Solar Energy Perspectives - IEA
Solar Energy Perspectives - IEA
Solar Energy Perspectives - IEA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Solar</strong> <strong>Energy</strong> <strong>Perspectives</strong>: Policies<br />
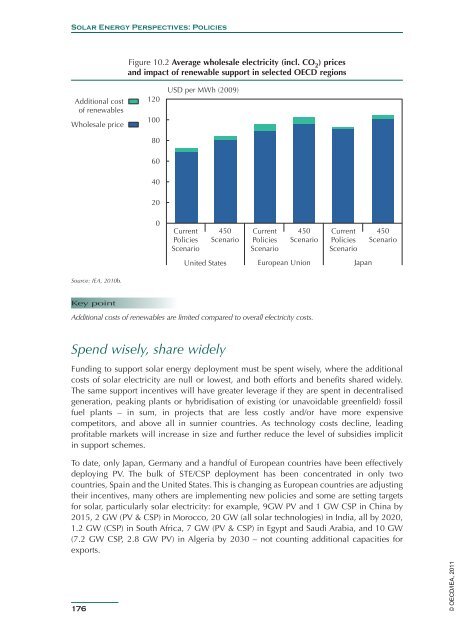
Figure 10.2 Average wholesale electricity (incl. CO 2 ) prices<br />
and impact of renewable support in selected OECD regions<br />
Additional cost<br />
of renewables<br />
Wholesale price<br />
120<br />
100<br />
80<br />
USD per MWh (2009)<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
0<br />
Current<br />
Policies<br />
Scenario<br />
450<br />
Scenario<br />
Current<br />
Policies<br />
Scenario<br />
450<br />
Scenario<br />
Current<br />
Policies<br />
Scenario<br />
United States European Union Japan<br />
450<br />
Scenario<br />
Source: <strong>IEA</strong>, 2010b.<br />
Key point<br />
Additional costs of renewables are limited compared to overall electricity costs.<br />
Spend wisely, share widely<br />
Funding to support solar energy deployment must be spent wisely, where the additional<br />
costs of solar electricity are null or lowest, and both efforts and benefits shared widely.<br />
The same support incentives will have greater leverage if they are spent in decentralised<br />
generation, peaking plants or hybridisation of existing (or unavoidable greenfield) fossil<br />
fuel plants – in sum, in projects that are less costly and/or have more expensive<br />
competitors, and above all in sunnier countries. As technology costs decline, leading<br />
profitable markets will increase in size and further reduce the level of subsidies implicit<br />
in support schemes.<br />
To date, only Japan, Germany and a handful of European countries have been effectively<br />
deploying PV. The bulk of STE/CSP deployment has been concentrated in only two<br />
countries, Spain and the United States. This is changing as European countries are adjusting<br />
their incentives, many others are implementing new policies and some are setting targets<br />
for solar, particularly solar electricity: for example, 9GW PV and 1 GW CSP in China by<br />
2015, 2 GW (PV & CSP) in Morocco, 20 GW (all solar technologies) in India, all by 2020,<br />
1.2 GW (CSP) in South Africa, 7 GW (PV & CSP) in Egypt and Saudi Arabia, and 10 GW<br />
(7.2 GW CSP, 2.8 GW PV) in Algeria by 2030 – not counting additional capacities for<br />
exports.<br />
176<br />
© OECD/<strong>IEA</strong>, 2011