- Page 1 and 2:
Christine Joyce Jenkin SUPPORTING T
- Page 3 and 4:
3.4 Ethics ........................
- Page 5 and 6:
Appendix C: Comparisons of Early Ch
- Page 7 and 8:
Attestation of Authorship I hereby
- Page 9 and 10:
It was extremely providential that
- Page 11 and 12:
Abstract Te Whāriki, the national
- Page 13 and 14:
Prologue This thesis is the story o
- Page 15 and 16:
ead in my room. The freedom to be o
- Page 17 and 18:
were spoken by some families in the
- Page 19 and 20:
I was drawn towards those methodolo
- Page 21 and 22:
educational journey, enrolling in a
- Page 23 and 24: means that centres which are parent
- Page 25 and 26: 1.1 Overview Chapter One: Backgroun
- Page 27 and 28: (all the time). It was from these b
- Page 29 and 30: lend of the positive workshop dimen
- Page 31 and 32: 3. Reality is created in the moment
- Page 33 and 34: preparing children for life and Wha
- Page 35 and 36: For early childhood teachers in Aot
- Page 37 and 38: However, in order to understand Te
- Page 39 and 40: karakia and waiata. In 1989 the Nat
- Page 41 and 42: constructing the curriculum were de
- Page 43 and 44: contributions to decision making”
- Page 45 and 46: Principle Three - Whānau Tangata F
- Page 47 and 48: traditional rituals that are still
- Page 49 and 50: Action development enabled Tiriti-b
- Page 51 and 52: contribution of this thesis are rev
- Page 53 and 54: language skills and growing cultura
- Page 55 and 56: opposed to the notion of bicultural
- Page 57 and 58: Secondly, as previous research (Het
- Page 59 and 60: iculturalism. It was found that thi
- Page 61 and 62: te reo Māori. The Western Canadian
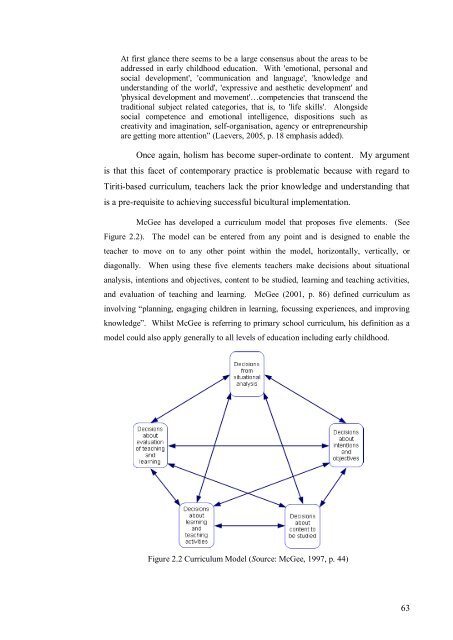
- Page 63 and 64: about Tiriti-based curriculum and t
- Page 65 and 66: I would argue, therefore, that this
- Page 67 and 68: directed by Margaret Carr and Wendy
- Page 69 and 70: implement Te Whāriki (May, 2001; N
- Page 71 and 72: effective practices, additionally,
- Page 73: was anxious to avoid both the prepa
- Page 77 and 78: 2.3.2 Philosophy From the start it
- Page 79 and 80: The implementation of Te Whāriki e
- Page 81 and 82: place to develop an early childhood
- Page 83 and 84: particularly relevant for Tiriti-ba
- Page 85 and 86: which had also been examined from a
- Page 87 and 88: e learnt like a curriculum subject
- Page 89 and 90: However, what is occurring in early
- Page 91 and 92: Inuktitut language. Thus, the curri
- Page 93 and 94: welcoming process in building those
- Page 95 and 96: this discussion is “how come you
- Page 97 and 98: ecently, Colbung, Glover, Rau and R
- Page 99 and 100: As already noted, a mixture of meth
- Page 101 and 102: this project my way of thinking was
- Page 103 and 104: early childhood setting. In particu
- Page 105 and 106: these are discussed in Chapter Four
- Page 107 and 108: with the research, either directly
- Page 109 and 110: The first one I read was by Madelin
- Page 111 and 112: do good research is to solve real p
- Page 113 and 114: The issues for these teachers, whic
- Page 115 and 116: The third stage encompasses the des
- Page 117 and 118: esearch cycles, both as method and
- Page 119 and 120: explained why I changed methodology
- Page 121 and 122: Table 3.3 summarises, how ethical p
- Page 123 and 124: opportunity to read reports and dis
- Page 125 and 126:
ecause the fieldwork needs to be th
- Page 127 and 128:
Despite my concerns about possible
- Page 129 and 130:
Study One, which I considered to be
- Page 131 and 132:
implemented within early childhood
- Page 133 and 134:
However, once I had started the dat
- Page 135 and 136:
confidential and therefore, as in C
- Page 137 and 138:
even more importantly research proc
- Page 139 and 140:
likely be at a different place on t
- Page 141 and 142:
discernable. However, as can been s
- Page 143 and 144:
approached a local centre that had
- Page 145 and 146:
(Oakley, 2000). Further, I assert t
- Page 147 and 148:
they haven‟t thought about the is
- Page 149 and 150:
The number of questionnaires distri
- Page 151 and 152:
curriculum in early childhood centr
- Page 153 and 154:
and challenges as they did this - t
- Page 155 and 156:
and appreciative inquiry was tape r
- Page 157 and 158:
4.3.2.4 Interviews During the analy
- Page 159 and 160:
clear to me they would use differen
- Page 161 and 162:
