page 119 and 120:
Barreiras Group, sandy re-covering
- Page 121 and 122:
consolidated The dominant aquifers
- Page 123 and 124:
Thus, the volume produced by a well
- Page 125 and 126:
is already understood that the cons
- Page 127 and 128:
the state of forests Approximately
- Page 129 and 130:
the 1960s, wood was really not a re
- Page 131 and 132:
Programme for Vegetal Charcoal-Base
- Page 133 and 134:
artefacts, it can reach up to US$15
- Page 135 and 136:
of the subject- ranging from quanti
- Page 137 and 138:
the state of the atmosphere The res
- Page 139 and 140:
destructive substances The Vienna C
- Page 141 and 142:
4 Brazil and the Climatic Change Co
- Page 143 and 144: effect gas emission than gasoline R
- Page 145 and 146: Thousand ha/year by satellite image
- Page 147 and 148: Brazilian marine and coastal enviro
- Page 149 and 150: ) The gradual expansion of the city
- Page 151 and 152: Concerning the rubbish, 90 percent
- Page 153 and 154: 5 Tourism Nowadays, tourism represe
- Page 155 and 156: Criciúma, Imbituba and Tubarão pr
- Page 157 and 158: the state of the environment in Bra
- Page 159 and 160: the state of the environment in Bra
- Page 161 and 162: The productivity of the North is hi
- Page 163 and 164: quality of the post-larvae, and the
- Page 165 and 166: level of sustainability Some have e
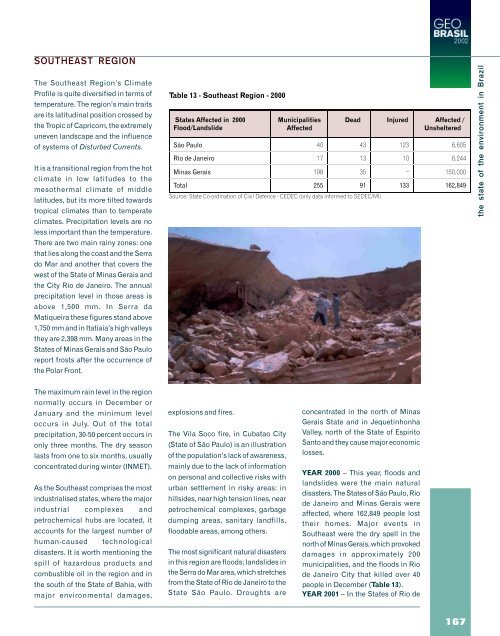
- Page 167 and 168: activity was initiated in the late
- Page 169 and 170: a tendency to decrease was observed
- Page 171 and 172: presented at least two possible cau
- Page 173 and 174: of the main marine fishing resource
- Page 175 and 176: protozoans and helminths that can b
- Page 177 and 178: c) Biological: dengue, yellow fever
- Page 179 and 180: There is a great need for a governm
- Page 181 and 182: the state of the environment in Bra
- Page 183 and 184: The dry season, as a disaster, is r
- Page 185 and 186: to cutting and burning forests for
- Page 187 and 188: Hail causes great losses in agricul
- Page 189 and 190: Accidents with Oil Spills The petro
- Page 191 and 192: NORTH REGION The North covers nearl
- Page 193: A lack of proper environmental awar
- Page 197 and 198: occurs in winter, and the minimum l
- Page 199 and 200: the state of the environment in Bra
- Page 201 and 202: growth rate and a slow down of this
- Page 203 and 204: There were later relatively stable
- Page 205 and 206: From that time on, demographic conc
- Page 207 and 208: Map 3 - Migration balance 1986 - 19
- Page 209 and 210: Table9-StructureoftheBrazilian indu
- Page 211 and 212: 34 Industrialisation and Spatial Re
- Page 213 and 214: obstacle to credit access and to of
- Page 215 and 216: most important action, therefore, i
- Page 217 and 218: In the Brazilian metropolitan regio
- Page 219 and 220: activities are more concentrated an
- Page 221 and 222: Another biomass power source adopte
- Page 223 and 224: ecreational activity In addition to
- Page 225 and 226: 115 Impact Indicators 1151 Health D
- Page 227 and 228: US$325 million/year) This amount is
- Page 229 and 230: Regarding the historical perspectiv
- Page 231 and 232: In 1999, homicides ranked first in
- Page 233 and 234: 123 Infectious and parasitic diseas
- Page 235 and 236: The state of health and the environ
- Page 237 and 238: The state of health and the environ
- Page 239 and 240: eassessment by North American healt
- Page 241 and 242: indicating the organisms were alrea
- Page 243 and 244: 125Atmospheric Pollution Atmospheri
- Page 245 and 246:
Every year, landslides during heavy
- Page 247 and 248:
chapter 3 policies feedback
- Page 249 and 250:
policies feedback 1. Inheritance an
- Page 251 and 252:
However, CCZEE limited itself to im
- Page 253 and 254:
