- Seite 1 und 2:
I Sensoren & Aktoren Vorlesung im S
- Seite 3 und 4:
III MST-Vertiefungslabor An alle Mi
- Seite 5 und 6:
1 Einleitung 1.1 Sensorik Die Senso
- Seite 7 und 8:
1.1.2 Definitionen nach DIN 13191 M
- Seite 9 und 10:
1.1.4 Übersicht über einige ausge
- Seite 11 und 12:
1.1.5.1 Einschub: Erläuterung vers
- Seite 13 und 14:
1.3 Kombination aus Sensorik und Ak
- Seite 15 und 16:
2 Bionik 2.1 Definition - Was ist B
- Seite 17 und 18:
Mögliche Messanordnungen: Bestimmu
- Seite 19 und 20:
Foto: Rumpler-Tropfenwagen, Deutsch
- Seite 21 und 22:
Nelumbo nucifera, die Heilige Lotus
- Seite 23 und 24:
Wirkung einer genoppten hydrophobe
- Seite 25 und 26:
3 Sensoren und Messwertverarbeitung
- Seite 27 und 28:
Schematische Darstellung eines Neur
- Seite 29 und 30:
Reizstärkekodierung über digitale
- Seite 31 und 32:
3.2 Die Rezeptoren der Haut Aufbau
- Seite 33 und 34:
3.2 (Fortsetzung) 3.2.2 Temperaturr
- Seite 35 und 36:
3) "visual-enhanced" Infrarotneuron
- Seite 37 und 38:
3.3.2 Photorezeptoren A. Stäbchen
- Seite 39 und 40:
Normierte Absorptionskurven der men
- Seite 41 und 42:
3.4 Akustische Sensoren - Gehör 3.
- Seite 43 und 44:
3.4.2 Aufbau des Ohres Labyrinth =
- Seite 45 und 46:
3.5 Chemische Sensoren - Geruchssin
- Seite 47 und 48:
Kodierung der chemikalischen Zusamm
- Seite 49 und 50:
Die Entstehung eines topologischen
- Seite 51 und 52:
3.8 Zusammenfassung zur Sensorik de
- Seite 53 und 54:
4.3 Struktur einer Messung Prinzip:
- Seite 55 und 56:
4.4.1 Static characteristics Calibr
- Seite 58 und 59:
Quelle: Lehrstuhl für Feinwerktech
- Seite 60 und 61:
5 Thermodynamische Grundlagen der S
- Seite 62 und 63:
in einem abgeschlossenen System (d.
- Seite 64 und 65:
5.7.1 Richtungen von Reaktionsablä
- Seite 66 und 67:
Kräfte, die spezifische Entropie S
- Seite 68 und 69:
Spektralpyrometer in Abhängigkeit
- Seite 70 und 71:
Silizium, rein Silizium, n-leitend
- Seite 72 und 73:
Verschaltung von Widerständen in e
- Seite 74 und 75:
Moderne miniaturisierte Bautypen in
- Seite 76 und 77:
Quelle: www.sensedu.com Measuring p
- Seite 78 und 79:
Obwohl der thermoelektrische Effekt
- Seite 80 und 81:
1. Ein Punkt als Spannung = Null de
- Seite 82 und 83: 79 Um eine hohe Kälteleistung zu e
- Seite 84 und 85: Ungewollte Thermospannungen an Kont
- Seite 86 und 87: Bei Temperaturänderung ändert sic
- Seite 88 und 89: Aus Symmetriegründen muss es einen
- Seite 90 und 91: The spontaneous polarization will b
- Seite 92 und 93: Umgebungstemperatur anspricht. Ein
- Seite 94 und 95: Bei den verwendeten thermometrische
- Seite 96 und 97: 90 a Stabausdehnungsthermometer 1 R
