- Page 1 and 2:
DELOREAN WORKSHOP MANUAL PJ. GRADY
- Page 3 and 4:
r r r • i r I r r I I Issued by:
- Page 5 and 6:
SERVICE ORGANISATION In order to pr
- Page 7 and 8:
i GENERAL SAFETY HINTS 1. Use the c
- Page 9 and 10:
• • r r r r r General Data CONT
- Page 11 and 12:
A:01:02 IGNITION SYSTEM (Contd.) Sp
- Page 13 and 14:
General Data A:02:01 ENGINE TUNING
- Page 15 and 16:
A:03:02 General Data DESCRIPTION TR
- Page 17 and 18:
A:03:04 General Data TORQUE FIGURES
- Page 19 and 20:
A — Overall Length B — Wheel Ba
- Page 21 and 22:
U 1 n PRE DELIVERY INSPECTION After
- Page 23 and 24:
I r r General Data LABEL IDENTIFICA
- Page 25 and 26:
f&T$ , W*$ fewt r jfi^T LABEL IDENT
- Page 27 and 28:
r r \r*l r
- Page 29 and 30:
IMPORTANT Fuel Tank B:01:01 REMOVIN
- Page 31 and 32:
Fuel Tank B:01:03 •
- Page 33 and 34:
Fig. 7 Number of Cylinders Bore Str
- Page 35 and 36:
TIGHTENING TORQUES-Figs. 3 and 4 No
- Page 37 and 38:
VALVE GUIDES Bore (mm) 8-8,022 (0.3
- Page 39 and 40:
r r r r r r r r r i r r CAMSHAFT Th
- Page 41 and 42:
REMOVING Disconnect battery. Remove
- Page 43 and 44: Remove coolant hoses at engine Remo
- Page 45 and 46: pm> fpg3\ ff&n, 0&t RETIGHTENING-TI
- Page 47 and 48: Tl^ty r •'•*'j "*& Fig. 27 SECO
- Page 49 and 50: • ^ * ? Remove the cylinder head
- Page 51 and 52: that the camshaft top is fully with
- Page 53 and 54: ROCKER SHAFTS DISMANTLING The oilwa
- Page 55 and 56: - f CHANGING The engine need not be
- Page 57 and 58: W&\ rrw\ EXAMPLE-Fig. 51 First meas
- Page 59 and 60: Check that each small end is lying
- Page 61 and 62: r Proceed in the same way for assem
- Page 63 and 64: IflTtl "
- Page 65 and 66: Remove the timing chains RH first t
- Page 67 and 68: C:07:06 Engine Fig. 79 Refit the cr
- Page 69 and 70: C:07:08 Engine ANGULAR TIGHTENING O
- Page 71 and 72: Fig. 91 Lubricate the cylinder head
- Page 73 and 74: Fig. 99 J 28860 Smear the crankshaf
- Page 75 and 76: REMOVING Main Bearing Oil Seal—Fl
- Page 77 and 78: - r REMOVING Drain engine oil Remov
- Page 79 and 80: T^T) ryift] 7^1 I •'•'l p*^ Oil
- Page 81 and 82: p^ is*l £T-- ? >'I I'-TVN) 1^1 •
- Page 83 and 84: NOTE: The arm has LH and RH threade
- Page 85 and 86: © "&•• ? o 9 (S> O C ,s '*•*
- Page 87 and 88: Fuel Emission and Exhaust System CO
- Page 89 and 90: V D:01:02 COMPONENT LOCATION Mixtur
- Page 91 and 92: D:01:04 Fuel, Emission and Exhaust
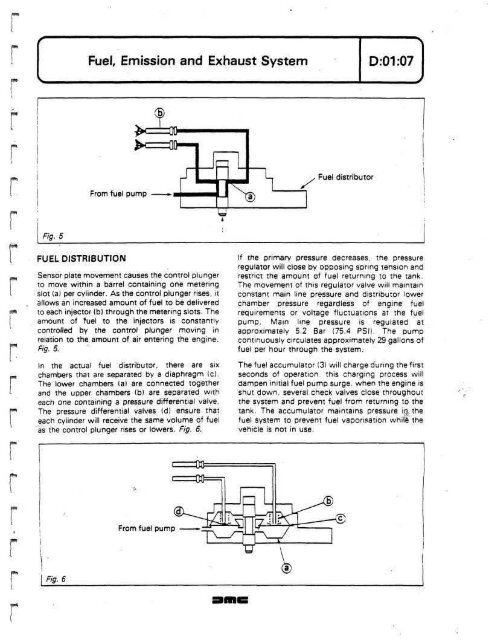
- Page 93: D:01:06 Fuel, Emission and Exhaust
- Page 97 and 98: D:01:10 Fuel, Emission and Exhaust
- Page 99 and 100: D:01:12 v. Fig. 12 High Control To
- Page 101 and 102: D:01:14 Fuel Emission and Exhaust S
- Page 103 and 104: D:01:16 Fuel, Emission and Exhaust
- Page 105 and 106: D:02:02 TEST GAUGE CONNECTION VALVE
- Page 107 and 108: &Wy Fuel, Emission and Exhaust Syst
- Page 109 and 110: Fuel, Emission and Exhaust System D
- Page 111 and 112: Fuel, Emission and Exhaust System D
- Page 113 and 114: Fuel, Emission and Exhaust System D
- Page 115 and 116: Fuel, Emission and Exhaust System D
- Page 117 and 118: f^ r^ P" 1 Jr*!> Fig. 31 Fuel, Emis
- Page 119 and 120: f^ H^I rm\ Pvf9| F/0. 34 Fuel, Emis
- Page 121 and 122: 7^:5 r^ K ''-i f*f!*l SPECIFICATION
