Online version: PDF - DTIE
Online version: PDF - DTIE
Online version: PDF - DTIE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
UNIT 1: WHERE DO WE STAND? THE STATE OF THE GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT<br />
025<br />
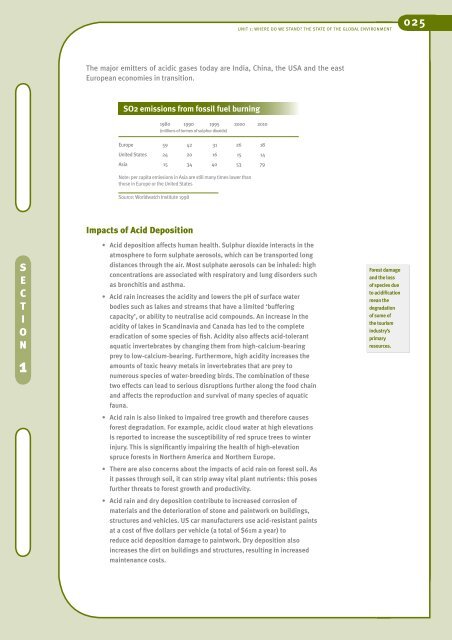
The major emitters of acidic gases today are India, China, the USA and the east<br />
European economies in transition.<br />
SO2 emissions from fossil fuel burning<br />
1980 1990 1995 2000 2010<br />
(millions of tonnes of sulphur dioxide)<br />
Europe 59 42 31 26 18<br />
United States 24 20 16 15 14<br />
Asia 15 34 40 53 79<br />
Note: per capita emissions in Asia are still many times lower than<br />
those in Europe or the United States<br />
Source: Worldwatch Institute 1998<br />
S<br />
E<br />
C<br />
T<br />
I<br />
O<br />
N<br />
1<br />
Impacts of Acid Deposition<br />
• Acid deposition affects human health. Sulphur dioxide interacts in the<br />
atmosphere to form sulphate aerosols, which can be transported long<br />
distances through the air. Most sulphate aerosols can be inhaled: high<br />
concentrations are associated with respiratory and lung disorders such<br />
as bronchitis and asthma.<br />
• Acid rain increases the acidity and lowers the pH of surface water<br />
bodies such as lakes and streams that have a limited ‘buffering<br />
capacity’, or ability to neutralise acid compounds. An increase in the<br />
acidity of lakes in Scandinavia and Canada has led to the complete<br />
eradication of some species of fish. Acidity also affects acid-tolerant<br />
aquatic invertebrates by changing them from high-calcium-bearing<br />
prey to low-calcium-bearing. Furthermore, high acidity increases the<br />
amounts of toxic heavy metals in invertebrates that are prey to<br />
numerous species of water-breeding birds. The combination of these<br />
two effects can lead to serious disruptions further along the food chain<br />
and affects the reproduction and survival of many species of aquatic<br />
fauna.<br />
• Acid rain is also linked to impaired tree growth and therefore causes<br />
forest degradation. For example, acidic cloud water at high elevations<br />
is reported to increase the susceptibility of red spruce trees to winter<br />
injury. This is significantly impairing the health of high-elevation<br />
spruce forests in Northern America and Northern Europe.<br />
• There are also concerns about the impacts of acid rain on forest soil. As<br />
it passes through soil, it can strip away vital plant nutrients: this poses<br />
further threats to forest growth and productivity.<br />
• Acid rain and dry deposition contribute to increased corrosion of<br />
materials and the deterioration of stone and paintwork on buildings,<br />
structures and vehicles. US car manufacturers use acid-resistant paints<br />
at a cost of five dollars per vehicle (a total of $61m a year) to<br />
reduce acid deposition damage to paintwork. Dry deposition also<br />
increases the dirt on buildings and structures, resulting in increased<br />
maintenance costs.<br />
Forest damage<br />
and the loss<br />
of species due<br />
to acidification<br />
mean the<br />
degradation<br />
of some of<br />
the tourism<br />
industry’s<br />
primary<br />
resources.