2. International Agreements Resulti
- Page 255 and 256:
policies feedback 227
- Page 257 and 258:
During recent years a few legal tex
- Page 259 and 260:
policies feedback 231
- Page 261 and 262:
Within the decentralisation issue l
- Page 263 and 264:
Because of these actions, concern f
- Page 265 and 266:
4. Sectorial Policy Responses and A
- Page 267 and 268:
criteria for the creation and manag
- Page 269 and 270:
Pantanal areas (www.bdt. fat.org.br
- Page 271 and 272:
populations, the maintenance of the
- Page 273 and 274:
4.2. Soil Governmental actions that
- Page 275 and 276:
a) To run a trend and stateanalysis
- Page 277 and 278:
as propellants for their aerosol sy
- Page 279 and 280:
4.2.3. Positive Impacts from the Us
- Page 281 and 282:
and São Paulo), or by elaborating
- Page 283 and 284:
possibilities of their use should b
- Page 285 and 286:
charging on productive processes as
- Page 287 and 288:
In general, the instituted model is
- Page 289 and 290:
4.4.5. Regulation It is demonstrate
- Page 291 and 292:
Parallel to the investigation effor
- Page 293 and 294:
monitoring and controlling forest u
- Page 295 and 296:
However, there are important knowle
- Page 297 and 298:
This total of 34.65 MtCO 2, during
- Page 299 and 300:
a) labelling programmeme to inform
- Page 301 and 302:
4.6.4. Specific Actions to Combat A
- Page 303 and 304:
4.7 Coastal and Sea Areas One of th
- Page 305 and 306:
4.8. Fishing The first aspect to be
- Page 307 and 308:
e) Creation of CEPED agencies - Aca
- Page 309 and 310:
Again, institutionally, a Secretary
- Page 311 and 312:
dissatisfaction by 50 per cent, by
- Page 313 and 314:
Urban environmental management also
- Page 315 and 316:
Despite being FUNASA’s direct res
- Page 317 and 318:
5. Challenges The government’s pr
- Page 319:
progressive lead Brazil towards the
- Page 323 and 324:
environmental management Overview C
- Page 325 and 326:
1. The Continuation of Environmenta
- Page 327 and 328:
Itajaí, and Florianópolis (SC), i
- Page 329 and 330:
Deforestation and cattle raising fo
- Page 331 and 332:
In the Pantanal Complex, native veg
- Page 333 and 334:
environmental management 305
- Page 335 and 336:
Chart 1-TrendScenario - Pressurre-I
- Page 337 and 338:
With regard to the plan for financi
- Page 339 and 340:
c) policies or actions that are not
- Page 341 and 342:
Desired Scenario - Impact-Response
- Page 343 and 344:
Table 1 - Deforestation expected al
- Page 345:
chapter 5 recommendations 317
- Page 348 and 349:
ecommendations decisive in the cons
- Page 350 and 351:
ecommendations d) Inter relationshi
- Page 352 and 353:
ecommendations c) that the governme
- Page 354 and 355:
6.6 Scenarios 6.7. Biodiversity and
- Page 356 and 357:
ecommendations 7.1. To reinfor einf
- Page 358 and 359:
ecommendations 8.3. Vulnerability a
- Page 361:
annexes es
- Page 364 and 365:
GEO Report - Statistical Annex - Me
- Page 366 and 367:
annex 1 - statistics - metadata ann
- Page 368 and 369:
annex 1 - statistics - metadata ann
- Page 370 and 371:
annex 1 - statistics - metadata ann
- Page 372 and 373:
annex 1 - statistics - metadata ann
- Page 374 and 375:
annex 1 - statistics - metadata Sou
- Page 376 and 377:
annex 1 - statistics - metadata ann
- Page 378 and 379:
annex 1 - statistics - metadata ann
- Page 380 and 381:
annex 1 - statistics - metadata ann
- Page 382 and 383:
annex 1 - statistics -metadata anne
- Page 384 and 385:
annex 1 - statistics -metadata anne
- Page 386 and 387:
annex 1 - statistics -metadata anne
- Page 388 and 389:
annex 1 - statistics -metadata anne
- Page 390 and 391:
annex 1 - statistics -metadata anne
- Page 392 and 393:
annex 1 - statistics -metadata anne
- Page 394 and 395:
annex 1 - statistics -metadata B.7.