- Page 123 and 124: D:05:02 Fuel, Emission and Exhaust
- Page 125 and 126: D:05:04 Fuel, Emission and Exhaust
- Page 127 and 128: Fig. 42 A purge valve located insid
- Page 129 and 130: Fuel Emission and Exhaust System D:
- Page 131 and 132: V Fuel Emission and Exhaust System
- Page 133 and 134: t— ^ REMOVING Fuel, Emission and
- Page 135 and 136: P"^ I I'f'M ~^"H «wi p v H GENERAL
- Page 137 and 138: Fmr-i P7^> P pfff rfa^ iwSS( J Fig.
- Page 139 and 140: pn f^i r i tin*!) C*'"''-1 pfi^l n?
- Page 141 and 142: ^T^H, ^ rrr^ • T?*!l REMOVAL Clut
- Page 143 and 144: fF&H 0h BLEEDING SYSTEM 1. Top up c
- Page 145 and 146:
Note: Do not use any cleaning fluid
- Page 147 and 148:
CLUTCH PIPING The clutch pipe leadi
- Page 149 and 150:
5fW| V "f»TJ - fr"h GENERAL DESCRI
- Page 151 and 152:
(TVS*) L I *W| M*J FFr^ff| GEAR RAT
- Page 153 and 154:
f •:' 1 Manual Transmission F:04:
- Page 155 and 156:
p"'4 /.•" iV-Ff r , ':'''^t TRANS
- Page 157 and 158:
Manual Transmission OVERHAULING TRA
- Page 159 and 160:
r r r r r r - r r r r r r r r r UNI
- Page 161 and 162:
1 r p*^ fr^) fiFrtr) 28. Clean the
- Page 163 and 164:
r r r • - r r r r r Fig 26 Fig. 2
- Page 165 and 166:
r i r r r r r r r i r I DIFFERENTIA
- Page 167 and 168:
Manual Transmission F:06:11 5. Remo
- Page 169 and 170:
CONTROLS DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
- Page 171 and 172:
- r r r r Automatic Transmission CO
- Page 173 and 174:
G:01:02 Automatic Transmission achi
- Page 175 and 176:
G:02:02 Automatic Transmission LOCA
- Page 177 and 178:
DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURE 1. Road test th
- Page 179 and 180:
FAULTS ENGINE STALLS UNEVEN IDLING
- Page 181 and 182:
Automatic Transmission G:05:01 CHEC
- Page 183 and 184:
Automatic Transmission G:05:03 / h
- Page 185 and 186:
5. Remove the solenoid mounting bol
- Page 187 and 188:
G:06:04 Automatic Transmission 8. R
- Page 189 and 190:
' r v 1. Disconnect the negative ba
- Page 191 and 192:
r i r r i r - • r j r r r i r r /
- Page 193 and 194:
fT
- Page 195 and 196:
JW^i !'••-'• f '^\ 7*$5 wm, r
- Page 197 and 198:
M pT^I TRANSMISSION UNIT DISASSEMBL
- Page 199 and 200:
i f^) irm] 1 L /BTO BRAKE B-1 - Fig
- Page 201 and 202:
i ' M p77iT| F0*t\ |f^'^T\ Fig. 50
- Page 203 and 204:
r Fig. 57 C-1 PISTON SEALS Fig. 55
- Page 205 and 206:
r r / V Fig. 60 Automatic Transmiss
- Page 207 and 208:
v FINAL DRIVE DISASSEMBLY Automatic
- Page 209 and 210:
r r Automatic Transmission G:09:03
- Page 211 and 212:
^ r \ Automatic Transmission G .09:
- Page 213 and 214:
J Fig. 78 SIDE GEAR TOOL Reassembly
- Page 215 and 216:
Automatic Transmission G:09:09 3. F
- Page 217 and 218:
fj*«r |" CONTENTS ft**? j GENERAL
- Page 219 and 220:
FW\ Location Lower column to univer
- Page 221 and 222:
H:03:02 Steering 5. Position and se
- Page 223 and 224:
REMOVAL - Fig. 7 1. Raise luggage c
- Page 225 and 226:
REMOVAL 1. Remove rack and previous
- Page 227 and 228:
Front Suspension J:01:01 GENERAL DE
- Page 229 and 230:
REMOVAL 1. Raise car on hoist. 2. R
- Page 231 and 232:
REMOVAL 1. Raise car on hoist. 2. R
- Page 233 and 234:
J REMOVAL 1. Raise car on hoist. 2.
