Zeitschrift für Rheumatologie – Supplement 1 - Deutsche ...
Zeitschrift für Rheumatologie – Supplement 1 - Deutsche ...
Zeitschrift für Rheumatologie – Supplement 1 - Deutsche ...
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
S6<br />
Abstracts<br />
Th e requirement of infl ammatory back pain for SpA to be diagnosed<br />
limits the sensitivity of the diagnostic algorithm.<br />
1. Rudwaleit, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2004; 63:535-43<br />
2. Rudwaleit, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52:1000-8<br />
FV1-6<br />
Validation of the spinal pain score (spips) as an instrument<br />
performed by the rheumatologist to assess disease activity in ankylosing<br />
spondylitis<br />
Song IHS., Haibel HH., Hilgert EH., Sieper JS., Rudwaleit MR.<br />
Med. Klinik I, <strong>Rheumatologie</strong>, Charité Campus Benjamin-Franklin<br />
Background: Th e objective assessment of disease activity in ankylosing<br />
spondylitis (AS) through the rheumatologist limited to patient based<br />
instruments (BASDAI, patient’s global).<br />
Objective: Evaluation of a spinal pain score (SpiPS) performed by the<br />
rheumatologist according to the OMERACT fi lters.<br />
Methods: Th e spinal pain score (range 0-16) was assessed according to<br />
the aspects of the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trail<br />
(OMERACT) fi lters (1) reproducibility, 2) truth, 3) discrimination and<br />
4) feasibility) in 4 diff erent AS populations (three clinical trial populations<br />
(n= 578) and an out-patient population (n= 154)).<br />
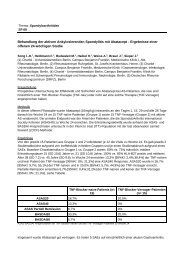
Results: Ad 1) Reproducibility: Intra-observer variability (assessed in 31<br />
AS patients) and inter-observer variability (assessed in 33 AS patients)<br />
showed a good correlation (Pearson correlation coeffi cient of 0.930 and<br />
0.789 respectively, p< 0.001). Th ere was a good intraclass correlation<br />
(0.93 and 0.84 respectively). Ad 2) Truth: Th e SpiPS showed a moderate<br />
to good correlation with the BASDAI: Pearson correlation coeffi cients<br />
were between 0.40 and 0.737 in the diff erent AS populations (p < 0.01).<br />
Th ere was no correlation between the SpiPS and C-reactive protein and<br />
ESR. Ad 3) Discrimination: SpiPS was sensitive to change: there was a<br />
signifi cant decrease of the SpiPS by 65.3% while the BASDAI improved<br />
signifi cantly by 53.8% aft er 12 weeks of treatment with TNF alpha inhibitors<br />
(n= 101). In one NSAID trial (n= 458) the SpiPS improved by<br />
37.3% while the BASDAI showed a signifi cant improvement by 26.5%.<br />
Ad 4) Feasibility: assessment of the SpiPS took on averaged 3-5 minutes<br />
and was easy to perform.<br />
Conclusion: Th e spinal pain score fulfi ls all aspects of the OMERACT<br />
fi lter with respect to reproducibility, truth, discrimination and feasibility.<br />
Th e SpiPS being performed by the rheumatologist may serve as an<br />
additional tool to assess the activity of back pain in AS. Th e application<br />
of the SpiPS in trials and daily practice is worth further investigation.<br />
FV1-7<br />
Results of an open label pilot study with 20 mg Methotrexate parenterally<br />
for the Treatment of Active Ankylosing Spondylitis<br />
Haibel H. 1 , Brandt HC. 1 , Song IH. 1 , Brandt A. 2 , Listing J. 3 , Rudwaleit M. 1 ,<br />
Sieper J. 1<br />
1 <strong>Rheumatologie</strong>, Charité CBF, 2 Medac GmbH, 3 Epidemiologie, <strong>Deutsche</strong>s<br />
Rheumaforschungszentrum<br />
Objective: Methotrexate is the most frequently used disease modifying<br />
antirheumatic drug (DMARD) in rheumatoid arthritis. However its<br />
effi cacy in the therapy of the axial manifestations in active ankylosing<br />
spondylitis (AS) remains unclear. Th e aim of the study was to examine<br />
the potential therapeutic eff ect of methotrexate 20 mg given weekly as<br />
subcutaneous (s.c.) injections in active ankylosing spondylitis (AS).<br />
Patients and Methods: Subcutaneous methotrexate 15 mg per week<br />
monotherapy was administered every week for 4 weeks followed by<br />
subcoutaneous methotrexate 20 mg per week for further 12 weeks in<br />