- Page 396 and 397:
annex 1 - statistics -metadata B.7.
- Page 398 and 399:
annex 1 - statistics -metadata B.7.
- Page 400 and 401:
annex 1 - statistics -metadata anne
- Page 402 and 403:
A. Socioeconomic and cultural facto
- Page 404 and 405:
A. State of the Environment and Tre
- Page 406 and 407:
B. Socioeconomic and Cultural Facto
- Page 408 and 409:
B. Socioeconomic and Cultural Facto
- Page 410 and 411:
annex 2 - main economic and environ
- Page 412 and 413:
annex 2 - main economic and environ
- Page 414 and 415:
annex 2 - main economic and environ
- Page 416 and 417:
annex x 3 - biodiversity annex 3 Th
- Page 418 and 419:
annex 3 - biodiversity anexo 3 The
- Page 420 and 421:
annex 3 - biodiversity annex 3 The
- Page 422 and 423:
annex 3 - biodiversity annex 3 394
- Page 424 and 425:
anexo 3 - biodiversity annex 3 396
- Page 426 and 427:
annex 4 - compilation of brazilian
- Page 428 and 429:
anexo 4 3. BIODIVERSITY LAW 5.197 0
- Page 430 and 431:
annex 4 - compilation of brazilian
- Page 432 and 433:
annex 4 - compilation of brazilian
- Page 434 and 435:
annex 4 - compilation of brazilian
- Page 436 and 437:
annex 4 - compilation of brazilian
- Page 438 and 439:
anexo 4 DECREE 03/22/1997 Regulates
- Page 440 and 441:
colaboradores anexo 2 FIOCRUZ - Fun
- Page 442 and 443:
ibliografia ASSOCIAÇÃO NACIONAL D
- Page 444 and 445:
ibliografia _____. Governo do Brasi
- Page 446 and 447:
ibliografia CASTAGNOLLI, N. Aquicul
- Page 448 and 449:
ibliografia _____. (2002a).Centro N
- Page 450 and 451:
ibliografia EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE P
- Page 452 and 453:
ibliografia FUNDAÇÃO SOS MATA ATL
- Page 454 and 455:
ibliografia _____. Recursos pesquei
- Page 456 and 457:
ibliografia KAGEYAMA P.Y. SOUZA L.M
- Page 458 and 459:
ibliografia MACHADO, G.V. Estimativ
- Page 460 and 461:
ibliografia _____.; Secretaria Espe
- Page 462 and 463:
ibliografia PARANÁ. Casa Civil - C
- Page 464 and 465:
ibliografia REDE INTRAGERENCIAL DE
- Page 466 and 467:
ibliografia SANTOS, J. R., T. KRUG,
- Page 468 and 469:
ibliografia TRAFFIC. 2000. El merca
- Page 470 and 471:
glossary y of the acronyms glossary
- Page 472 and 473:
CESP - Companhia Energética de Sã
- Page 474 and 475:
IPT - Instituto de Pesquisas Tecnol
- Page 476 and 477:
REVIZEE - Programa de Avaliação d