- Page 235 and 236:
~ J REMOVAL Front Suspension J:08:0
- Page 237 and 238:
r r r r J REMOVAL 1 Raise car on ho
- Page 239 and 240:
REMOVAL 1. Raise car on hoist, and
- Page 241 and 242:
Contents GENERAL DESCRIPTION K.01.0
- Page 243 and 244:
r r K:01:02 Rear Suspension
- Page 245 and 246:
;v?f?*) REMOVAL 1. Raise car on hoi
- Page 247 and 248:
REMOVAL Rear Suspension 1. Raise ca
- Page 249 and 250:
REMOVAL 1. Raise car on hoist. TRAI
- Page 251 and 252:
' 1. Check rear wheels for rim run
- Page 253 and 254:
r i r r r r r r I r r r r r I V* RE
- Page 255 and 256:
i-rw-] r r The vehicle is equipped
- Page 257 and 258:
T^M- w^ ••rrrr] J 1 ""?^ t ; -'
- Page 259 and 260:
Brakes, Wheels and Tyres 10. 11. Br
- Page 261 and 262:
installed. If the cylinder bore is
- Page 263 and 264:
I r REMOVAL 1. Remove brake disc pa
- Page 265 and 266:
jpffi pTI^ #6§ n*wi REMOVAL-Fig. 9
- Page 267 and 268:
BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER/FLUID RESERVO
- Page 269 and 270:
Automatic transmission only, Instal
- Page 271 and 272:
r r r r r r i r r r Brakes, Wheels
- Page 273 and 274:
1.1^-1 pwr^i jfrn^t ?TW$ r |!$P*I W
- Page 275 and 276:
'^WJ) p*sq pfl*V I The ignition sys
- Page 277 and 278:
J Electrical System and Instruments
- Page 279 and 280:
REMOVING - Fig. 7 DISCONNECT BATTER
- Page 281 and 282:
•jTv^ -ft'MWl rp9r\ REMOVING THE
- Page 283 and 284:
I r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r r
- Page 285 and 286:
REMOVING - Fig. 17 1. Disconnect Ba
- Page 287 and 288:
REMOVING THE DIODE CARRIER - Fig. 1
- Page 289 and 290:
PF*1 f$&8) H*pi} T^JW) f^M MBQ) 1.
- Page 291 and 292:
M:05:02 Electrical System and Instr
- Page 293 and 294:
M :05:04 Electrical System and Inst
- Page 295 and 296:
M:06:02 Electrical System and Instr
- Page 297 and 298:
State-of-Charge (Example) A complet
- Page 299 and 300:
M:06:06 Electrical System and Instr
- Page 301 and 302:
X23C83U43 :C3H8C93!L153 JC4D1L10X16
- Page 303 and 304:
HORNS - Fig. 32 Twin high and low t
- Page 305 and 306:
M:09:02 Electrical System and Instr
- Page 307 and 308:
i F^I f Electrical System and Instr
- Page 309 and 310:
HEAD LAMP UNIT REMOVING - REFITTING
- Page 311 and 312:
Electrical System and Instruments J
- Page 313 and 314:
J Electrical System and Instruments
- Page 315 and 316:
*TO| fW^ SIDE/HEADLAMP SWITCH REMOV
- Page 317 and 318:
PT5 |VfW) pr^ rfTWi Electrical Syst
- Page 319 and 320:
pwj fW\ nm?i ffWKTi F^*i ITl*fl) ->
- Page 321 and 322:
r Electrical System and Instruments
- Page 323 and 324:
r Electrical System and Instruments
- Page 325 and 326:
J Electrical System and Instruments
- Page 327 and 328:
j .f?