- Seite 98 und 99: Messfeder zur Temperaturanzeige üb
- Seite 100 und 101: Durch eine entsprechende Schnittric
- Seite 102 und 103: mit T absolute Temperatur, To belie
- Seite 104 und 105: Oxidationserscheinungen und Staubab
- Seite 106 und 107: 6.5.1.2 Bauformen Schaltung Wärmev
- Seite 108 und 109: Leitungsdruck Reaktionszeit Bauform
- Seite 110 und 111: 6.6 Vergleich der Eigenschaften der
- Seite 112 und 113: output. • Linearity: Platinum and
- Seite 114 und 115: 7 Längen- und Winkelmessung 7.1 Ei
- Seite 116 und 117: mit R 2 U2 = UH R 0 x R = R 2 0 l0
- Seite 118 und 119: Zylinderspule mit ferromagnetischem
- Seite 120 und 121: 7.4.2.1 Typische Kenndaten (Tauch-
- Seite 122 und 123: 116 Neben dem Parallelplattenkonden
- Seite 124 und 125: 7.4.4 Zusammenfassung: Geometriemes
- Seite 126 und 127: Optischer inkrementaler Längengebe
- Seite 128 und 129: 7.5.1.1 Inkrementale Drehwinkel-Sen
- Seite 130 und 131: Das Inductosyn besteht aus einer Sk
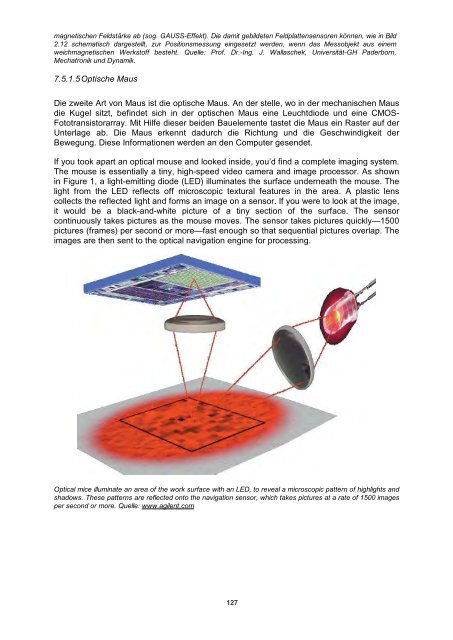
- Seite 134 und 135: The Navigation Engine identifies co
- Seite 136 und 137: Dual-, Gray- und BCD-Codelineal. Di
- Seite 138 und 139: 7.5.2.2 Beispiel für einen bildgeb
- Seite 140 und 141: 7.5.3 Weitere Positionsbestimmungss
- Seite 142 und 143: Die Intensitätsabnahme wird unter
- Seite 144 und 145: Impuls-Echo-Prinzip für eine Objek
- Seite 146 und 147: Anwendungen Mit Ultraschall-Präsen
- Seite 148 und 149: Bauformen Lautsprecher- und Mikroph
- Seite 150 und 151: Geschwindigkeit und Winkelgeschwind
- Seite 152 und 153: • Hysteresefreiheit Anwendungen
- Seite 154 und 155: the voltage output of this sensor i
- Seite 156 und 157: Messprinzip über Dehnmessstreifen
- Seite 158 und 159: DMS Beschleunigungssensor in Dicksc
- Seite 160 und 161: Accelerometer based on Si surface m
- Seite 162 und 163: Piezoelektrischer Effekt in lonenkr
- Seite 164 und 165: ε0 elektr. Feldkonstante, Qoberfl:
- Seite 166 und 167: Die Resonanzfrequenz wird häufig d
- Seite 168 und 169: Ausgangslast an SigOut: > 100 kΩ
- Seite 170 und 171: Massesensoren Einleitung Masse ist
- Seite 172 und 173: Sauerbrey-Gleichung für die Freque
- Seite 174 und 175: * Newton’sche Flüssigkeiten, in
- Seite 176 und 177: Three total units were required for
- Seite 178 und 179: Typische Drucksensoren für mbar bi
- Seite 180 und 181: sensitivity factor and the gauge fa
- Seite 182 und 183:
Glasfaser-Reflexions-Drucksensoren
- Seite 184 und 185:
Induktive Drucksensoren Drucksensor
- Seite 186 und 187:
Wärmeleitung - Vakuummeter Bereich
- Seite 188 und 189:
ITES - Kapazitiver Drucksensor in O
- Seite 190 und 191:
187
- Seite 192 und 193:
