Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Metal and Ceramic ...
Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Metal and Ceramic ...
Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Metal and Ceramic ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
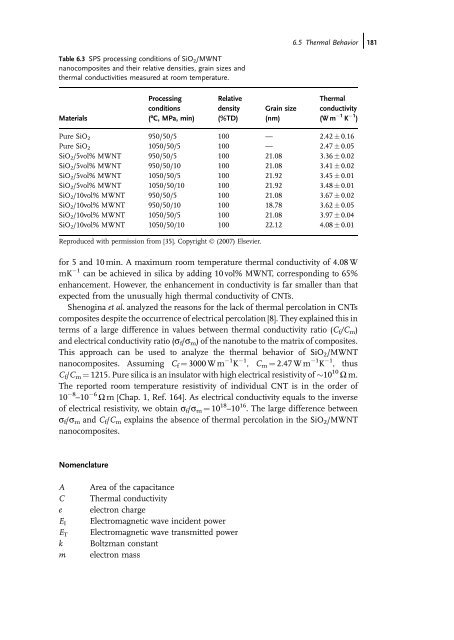
Table 6.3 SPS processing conditions of SiO2/MWNT<br />
nanocomposites <strong>and</strong> their relative densities, grain sizes <strong>and</strong><br />
thermal conductivities measured at room temperature.<br />
Materials<br />
for 5 <strong>and</strong> 10 min. A maximum room temperature thermal conductivity of 4.08 W<br />
mK 1 can be achieved in silica by adding 10 vol% MWNT, corresponding to 65%<br />
enhancement. However, the enhancement in conductivity is far smaller than that<br />
expected from the unusually high thermal conductivity of CNTs.<br />
Shenogina et al. analyzed the reasons for the lack of thermal percolation in CNTs<br />
composites despite the occurrence of electrical percolation [8]. They explained this in<br />
terms of a large difference in values between thermal conductivity ratio (Cf/Cm)<br />
<strong>and</strong> electrical conductivity ratio (sf/sm) of the nanotube to the matrix of composites.<br />
This approach can be used to analyze the thermal behavior of SiO2/MWNT<br />
nanocomposites. Assuming Cf ¼ 3000 W m 1 K 1 , Cm ¼ 2.47 W m 1 K 1 , thus<br />
Cf/Cm ¼ 1215. Pure silica is an insulator with high electrical resistivity of 10 10 W m.<br />
The reported room temperature resistivity of individual CNT is in the order of<br />
10 8 –10 6 W m [Chap. 1, Ref. 164]. As electrical conductivity equals to the inverse<br />
of electrical resistivity, we obtain sf/sm ¼ 10 18 –10 16 . The large difference between<br />
sf/sm <strong>and</strong> Cf/Cm explains the absence of thermal percolation in the SiO2/MWNT<br />
nanocomposites.<br />
Nomenclature<br />
Processing<br />
conditions<br />
(ºC, MPa, min)<br />
Relative<br />
density<br />
(%TD)<br />
A Area of the capacitance<br />
C Thermal conductivity<br />
e electron charge<br />
EI Electromagnetic wave incident power<br />
ET Electromagnetic wave transmitted power<br />
k Boltzman constant<br />
m electron mass<br />
Grain size<br />
(nm)<br />
Thermal<br />
conductivity<br />
(W m 1 K 1 )<br />
Pure SiO2 950/50/5 100 — 2.42 0.16<br />
Pure SiO 2 1050/50/5 100 — 2.47 0.05<br />
SiO2/5vol% MWNT 950/50/5 100 21.08 3.36 0.02<br />
SiO 2/5vol% MWNT 950/50/10 100 21.08 3.41 0.02<br />
SiO2/5vol% MWNT 1050/50/5 100 21.92 3.45 0.01<br />
SiO 2/5vol% MWNT 1050/50/10 100 21.92 3.48 0.01<br />
SiO2/10vol% MWNT 950/50/5 100 21.08 3.67 0.02<br />
SiO 2/10vol% MWNT 950/50/10 100 18.78 3.62 0.05<br />
SiO2/10vol% MWNT 1050/50/5 100 21.08 3.97 0.04<br />
SiO2/10vol% MWNT 1050/50/10 100 22.12 4.08 0.01<br />
Reproduced with permission from [35]. Copyright Ó (2007) Elsevier.<br />
6.5 Thermal Behaviorj181