Studies on the use of nano zinc oxide and modified silica in NR, CR ...
Studies on the use of nano zinc oxide and modified silica in NR, CR ...
Studies on the use of nano zinc oxide and modified silica in NR, CR ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 6<br />
107<br />
Physical properties such as modulus, tensile strength, el<strong>on</strong>gati<strong>on</strong> at<br />
break, tear strength, hardness, heat build-up, compressi<strong>on</strong> set, flex resistance,<br />
abrasi<strong>on</strong> resistance <strong>and</strong> age<strong>in</strong>g resistance were studied as per <strong>the</strong> relevant<br />
ASTM st<strong>and</strong>ards. Swell<strong>in</strong>g studies were <strong>use</strong>d to study <strong>the</strong> crossl<strong>in</strong>k density.<br />
The equilibrium swell<strong>in</strong>g studies <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> compounds were carried out <strong>in</strong><br />
toluene <strong>and</strong> crossl<strong>in</strong>k densities were calculated us<strong>in</strong>g Flory-Rehner equati<strong>on</strong>.<br />
6.3 Results <strong>and</strong> discussi<strong>on</strong><br />
6.3.1 Cure characteristics<br />
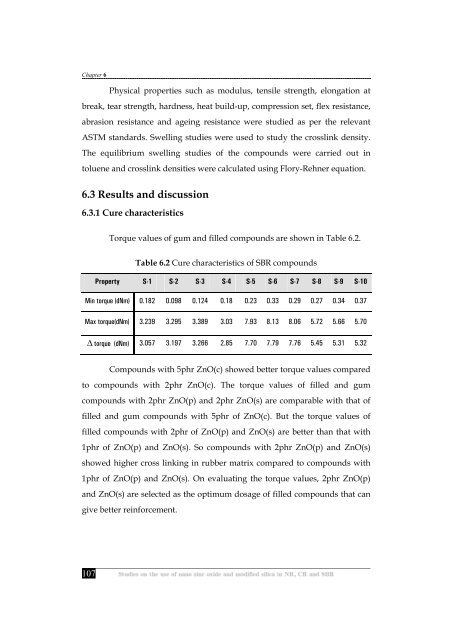
Torque values <strong>of</strong> gum <strong>and</strong> filled compounds are shown <strong>in</strong> Table 6.2.<br />
Table 6.2 Cure characteristics <strong>of</strong> SBR compounds<br />
Property S-1 S-2 S-3 S-4 S-5 S-6 S-7 S-8 S-9 S-10<br />
M<strong>in</strong> torque (dNm) 0.182 0.098 0.124 0.18 0.23 0.33 0.29 0.27 0.34 0.37<br />
Max torque(dNm) 3.239 3.295 3.389 3.03 7.93 8.13 8.06 5.72 5.66 5.70<br />
∆ torque (dNm) 3.057 3.197 3.266 2.85 7.70 7.79 7.76 5.45 5.31 5.32<br />
Compounds with 5phr ZnO(c) showed better torque values compared<br />
to compounds with 2phr ZnO(c). The torque values <strong>of</strong> filled <strong>and</strong> gum<br />
compounds with 2phr ZnO(p) <strong>and</strong> 2phr ZnO(s) are comparable with that <strong>of</strong><br />
filled <strong>and</strong> gum compounds with 5phr <strong>of</strong> ZnO(c). But <strong>the</strong> torque values <strong>of</strong><br />
filled compounds with 2phr <strong>of</strong> ZnO(p) <strong>and</strong> ZnO(s) are better than that with<br />
1phr <strong>of</strong> ZnO(p) <strong>and</strong> ZnO(s). So compounds with 2phr ZnO(p) <strong>and</strong> ZnO(s)<br />
showed higher cross l<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> rubber matrix compared to compounds with<br />
1phr <strong>of</strong> ZnO(p) <strong>and</strong> ZnO(s). On evaluat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> torque values, 2phr ZnO(p)<br />
<strong>and</strong> ZnO(s) are selected as <strong>the</strong> optimum dosage <strong>of</strong> filled compounds that can<br />
give better re<strong>in</strong>forcement.