4.4.2 Critical Conversations One of
- Page 163 and 164:
passionate writing” (Ellis & Boch
- Page 165 and 166:
4.4.6 Data Analysis Extracting mean
- Page 167 and 168:
Chapter Five: Findings from Within
- Page 169 and 170:
Prior to the research, staff had pa
- Page 171 and 172:
child-initiated. There was, however
- Page 173 and 174:
Although being reliant on Māori te
- Page 175 and 176:
Nevertheless, as I discussed in cha
- Page 177 and 178:
where she had participated in bicul
- Page 179 and 180:
5.3.1 Whanaungatanga The teachers i
- Page 181 and 182:
kindergarten fathers responded to t
- Page 183 and 184:
5.4 Case Study Three Case Study Thr
- Page 185 and 186:
I learnt a lot of Māori - like how
- Page 187 and 188:
to incorporate tikanga they had ide
- Page 189 and 190:
Similarly, Shani reflected on how p
- Page 191 and 192:
as Peggy feeling unsupported in thi
- Page 193 and 194:
Well, we made Māori bread the othe
- Page 195 and 196:
Chris J: I thought there was a lot
- Page 197 and 198:
the extent to which the programme w
- Page 199 and 200:
6.2 Information about Questionnaire
- Page 201 and 202:
incorporated some idea of partnersh
- Page 203 and 204:
eing desirable, understanding what
- Page 205 and 206:
6.4.1 Team or Whole-of-centre Appro
- Page 207 and 208:
To summarise across the three cases
- Page 209 and 210:
Support from someone knowledgeable
- Page 211 and 212:
their own whāriki and that this is
- Page 213 and 214:
feature of the ideal bicultural cur
- Page 215 and 216:
What also encouraged teachers to co
- Page 217 and 218:
me, wash your hands, and come here.
- Page 219 and 220:
Brodie saw how her initial attempts
- Page 221 and 222:
enough in te reo Māori to offer th
- Page 223 and 224:
Bring Māori people into the centre
- Page 225 and 226:
The following week Alison recorded
- Page 227 and 228:
However, for Case Study One teacher
- Page 229 and 230:
The emerging point is that sustaini
- Page 231 and 232:
did not understand te reo Māori me
- Page 233 and 234:
informal discussion about implement
- Page 235 and 236:
Not everyone feels confident to del
- Page 237 and 238:
We should recognise the important p
- Page 239 and 240:
only another of many cultures in Ao
- Page 241 and 242:
Chapter Seven: Discussion and Concl
- Page 243 and 244:
The second dimension for Tiriti-bas
- Page 245 and 246:
ōna tikanga. This thesis has shown
- Page 247 and 248:
that was also discussed in chapter
- Page 249 and 250:
The success of the three distinct c
- Page 251 and 252:
Thus, action development is what I
- Page 253 and 254:
noted Te Whāriki lacks specific co
- Page 255 and 256:
This continuum depicts movement fro
- Page 257 and 258:
fearfulness about making mistakes a
- Page 259 and 260:
and Case Study Three respectively w
- Page 261 and 262:
which is why it is in the central p
- Page 263 and 264:
connecting with indigenous people a
- Page 265 and 266:
and understanding. They reasoned th
- Page 267 and 268:
education and care centres, the onu
- Page 269 and 270:
Similarly to early childhood centre
- Page 271 and 272:
Teachers want to include Tiriti-bas
- Page 273 and 274:
Committee. Finding a balance in wor
- Page 275 and 276:
7.9 The Last Word Early childhood t
- Page 277 and 278:
Piritahi Dining room Piupiu Flax sk
- Page 279 and 280:
Te Tiriti o Waitangi/ Treaty of Wai
- Page 281 and 282:
7. Please put a tick in the box tha
- Page 283 and 284:
Appendix B: Te Tiriti o Waitangi (M
- Page 285 and 286:
Mana Atua Well-being The health and
- Page 287 and 288:
Te Whāriki Goals Reflective Questi
- Page 289 and 290:
Appendix D: Ethics Approval 277
- Page 291 and 292:
279
- Page 293 and 294:
correct te reo Māori me ōna tikan
- Page 295 and 296:
Benton, M. (1979). Māori English:
- Page 297 and 298:
Cardno, C. (2003). Action research:
- Page 299 and 300:
Crotty, M. (1998). Introduction: Th
- Page 301 and 302:
Education Review Office (1998). The
- Page 303 and 304:
Hansen, J. (2005). On developing an
- Page 305 and 306:
Kane, R. (2005). Initial teacher ed
- Page 307 and 308:
Revised and expanded from case stud
- Page 309 and 310:
Moon, P. (2002). The path to the Tr
- Page 311 and 312:
O'Laoire, M. (1996). Developing lan
- Page 313 and 314:
Ritchie, J. (2002b). "It's becoming
- Page 315 and 316:
Smith, L. T. (1999). Decolonizing m
- Page 317 and 318:
Walker, R. (2008). The philosophy o