Quelle: Sensortechnik, S. 392 189
- Seite 194 und 195:
Lichttechnische Begriffe Helligkeit
- Seite 196 und 197:
Typische lichttechnische Zahlenwert
- Seite 198 und 199:
- Gassensoren Typischer Wirkungsgra
- Seite 200 und 201:
Eigenschaften: - Phototransistor (2
- Seite 202 und 203:
(Energienivaues im Ortsraum) sind i
- Seite 204 und 205:
E g E hν EL EV ED hν EA Der erste
- Seite 206 und 207:
Diffusionsspannung, so dass gilt: U
- Seite 208 und 209:
Die pin-Diode besteht aus einer bre
- Seite 210 und 211:
shifted by one location. After a de
- Seite 212 und 213:
Schieberegister die nächste Pixelz
- Seite 214 und 215:
Unterschiede zwischen CCD und APS-C
- Seite 216 und 217:
Beispiel Agilent CMOS Sensor für d
- Seite 218 und 219:
Am Rande Fleißige Tierchen - Spinn
- Seite 220 und 221:
Beispiel für eine substanzspezifis
- Seite 222 und 223:
YSZ: Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia. Qu
- Seite 224 und 225:
Tagushi CO-Gassensor: Resistive Sen
- Seite 226 und 227:
Die Vorteile von Feldeffekttransist
- Seite 228 und 229:
Wasserstoff-Pd-Gassensoren auf meta
- Seite 230 und 231:
The structure and operation princip
- Seite 232 und 233:
H + die Funktion der Ansteuerspannu
- Seite 234 und 235:
Kombination von Sensorik und Aktori
- Seite 236 und 237:
Zuordnung von Betätigungsenergien
- Seite 238 und 239:
Ausgewählte Einsatzmöglichkeiten
- Seite 240 und 241:
Der Drehratensensor misst die Drehb
- Seite 242 und 243:
Legt man an die Generatorspule eine
- Seite 244 und 245:
• Wechselstrom-Asynchronmotoren =
- Seite 246 und 247:
a) Innenliegender Trommelrotor, fre
- Seite 248 und 249:
Elektronisch kommmutierter (bürste
- Seite 250 und 251:
Wegen ihrer einfachen Konstruktion
- Seite 252 und 253:
folgenden Abbildungen skizziert. Zu
- Seite 254 und 255:
leistungsfähigen Motoren mit einem
- Seite 256 und 257:
Abgeformte Strukturen aus WC/Co-ges
- Seite 258 und 259:
Realisierung schneller Steuerstreck
- Seite 260 und 261:
Pneumatische Stellelemente, meist p
- Seite 262 und 263:
austenitische Chrom-Nickel-Stähle.
- Seite 264 und 265:
Verhalten einer Gedächtnislegierun
- Seite 266 und 267:
Rolling robot High jump: The rollin
- Seite 268 und 269:
elastbaren Ketten agglomerieren. Di
- Seite 270 und 271:
Magnetorheologische Flüssigkeiten
- Seite 272 und 273:
Möglicher mechanischer Aufbau eine
- Seite 274 und 275:
Bauformen. Quelle: http://wwwags.in
- Seite 276 und 277:
Auswahl einiger wichtiger Einsatzge
- Seite 278 und 279:
Silben stehen für Terbium und für
- Seite 280 und 281:
Quelle: http://wwwags.informatik.un
- Seite 282 und 283:
Beispiele für weitere leitfähige