GEO Brasil - UNEP
GEO Brasil - UNEP
GEO Brasil - UNEP
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
that, it may be a possible solution to<br />
reduce the need for occupation and<br />
agricultural use of land by increasing<br />
agricultural income, production and<br />
productivity To accomplish that, it is<br />
necessary to implement new credit<br />
policies in order to enable<br />
technological investment and access<br />
to credit to overcome high financial<br />
costs These policies should also<br />
include the participation of small<br />
farmers For this to occur, alternative<br />
solutions should be found in order to<br />
guarantees, liabilities and other issues<br />
that cannot be controlled by these<br />
farmers<br />
The national livestock is the second<br />
largest in the world, estimated in 157<br />
million heads of cattle (32 million dairy<br />
cattle and 125 million beef cattle)<br />
distributed among 16 million raising<br />
farms In order to reach these<br />
numbers, it was necessary to recycle<br />
pasturelands Thus, the use of<br />
cultivated pastures prevailed over<br />
other types of land management This<br />
demonstrates spatial movement and<br />
has been relatively important to the<br />
expansion of the agricultural frontier<br />
in Brazil A comparative analysis using<br />
aggregated data shows that the<br />
cultivation of pasture areas has been<br />
done beyond land capacity, except for<br />
the North (see figure 8)<br />
Although this comparison does not<br />
necessarily indicate that agricultural<br />
activity is taking place on less<br />
appropriate or inappropriate land, it<br />
works as an indirect indicator of land<br />
pressure Consequently, because of<br />
the lower comparative profitability of<br />
agricultural land, there is a tendency<br />
to replace it with natural or cultivated<br />
pastures in the South, Southeast and<br />
MidWest Regions<br />
A report on the average profitability<br />
in the raising sector reveals that<br />
medium size cattle raisers own an<br />
average of 75 heads of cattle, which<br />
represents a R$ 100 monthly income,<br />
considering a 15 percent net margin<br />
(EMBRAPA 2001- unofficial estimate<br />
from aggregated data) These figures<br />
illustrate the difficulties faced by<br />
small producers and the pressure<br />
exerted on less appropriate land like<br />
that situated in mountainous regions<br />
of the Southeast Thus, there is a<br />
need for programmes and policies<br />
regarding agriculture diversification/<br />
organisation, pasture and soil<br />
recovery and even the reforestation<br />
of threatened biomes<br />
Pasture degradation is a cause for<br />
concern in Brazil, chiefly because of the<br />
current extension of land in use Even<br />
though technological alternatives are<br />
available, the low profitability, specially<br />
of small and medium cattle raisers,<br />
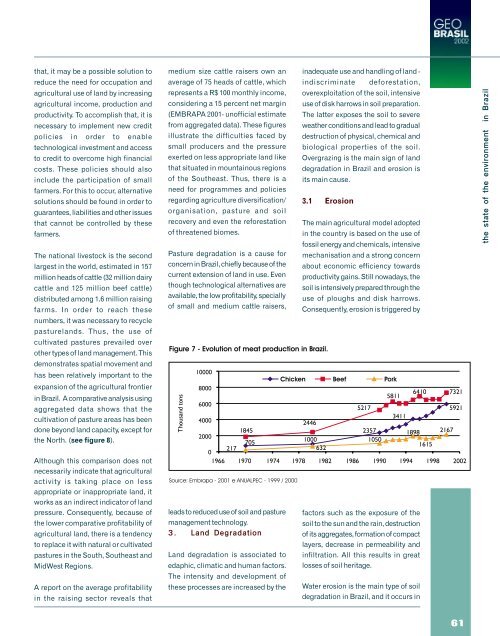
Figure 7 - Evolution of meat production in Brazil.<br />
Thousand tons<br />
10000<br />
Chicken Beef Pork<br />
8000<br />
6410 7321<br />
5811<br />
6000<br />
5217<br />
5921<br />
3411<br />
4000<br />
2446<br />
1845<br />
2357 1898 2167<br />
2000<br />
705<br />
1000<br />
1050<br />
1615<br />
217 632<br />
0<br />
1966 1970 1974 1978 1982 1986 1990 1994 1998 2002<br />
Source: Embrapa - 2001 e ANUALPEC - 1999 / 2000<br />
leads to reduced use of soil and pasture<br />
management technology<br />
3 Land Degradation<br />
Land degradation is associated to<br />
edaphic, climatic and human factors<br />
The intensity and development of<br />
these processes are increased by the<br />
inadequate use and handling of land -<br />
indiscriminate deforestation,<br />
overexploitation of the soil, intensive<br />
use of disk harrows in soil preparation<br />
The latter exposes the soil to severe<br />
weather conditions and lead to gradual<br />
destruction of physical, chemical and<br />
biological properties of the soil<br />
Overgrazing is the main sign of land<br />
degradation in Brazil and erosion is<br />
its main cause<br />
31<br />
Erosion<br />
The main agricultural model adopted<br />
in the country is based on the use of<br />
fossil energy and chemicals, intensive<br />
mechanisation and a strong concern<br />
about economic efficiency towards<br />
productivity gains Still nowadays, the<br />
soil is intensively prepared through the<br />
use of ploughs and disk harrows<br />
Consequently, erosion is triggered by<br />
factors such as the exposure of the<br />
soil to the sun and the rain, destruction<br />
of its aggregates, formation of compact<br />
layers, decrease in permeability and<br />
infiltration All this results in great<br />
losses of soil heritage<br />
Water erosion is the main type of soil<br />
degradation in Brazil, and it occurs in<br />
the state of the environment in Brazil<br />
61