Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Metal and Ceramic ...
Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Metal and Ceramic ...
Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Metal and Ceramic ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
5.4.3<br />
Titania Matrix<br />
Titania (TiO2) is a semiconducting oxide with high photocatalytic ability. It finds<br />
application in many technological areas such as microelectronics, photocatalysis<br />
<strong>and</strong> sensors [95–97]. Titania is also an important bioceramic coating material for<br />
metal implants due to its excellent biocompatibility [98, 99]. Incorporating CNTs into<br />
titania can lead to the development of novel composite materials with advanced<br />
functional properties for photocatalytic, microelectronic <strong>and</strong> biomedical applications<br />
[100]. The techniques used for forming titania-CNT nanocomposites include<br />
heterocoagulation, sol-gel <strong>and</strong> hydrothermal treatment.<br />
Sun <strong>and</strong> Gao employed heterocoagulation to deposit titania on MWNTs [62].<br />
In the process, ammonia-treated MWNTs were dispersed ultrasonically in water<br />
containing cationic PEI. Titania nanoparticles with sizes less than 10 nm were<br />
dispersed in water under sonication <strong>and</strong> the pH value was adjusted by adding<br />
NaOH. Titania drops were then added to the nanotube suspension under a pH of 8.<br />
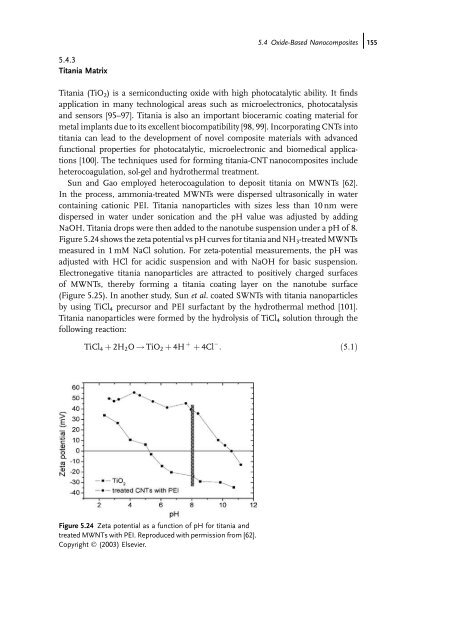
Figure 5.24 shows the zeta potential vs pH curves for titania <strong>and</strong> NH 3-treated MWNTs<br />
measured in 1 mM NaCl solution. For zeta-potential measurements, the pH was<br />
adjusted with HCl for acidic suspension <strong>and</strong> with NaOH for basic suspension.<br />
Electronegative titania nanoparticles are attracted to positively charged surfaces<br />
of MWNTs, thereby forming a titania coating layer on the nanotube surface<br />
(Figure 5.25). In another study, Sun et al. coated SWNTs with titania nanoparticles<br />
by using TiCl4 precursor <strong>and</strong> PEI surfactant by the hydrothermal method [101].<br />
Titania nanoparticles were formed by the hydrolysis of TiCl4 solution through the<br />
following reaction:<br />
TiCl4 þ 2H2O ! TiO2 þ 4H þ þ 4Cl : ð5:1Þ<br />
Figure 5.24 Zeta potential as a function of pH for titania <strong>and</strong><br />
treated MWNTs with PEI. Reproduced with permission from [62].<br />
Copyright Ó (2003) Elsevier.<br />
5.4 Oxide-Based Nanocompositesj155