20 patients (14 males, 6 females; mean age 40 years, range 24<strong>–</strong>59; mean<br />
disease duration 14 years, range 1<strong>–</strong>39; 85% HLA-B27 positive) with active<br />
AS (mean Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Activity Index or BASDAI<br />
of 5.6, range 4<strong>–</strong>9.3). All patients suff ered from spinal pain and 7 patients<br />
also had peripheral arthritis. Clinical outcome assessments inclu-<br />
| <strong>Zeitschrift</strong> <strong>für</strong> <strong>Rheumatologie</strong> · <strong>Supplement</strong> 1 · 2006<br />
ded Disease Activity (BASDAI), patient’s, and physician’s global assessments<br />
(NRS), function (BASFI), spinal mobility (BASMI), peripheral<br />
joint assessment, quality of life (SF-36), and C-reactive protein (CRP).<br />
Th e primary endpoint was a ≥20% response according to the Assessment<br />
in AS (ASAS) working group improvement criteria at Week 16.<br />
Results: Using an intention-to-treat analysis, ASAS 20 was achieved in<br />
only 25% of patients. An ASAS 40 response was achieved in 10% of patients<br />
and nobody reached an ASAS 70 response or the ASAS criteria for<br />
partial remission For the mean BASDAI there was no change between<br />
baseline and week 16 (baseline 5.6 versus week 16 5.6). Th ere was no<br />
improvement in any of the clinical parameters or the CRP, except a<br />
small but non-signifi cant decrease in the number of swollen joints in<br />
the 7 patients suff ering from peripheral arthritis (number of swollen<br />
joints at baseline 4.7 versus 1.2 at week 16).<br />
Conclusions: In this open study, methotrexate did not show any benefi t<br />
for the axial symptoms in patients with active AS beyond an expected<br />
placebo-response. Th us, despite current practice, methotrexate should<br />
not be used for this indication.<br />
FV2 Abstract Session II: Rheumatoid Arthritis<br />
FV2-1<br />
Behandlung von Kindern mit juveniler rheumatoider Arthritis (JRA)<br />
mit Adalimumab <strong>–</strong> Studienergebnisse nach 48 Wochen<br />
Horneff G. 1 , Ruperto N. 2 , Martini A. 3 , Carcereri R. 4<br />
1 Department of Paediactrics, Asklepios Clinic Sankt Augustin, Germany,<br />
2 Pediatrics II, PRINTO-IRCCS G Gaslini, Genova, Italy, 3 PRINTO-IRCCS G<br />
Gaslini, Genova, Italy, 4 Immunosciences, Abbott GmbH and Co. KG, Ludwigshafen,<br />
Germany<br />
Hintergrund: Vorläufi ge Ergebnisse einer off enen Studie an 171 JRA-<br />
Patienten zeigten, dass eine 16-wöchige Th erapie mit Adalimumab<br />
(ADA) zu einer Verbesserung der klinischen Zeichen und Symptome<br />
führte. Mehr als 50% der Patienten erreichten ein Ped-ACR70-Ansprechen.<br />
Ziele: Mit Hilfe dieser Fortsetzungsstudie sollte die Sicherheit und<br />
Wirksamkeit der ADA-Behandlung bei Patienten mit JRA untersucht<br />
werden, bei denen in der off enen Pilotstudie ein Th erapieansprechen<br />
erzielt werden konnte.<br />
Methoden: Patienten mit einem Ped-ACR30-Ansprechen erhielten<br />
in der nachfolgenden doppelblinden Studienphase über 32 Wochen<br />
entweder 24 mg Adalimumab/m2 KOF s.c. alle 14 Tage oder Placebo<br />
(PBO). Primärer Endpunkt war ein Wiederauffl ammen der Symptomatik<br />
defi niert als (1) >30%ige Verschlechterung im Vergleich zum<br />
Ausgangswert in ≥ 3 der 6 Hauptkriterien des Ped-ACR, (2) nicht weniger<br />
als 2 betroff ene Gelenke und (3) >30%ige Verbesserung in nicht<br />
mehr als 1 der 6 Kriterien.<br />
Ergebnisse: Am Ende der 16-wöchigen off enen Pilotstudie erreichten<br />
83% der Patienten ACR30, 74% ACR50 und 52% ACR70. 133 Patienten<br />
(77% Mädchen, mittleres Alter 11,2 Jahre) wurden in die doppelblinde<br />
Studie überführt, 65% erhielten eine MTX-Begleittherapie. Unter<br />
ADA zeigten signifi kant weniger Patienten ein Wiederauffl ammen<br />
der Symptomatik als unter Placebo, sowohl ohne(43,3% vs. 71,4%,<br />
p= 0,031) als auch mit MTX-Begleittherapie (36,8% vs. 64,9%, p=<br />
0,015). Das ACR30/50/70-Ansprechen war in der 48. Woche, d.h. am<br />
Ende der doppelblinden Studienphase, bei den ADA-Patienten signifi -<br />
kant höher (60%/59%/56%) als bei den PBO-Patienten (35%/35%/28%),<br />
(p