Solar Energy Perspectives - IEA
Solar Energy Perspectives - IEA
Solar Energy Perspectives - IEA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 3: <strong>Solar</strong> electricity<br />
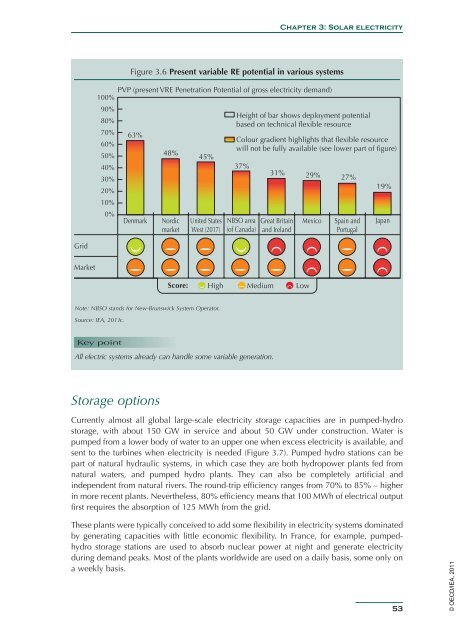
Figure 3.6 Present variable RE potential in various systems<br />
PVP (present VRE Penetration Potential of gross electricity demand)<br />
100%<br />
90%<br />
Height of bar shows deployment potential<br />
80%<br />
based on technical flexible resource<br />
70% 63%<br />
Colour gradient highlights that flexible resource<br />
60%<br />
will not be fully available (see lower part of figure)<br />
50%<br />
48%<br />
45%<br />
40%<br />
37%<br />
31% 29%<br />
30%<br />
27%<br />
20%<br />
19%<br />
10%<br />
0%<br />
Denmark Nordic<br />
market<br />
United States<br />
West (2017)<br />
NBSO area<br />
(of Canada)<br />
Mexico<br />
Japan<br />
Great Britain<br />
and Ireland<br />
Spain and<br />
Portugal<br />
Grid<br />
Market<br />
Score:<br />
High Medium Low<br />
Note: NBSO stands for New-Brunswick System Operator.<br />
Source: <strong>IEA</strong>, 2011c .<br />
Key point<br />
All electric systems already can handle some variable generation.<br />
Storage options<br />
Currently almost all global large-scale electricity storage capacities are in pumped-hydro<br />
storage, with about 150 GW in service and about 50 GW under construction. Water is<br />
pumped from a lower body of water to an upper one when excess electricity is available, and<br />
sent to the turbines when electricity is needed (Figure 3.7). Pumped hydro stations can be<br />
part of natural hydraulic systems, in which case they are both hydropower plants fed from<br />
natural waters, and pumped hydro plants. They can also be completely artificial and<br />
independent from natural rivers. The round-trip efficiency ranges from 70% to 85% – higher<br />
in more recent plants. Nevertheless, 80% efficiency means that 100 MWh of electrical output<br />
first requires the absorption of 125 MWh from the grid.<br />
These plants were typically conceived to add some flexibility in electricity systems dominated<br />
by generating capacities with little economic flexibility. In France, for example, pumpedhydro<br />
storage stations are used to absorb nuclear power at night and generate electricity<br />
during demand peaks. Most of the plants worldwide are used on a daily basis, some only on<br />
a weekly basis.<br />
53<br />
© OECD/<strong>IEA</strong>, 2011