Solar Energy Perspectives - IEA
Solar Energy Perspectives - IEA
Solar Energy Perspectives - IEA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Solar</strong> <strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Perspectives</strong>: <strong>Solar</strong> heat<br />
The most simple devices, so-called “unglazed collectors”, used for example to warm the<br />
water of swimming pools (mostly in Australia, Canada and the United States) or outside<br />
showers, are just black hoses lying on the ground or attached to the shower structure.<br />
Unglazed systems can also warm the air (see below under flat-plate collectors).<br />
For higher temperature applications, including ensuring the availability of sanitary hot water,<br />
one must use flat-plate collectors or evacuated tubes. Advanced flat-plate and compound<br />
parabolic collectors (CPC) allow working temperatures of 100°C to 160°C. Concentrating<br />
collectors (Fresnel, parabolic troughs, dishes and towers or central receivers, ovens) allow<br />
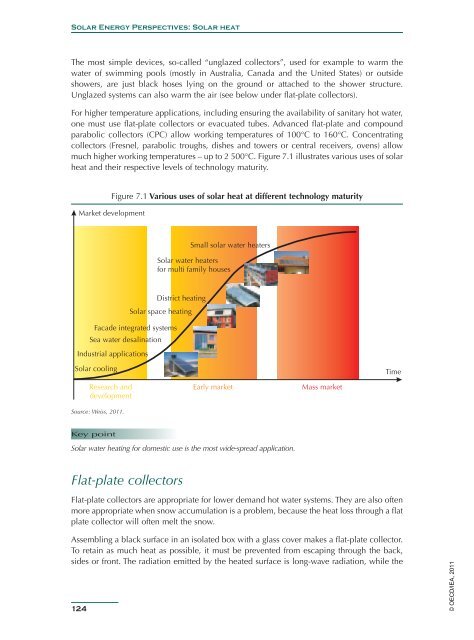
much higher working temperatures – up to 2 500°C. Figure 7.1 illustrates various uses of solar<br />
heat and their respective levels of technology maturity.<br />
Figure 7.1 Various uses of solar heat at different technology maturity<br />
Market development<br />
Small solar water heaters<br />
<strong>Solar</strong> water heaters<br />
for multi family houses<br />
District heating<br />
<strong>Solar</strong> space heating<br />
Facade integrated systems<br />
Sea water desalination<br />
Industrial applications<br />
<strong>Solar</strong> cooling<br />
Time<br />
Research and<br />
development<br />
Source: Weiss, 2011.<br />
Early market<br />
Mass market<br />
Key point<br />
<strong>Solar</strong> water heating for domestic use is the most wide-spread application.<br />
Flat-plate collectors<br />
Flat-plate collectors are appropriate for lower demand hot water systems. They are also often<br />
more appropriate when snow accumulation is a problem, because the heat loss through a flat<br />
plate collector will often melt the snow.<br />
Assembling a black surface in an isolated box with a glass cover makes a flat-plate collector.<br />
To retain as much heat as possible, it must be prevented from escaping through the back,<br />
sides or front. The radiation emitted by the heated surface is long-wave radiation, while the<br />
124<br />
© OECD/<strong>IEA</strong>, 2011