to read the full report - Ecolateral by Peter Jones
to read the full report - Ecolateral by Peter Jones
to read the full report - Ecolateral by Peter Jones
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
148<br />
Evaluation of Opportunities for Converting Indigenous UK Wastes <strong>to</strong> Wastes and Energy<br />
AEA/ED45551/Issue 1<br />
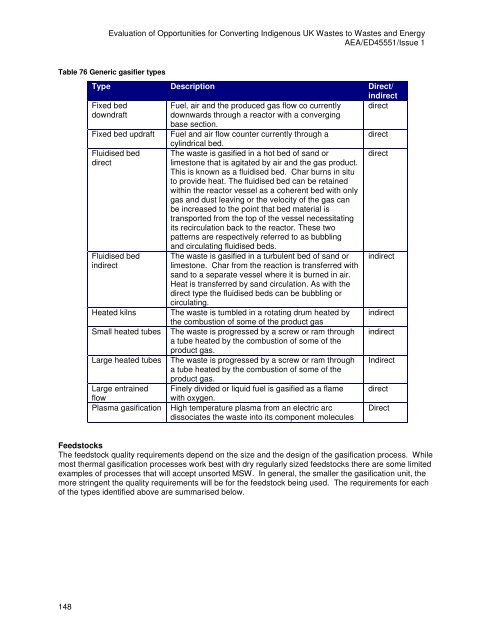
Table 76 Generic gasifier types<br />
Type Description Direct/<br />
indirect<br />
Fixed bed Fuel, air and <strong>the</strong> produced gas flow co currently direct<br />
downdraft downwards through a reac<strong>to</strong>r with a converging<br />
base section.<br />
Fixed bed updraft Fuel and air flow counter currently through a<br />
cylindrical bed.<br />
direct<br />
Fluidised bed The waste is gasified in a hot bed of sand or direct<br />
direct<br />
limes<strong>to</strong>ne that is agitated <strong>by</strong> air and <strong>the</strong> gas product.<br />
This is known as a fluidised bed. Char burns in situ<br />
<strong>to</strong> provide heat. The fluidised bed can be retained<br />
within <strong>the</strong> reac<strong>to</strong>r vessel as a coherent bed with only<br />
gas and dust leaving or <strong>the</strong> velocity of <strong>the</strong> gas can<br />
be increased <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> point that bed material is<br />
transported from <strong>the</strong> <strong>to</strong>p of <strong>the</strong> vessel necessitating<br />
its recirculation back <strong>to</strong> <strong>the</strong> reac<strong>to</strong>r. These two<br />
patterns are respectively referred <strong>to</strong> as bubbling<br />
and circulating fluidised beds.<br />
Fluidised bed The waste is gasified in a turbulent bed of sand or indirect<br />
indirect<br />
limes<strong>to</strong>ne. Char from <strong>the</strong> reaction is transferred with<br />
sand <strong>to</strong> a separate vessel where it is burned in air.<br />
Heat is transferred <strong>by</strong> sand circulation. As with <strong>the</strong><br />
direct type <strong>the</strong> fluidised beds can be bubbling or<br />
circulating.<br />
Heated kilns The waste is tumbled in a rotating drum heated <strong>by</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> combustion of some of <strong>the</strong> product gas<br />
indirect<br />
Small heated tubes The waste is progressed <strong>by</strong> a screw or ram through<br />
a tube heated <strong>by</strong> <strong>the</strong> combustion of some of <strong>the</strong><br />
product gas.<br />
indirect<br />
Large heated tubes The waste is progressed <strong>by</strong> a screw or ram through<br />
a tube heated <strong>by</strong> <strong>the</strong> combustion of some of <strong>the</strong><br />
product gas.<br />
Indirect<br />
Large entrained Finely divided or liquid fuel is gasified as a flame direct<br />
flow<br />
with oxygen.<br />
Plasma gasification High temperature plasma from an electric arc<br />
dissociates <strong>the</strong> waste in<strong>to</strong> its component molecules<br />
Direct<br />
Feeds<strong>to</strong>cks<br />
The feeds<strong>to</strong>ck quality requirements depend on <strong>the</strong> size and <strong>the</strong> design of <strong>the</strong> gasification process. While<br />
most <strong>the</strong>rmal gasification processes work best with dry regularly sized feeds<strong>to</strong>cks <strong>the</strong>re are some limited<br />
examples of processes that will accept unsorted MSW. In general, <strong>the</strong> smaller <strong>the</strong> gasification unit, <strong>the</strong><br />
more stringent <strong>the</strong> quality requirements will be for <strong>the</strong> feeds<strong>to</strong>ck being used. The requirements for each<br />
of <strong>the</strong> types identified above are summarised below.