- Page 329 and 330:
ffiytxy . J jffS^ Electrical System
- Page 331 and 332:
P 1 "^ IW'I r J f— V Electrical S
- Page 333 and 334:
|HW\ ^•r^n r^*i ^ Electrical Syst
- Page 335 and 336:
j •"fW'-wl . p^£\ I J Electrical
- Page 337 and 338:
j 1 :^' 1 ;! [fP*fl" "•y&i J Elec
- Page 339 and 340:
P'fTTB! '•5*TT) Electrical System
- Page 341 and 342:
i"^5r^ |WW| Electrical pw| L I \ I
- Page 343 and 344:
•wi »-;,^) J Electrical System a
- Page 345 and 346:
Pf*5j f^\ ,^wv 1 J fWW( JIM) p*B^ E
- Page 347 and 348:
p^?i jlfaj \vvtfl ffWrft J Electric
- Page 349 and 350:
I > P Heating and Air Conditioning
- Page 351 and 352:
The layout of the heater/air condit
- Page 353 and 354:
The temperature control should be t
- Page 355 and 356:
N:01:06 Heating and Air Conditionin
- Page 357 and 358:
N:01:08 Heating and Air Conditionin
- Page 359 and 360:
v Heating and Air Conditioning SPEC
- Page 361 and 362:
Heating and Air Conditioning N:02:0
- Page 363 and 364:
N .03:02 Heating and Air Conditioni
- Page 365 and 366:
v Heating and Air Conditioning Air
- Page 367 and 368:
J Heating and Air Conditioning N:05
- Page 369 and 370:
N:06:02 Heating and Air Conditionin
- Page 371 and 372:
J REMOVING HEATER/AIR CONDITIONING
- Page 373 and 374:
u a n ALL DIMENSIONS REFER TO WRENC
- Page 375 and 376:
Heating and Air Conditioning IM:08:
- Page 377 and 378:
J Heating and Air Conditioning N:08
- Page 379 and 380:
J Heating and Air Conditioning N .0
- Page 381 and 382:
Heating and Air Conditioning ;3^\»
- Page 383 and 384:
J INSTALLING COMPRESSOR Heating and
- Page 385 and 386:
J 1 2 3 4 i 5 i 1 ! ! 1 ! ! I ; i i
- Page 387 and 388:
J Heating and Air Conditioning N:08
- Page 389 and 390:
J Heating and Air Conditioning 3. D
- Page 391 and 392:
Heating and Air Conditioning N .08:
- Page 393 and 394:
NOT ENOUGH COOLING Move temperature
- Page 395 and 396:
N:09:04 Heating and Air Conditionin
- Page 397 and 398:
J Heating and Air Conditioning N:10
- Page 399 and 400:
The preceding Trouble Shooting Char
- Page 401 and 402:
Heating and Air Conditioning N:10:0
- Page 403 and 404:
J Heating and Air Conditioning N:10
- Page 405 and 406:
Heating and Air Conditioning Step 6
- Page 407 and 408:
JTffi^ J Heating and Air Conditioni
- Page 409 and 410:
f: :' ! .-^.*VJ ^ J Heating and Air
- Page 411 and 412:
a^i Fnff&J Ff^\ J CONTENTS GLASS RE
- Page 413 and 414:
STANDARD SECTIONAL REPAIR MOULDINGS
- Page 415 and 416:
(3) When completely cured, drill a
- Page 417 and 418:
FRONT FENDER, LEFT OR RIGHT - Rg. 1
- Page 419 and 420:
4. Install four screws securing rea
- Page 421 and 422:
2. Before fitting replacement, chec
- Page 423 and 424:
3. Mark angular position of torsion
- Page 425 and 426:
3. Remove handle and disconnect rel
- Page 427 and 428:
9. Move the interior locking contro
- Page 429 and 430:
3. Remove nut securing cable housin
- Page 431 and 432:
REAR WINDOW SUNSHADE LOUVRE Removal
- Page 433 and 434:
13. Position and secure front grill
- Page 437:
POWER WINDOW REGULATOR ASSEMBLY Rem
- Page 440 and 441:
" FIXED DOOR GLASS If replacement f
- Page 442 and 443:
j CONSOLE - Fig. 14 Removal 1. Disc
- Page 444 and 445:
J 6. Install either the left door p
- Page 446 and 447:
l» J CONTENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION
- Page 448 and 449:
L ^ Chassis R:02:01 DIMENSIONS )
- Page 450 and 451:
A B C D E F G H 1 J K L M N 0 P 255
- Page 452 and 453:
• • ' ~ T »