motivational analysis of organizations
motivational analysis of organizations
motivational analysis of organizations
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Other Variables<br />
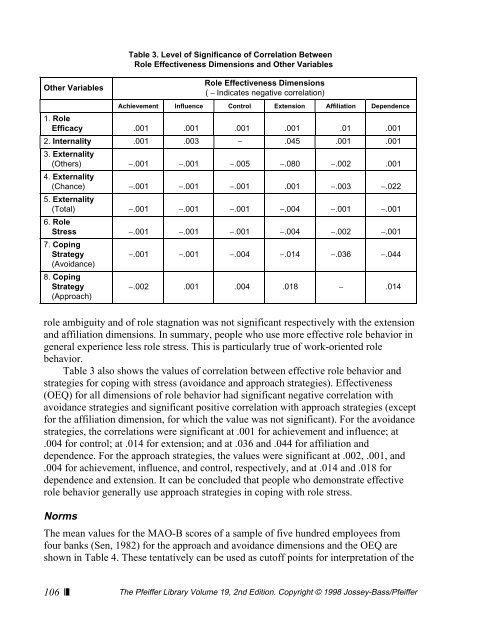
role ambiguity and <strong>of</strong> role stagnation was not significant respectively with the extension<br />
and affiliation dimensions. In summary, people who use more effective role behavior in<br />
general experience less role stress. This is particularly true <strong>of</strong> work-oriented role<br />
behavior.<br />
Table 3 also shows the values <strong>of</strong> correlation between effective role behavior and<br />
strategies for coping with stress (avoidance and approach strategies). Effectiveness<br />
(OEQ) for all dimensions <strong>of</strong> role behavior had significant negative correlation with<br />
avoidance strategies and significant positive correlation with approach strategies (except<br />
for the affiliation dimension, for which the value was not significant). For the avoidance<br />
strategies, the correlations were significant at .001 for achievement and influence; at<br />
.004 for control; at .014 for extension; and at .036 and .044 for affiliation and<br />
dependence. For the approach strategies, the values were significant at .002, .001, and<br />
.004 for achievement, influence, and control, respectively, and at .014 and .018 for<br />
dependence and extension. It can be concluded that people who demonstrate effective<br />
role behavior generally use approach strategies in coping with role stress.<br />
Norms<br />
The mean values for the MAO-B scores <strong>of</strong> a sample <strong>of</strong> five hundred employees from<br />
four banks (Sen, 1982) for the approach and avoidance dimensions and the OEQ are<br />
shown in Table 4. These tentatively can be used as cut<strong>of</strong>f points for interpretation <strong>of</strong> the<br />
106 ❘❚<br />
Table 3. Level <strong>of</strong> Significance <strong>of</strong> Correlation Between<br />
Role Effectiveness Dimensions and Other Variables<br />
Role Effectiveness Dimensions<br />
( − Indicates negative correlation)<br />
Achievement Influence Control Extension Affiliation Dependence<br />
1. Role<br />
Efficacy .001 .001 .001 .001 .01 .001<br />
2. Internality .001 .003 − .045 .001 .001<br />
3. Externality<br />
(Others) −.001 −.001 −.005 −.080 −.002 .001<br />
4. Externality<br />
(Chance) −.001 −.001 −.001 .001 −.003 −.022<br />
5. Externality<br />
(Total) −.001 −.001 −.001 −.004 −.001 −.001<br />
6. Role<br />
Stress −.001 −.001 −.001 −.004 −.002 −.001<br />
7. Coping<br />
Strategy<br />
(Avoidance)<br />
8. Coping<br />
Strategy<br />
(Approach)<br />
−.001 −.001 −.004 −.014 −.036 −.044<br />
−.002 .001 .004 .018 − .014<br />
The Pfeiffer Library Volume 19, 2nd Edition. Copyright © 1998 Jossey-Bass/Pfeiffer