Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Metal and Ceramic ...
Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Metal and Ceramic ...
Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Metal and Ceramic ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
component shape [53–55, 61–63]. A stable colloid with well dispersed particles<br />
produces a dense <strong>and</strong> homogeneous powder. The interparticle colloidal forces can be<br />
manipulated by adjusting the pH or by adding a dispersant. The stability of aqueous<br />
colloidal suspension can be controlled by creating like charges of sufficient magnitude<br />
on the surfaces of ceramic particles, known as electrostatic stabilization.<br />
Alternatively, ionic polymer dispersant is added to the suspension such that<br />
polymeric chains adsorb on ceramic particle surfaces creating steric repulsion.<br />
Electrosteric stabilization that combines both ionic <strong>and</strong> polymer dispersant mechanisms<br />
is more effective for obtaining a well-dispersed suspension [64, 65].<br />
As CNTs <strong>and</strong> alumina particles show extensive agglomeration, they must disperse<br />
independently in organic suspensions. When two sols of opposite sign are mixed,<br />
mutual coagulation takes place. Under a properly selected pH range, alumina<br />
particles adsorb onto CNT surfaces through electrostatic interaction. Recently, Sun<br />
et al. fabricated alumina-CNTnanocomposites by means of colloidal processing [61].<br />
<strong>Carbon</strong> nanotubes were treated with ammonia gas at 600 C for 3 h, <strong>and</strong> then<br />
dispersed in cationic type polyethyleneamine (PEI) solution. The treated CNTs exhibit<br />
positive charge in a wide pH range on the basis of zeta potential measurement. Zeta<br />
potential is defined as the electrokinetic potential of particulate dispersions associated<br />
with the magnitude of electrical charge at the double layer of colloidal systems. It is<br />
commonly used to measure the magnitude of attraction or repulsion between<br />
dispersed particles [66]. Alumina nanoparticles (30 nm) were dispersed independently<br />
in anionic type poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) solution, yielding electronegative charges on<br />
particle surfaces. Sodium hydroxide was used to adjust the pH of suspension solution.<br />
The alumina suspension with PAA was dripped into the CNTsuspension containing<br />
PEI under sonication. The pH value was kept at 8 for the coating of alumina on CNTs.<br />
In another study, pristine CNTs were dispersed in anionic type sodium dodecyl<br />
sulfate (SDS) solution, forming electronegative charges on nanotube surfaces [62].<br />
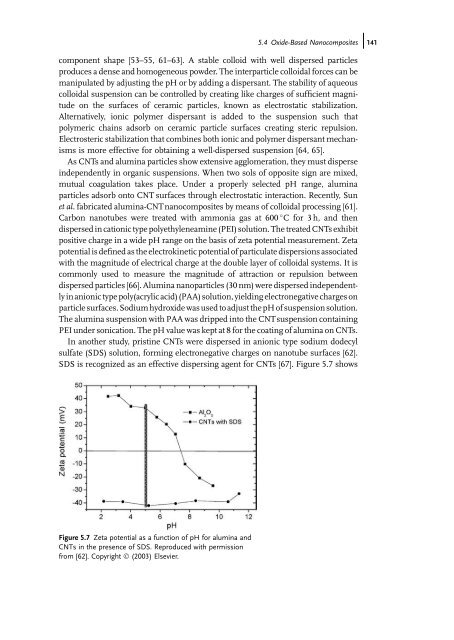
SDS is recognized as an effective dispersing agent for CNTs [67]. Figure 5.7 shows<br />
Figure 5.7 Zeta potential as a function of pH for alumina <strong>and</strong><br />
CNTs in the presence of SDS. Reproduced with permission<br />
from [62]. Copyright Ó (2003) Elsevier.<br />
5.4 Oxide-Based Nanocompositesj141