MMC User Manual - AMS Neve
MMC User Manual - AMS Neve
MMC User Manual - AMS Neve
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Automation<br />
Controls that can be Automated<br />
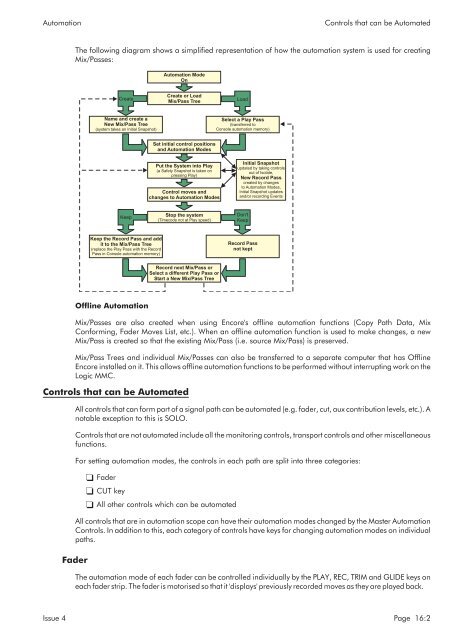
The following diagram shows a simplified representation of how the automation system is used for creating<br />
Mix/Passes:<br />
Automation Mode<br />
On<br />
Create<br />
Create or Load<br />
Mix/Pass Tree<br />
Load<br />
Name and create a<br />
New Mix/Pass Tree<br />
(system takes an Initial Snapshot)<br />
Select a Play Pass<br />
(transferred to<br />
Console automation memory)<br />
Set initial control positions<br />
and Automation Modes<br />
Put the System into Play<br />
(a Safety Snapshot is taken on<br />
pressing Play)<br />
Control moves and<br />
changes to Automation Modes<br />
Initial Snapshot<br />
updated by taking controls<br />
out of Isolate,<br />
New Record Pass<br />
created by changes<br />
to Automation Modes,<br />
Initial Snapshot updates<br />
and/or recording Events<br />
Keep<br />
Stop the system<br />
(Timecode not at Play speed)<br />
Don't<br />
Keep<br />
Keep the Record Pass and add<br />
it to the Mix/Pass Tree<br />
(replace the Play Pass with the Record<br />
Pass in Console automation memory)<br />
Record Pass<br />
not kept<br />
Record next Mix/Pass or<br />
Select a different Play Pass or<br />
Start a New Mix/Pass Tree<br />
Offline Automation<br />
Mix/Passes are also created when using Encore's offline automation functions (Copy Path Data, Mix<br />
Conforming, Fader Moves List, etc.). When an offline automation function is used to make changes, a new<br />
Mix/Pass is created so that the existing Mix/Pass (i.e. source Mix/Pass) is preserved.<br />
Mix/Pass Trees and individual Mix/Passes can also be transferred to a separate computer that has Offline<br />
Encore installed on it. This allows offline automation functions to be performed without interrupting work on the<br />
Logic <strong>MMC</strong>.<br />
Controls that can be Automated<br />
All controls that can form part of a signal path can be automated (e.g. fader, cut, aux contribution levels, etc.). A<br />
notable exception to this is SOLO.<br />
Controls that are not automated include all the monitoring controls, transport controls and other miscellaneous<br />
functions.<br />
For setting automation modes, the controls in each path are split into three categories:<br />
Fader<br />
CUT key<br />
All other controls which can be automated<br />
All controls that are in automation scope can have their automation modes changed by the Master Automation<br />
Controls. In addition to this, each category of controls have keys for changing automation modes on individual<br />
paths.<br />
Fader<br />
The automation mode of each fader can be controlled individually by the PLAY, REC, TRIM and GLIDE keys on<br />
each fader strip. The fader is motorised so that it 'displays' previously recorded moves as they are played back.<br />
Issue 4 Page 16:2