Pan-Pacific Conference XXXIV. Designing New Business Models in Developing Economies
This publication represents the Proceedings of the 34th Annual Pan-Pacific Conference being held in Lima, Peru May 29-31, 2017. The Pan-Pacific Conference has served as an important forum for the exchange of ideas and information for promoting understanding and cooperation among the peoples of the world since 1984. Last year, we had a memorable conference in Miri, Malaysia, in cooperation with Curtin University Sarawak, under the theme of “Building a Smart Society through Innovation and Co-creation.” Professor Pauline Ho served as Chair of the Local Organizing Committee, with strong leadership support of Pro Vice-Chancellor Professor Jim Mienczakowski and Dean Jonathan Winterton.
This publication represents the Proceedings of the 34th Annual Pan-Pacific Conference being held in Lima, Peru May 29-31, 2017. The Pan-Pacific Conference has served as an important forum for the exchange of ideas and information for promoting understanding and cooperation among the peoples of the world since 1984. Last year, we had a memorable conference in Miri, Malaysia, in cooperation with Curtin University Sarawak, under the theme of “Building a Smart Society through Innovation and Co-creation.” Professor Pauline Ho served as Chair of the Local Organizing Committee, with strong leadership support of Pro Vice-Chancellor Professor Jim Mienczakowski and Dean Jonathan Winterton.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
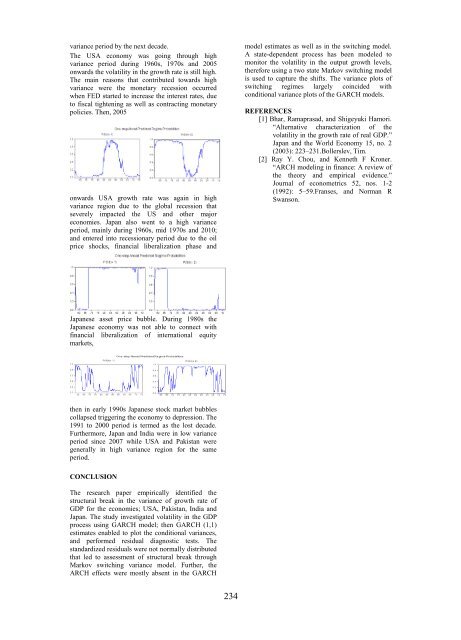
variance period by the next decade.<br />
The USA economy was go<strong>in</strong>g through high<br />
variance period dur<strong>in</strong>g 1960s, 1970s and 2005<br />
onwards the volatility <strong>in</strong> the growth rate is still high.<br />
The ma<strong>in</strong> reasons that contributed towards high<br />
variance were the monetary recession occurred<br />
when FED started to <strong>in</strong>crease the <strong>in</strong>terest rates, due<br />
to fiscal tighten<strong>in</strong>g as well as contract<strong>in</strong>g monetary<br />
policies. Then, 2005<br />
onwards USA growth rate was aga<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> high<br />
variance region due to the global recession that<br />
severely impacted the US and other major<br />
economies. Japan also went to a high variance<br />
period, ma<strong>in</strong>ly dur<strong>in</strong>g 1960s, mid 1970s and 2010;<br />
and entered <strong>in</strong>to recessionary period due to the oil<br />
price shocks, f<strong>in</strong>ancial liberalization phase and<br />
model estimates as well as <strong>in</strong> the switch<strong>in</strong>g model.<br />
A state-dependent process has been modeled to<br />
monitor the volatility <strong>in</strong> the output growth levels,<br />
therefore us<strong>in</strong>g a two state Markov switch<strong>in</strong>g model<br />
is used to capture the shifts. The variance plots of<br />
switch<strong>in</strong>g regimes largely co<strong>in</strong>cided with<br />
conditional variance plots of the GARCH models.<br />
REFERENCES<br />
[1] Bhar, Ramaprasad, and Shigeyuki Hamori.<br />
“Alternative characterization of the<br />
volatility <strong>in</strong> the growth rate of real GDP.”<br />
Japan and the World Economy 15, no. 2<br />
(2003): 223–231.Bollerslev, Tim.<br />
[2] Ray Y. Chou, and Kenneth F Kroner.<br />
“ARCH model<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> f<strong>in</strong>ance: A review of<br />
the theory and empirical evidence.”<br />
Journal of econometrics 52, nos. 1-2<br />
(1992): 5–59.Franses, and Norman R<br />
Swanson.<br />
Japanese asset price bubble. Dur<strong>in</strong>g 1980s the<br />
Japanese economy was not able to connect with<br />
f<strong>in</strong>ancial liberalization of <strong>in</strong>ternational equity<br />
markets,<br />
then <strong>in</strong> early 1990s Japanese stock market bubbles<br />
collapsed trigger<strong>in</strong>g the economy to depression. The<br />
1991 to 2000 period is termed as the lost decade.<br />
Furthermore, Japan and India were <strong>in</strong> low variance<br />
period s<strong>in</strong>ce 2007 while USA and Pakistan were<br />
generally <strong>in</strong> high variance region for the same<br />
period.<br />
CONCLUSION<br />
The research paper empirically identified the<br />
structural break <strong>in</strong> the variance of growth rate of<br />
GDP for the economies; USA, Pakistan, India and<br />
Japan. The study <strong>in</strong>vestigated volatility <strong>in</strong> the GDP<br />
process us<strong>in</strong>g GARCH model; then GARCH (1,1)<br />
estimates enabled to plot the conditional variances,<br />
and performed residual diagnostic tests. The<br />
standardized residuals were not normally distributed<br />
that led to assessment of structural break through<br />
Markov switch<strong>in</strong>g variance model. Further, the<br />
ARCH effects were mostly absent <strong>in</strong> the GARCH<br />
234