- Page 1 and 2:
- --- - - --~ -----31D / D-9tcCultu
- Page 3:
--------Culture and Ecology ofChaco
- Page 6 and 7:
3. THE PRECERAMIC PERIOD IN CHACO C
- Page 8 and 9:
History of the Chaco Navajo '" . .
- Page 10 and 11:
~~~-------3.21. Overview of Sheep C
- Page 12 and 13:
10.12. Map 5, locating Historic per
- Page 14 and 15:
-- - -- - ---- ~----- - --B.I. Cera
- Page 16 and 17:
List of participants in the School
- Page 18 and 19:
1971, Robert H. Lister, then at the
- Page 20 and 21:
Personnel associated with the Chaco
- Page 22 and 23:
For this volume, lowe special thank
- Page 24 and 25:
2 Chaco Project Synthesis50. J •
- Page 26 and 27:
4 Chaco Project Synthesisand the fe
- Page 28 and 29:
6 Chaco Project Synthesispainted Es
- Page 30 and 31:
----------------------------------8
- Page 32 and 33:
10 Chaco Project SynthesisFigure 1.
- Page 34 and 35:
- - ----- -------------------------
- Page 36 and 37:
14 Chaco Project SynthesisCompariso
- Page 38 and 39:
16 Chaco Project SynthesisDuring ex
- Page 40 and 41:
18 Chaco Project Synthesisobsidian
- Page 43 and 44:
Chapter TwoThe Environment and Natu
- Page 45 and 46:
-- --------------------- --------En
- Page 47 and 48:
Environment and Natural Resources 2
- Page 49:
Environment and Natural Resources 2
- Page 52 and 53:
~~~--~~~~ --30 Chaco Project Synthe
- Page 54 and 55:
32 Chaco Project SynthesisA few yea
- Page 56 and 57:
------------------------.34 Chaco P
- Page 58 and 59:
36 Chaco Project Synthesismeasureme
- Page 60 and 61: 38 Chaco Project SynthesisLybrook,
- Page 62 and 63: 40 Chaco Project Synthesis
- Page 64 and 65: - -~~------~- --- - ---------------
- Page 66 and 67: 44 Chaco Project Synthesisflavescen
- Page 68 and 69: 46 Chaco Project Synthesisnel prese
- Page 70 and 71: -------48 Chaco Project SynthesisYI
- Page 72 and 73: 50 Chaco Project Synthesiswas proba
- Page 74 and 75: 52 Chaco Project Synthesis1981 [sic
- Page 76 and 77: 901to925950to9751001to10251050to107
- Page 78 and 79: 56 Chaco Project Synthesisamined th
- Page 80 and 81: -----------------------------------
- Page 82 and 83: -----------------------------
- Page 84 and 85: 62 Chaco Project Synthesisto the So
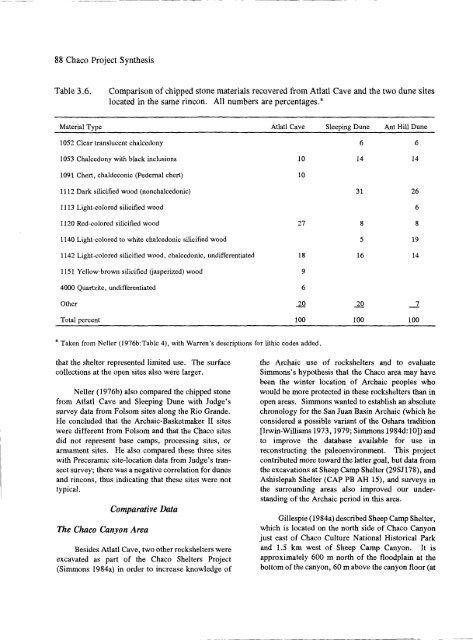
- Page 86 and 87: 64 Chaco Project SynthesisTable 3.1
- Page 88 and 89: 66 Chaco Project SynthesisTable 3.3
- Page 90 and 91: 68 Chaco Project SynthesisTable 3.5
- Page 92 and 93: 70 Chaco Project Synthesisshallow c
- Page 94 and 95: 72 Chaco Project Synthesis..... ~--
- Page 96 and 97: 74 Chaco Project Synthesis./-""\I \
- Page 98 and 99: 76 Chaco Project Synthesis.. N20 I-
- Page 100 and 101: 78 Chaco Project Synthesisthe first
- Page 102 and 103: ----------------80 Chaco Project Sy
- Page 104 and 105: ---------------------~---- ---- ---
- Page 106 and 107: 84 Chaco Project SynthesisFigure 3.
- Page 108 and 109: --------86 Chaco Project Synthesis.
- Page 112 and 113: 90 Chaco Project SynthesisThe secon
- Page 114 and 115: 92 Chaco Project SynthesisYears B.P
- Page 116 and 117: 94 Chaco Project Synthesispression
- Page 118 and 119: ----------------------96 Chaco Proj
- Page 120 and 121: 98 Chaco Project SynthesisFigure 4.
- Page 122 and 123: --------------------- ~~~~-~~-100 C
- Page 124 and 125: Figure 4.2.Identified Basketmaker I
- Page 126 and 127: ooo00 0o 0 00o 0 0qo000 00 "~""" 0~
- Page 129 and 130: •BftlO€)•••• oI
- Page 131 and 132: Output File Types 115Intensity File
- Page 133 and 134: Basketmaker III to Pueblo I 111stor
- Page 135 and 136: Basketmaker III to Pueblo I 113and
- Page 137 and 138: Basketmaker III to Pueblo I 115peop
- Page 139 and 140: Basketmaker III to Pueblo I 117and
- Page 141 and 142: Basketmaker III to Pueblo I 119Fami
- Page 143 and 144: Basketmaker III to Pueblo I 121by a
- Page 145 and 146: ------- - -----------------Basketma
- Page 147 and 148: --------Basketmaker III to Pueblo I
- Page 149 and 150: Chapter FiveThe Florescence of the
- Page 151 and 152: ~----------------------------------
- Page 153 and 154: The Florescence 131ExcavationsData
- Page 155 and 156: ------ -- - -- --The Florescence 13
- Page 157 and 158: FP5ooo1
- Page 159 and 160: Plthou •• C~f 8 0 0-: ~oo:~g(_-
- Page 161 and 162:
TRASH MOUNDoIoFigure 5.5. Map of 29
- Page 163 and 164:
The Florescence 141on-white, and Ga
- Page 165 and 166:
The Florescence 143Other Small Hous
- Page 167 and 168:
\ I\ II :: \1 I: I a ..\\\ l .-'';~
- Page 169 and 170:
II/ffII,II( /IMOOI:AIIaccOSIl(lAC,"
- Page 171 and 172:
IffFI//II/IIjI,//III" 1111001:"'"II
- Page 173 and 174:
, ,, fI f, If ,I f/ ,"If MCOCR~I A[
- Page 175 and 176:
Great No1lh Road J• StoifS.......
- Page 177 and 178:
,I MC~t~ij/ ':'.b'_''"'o/!PUEBLO AL
- Page 179 and 180:
The Florescence 157Recently Wills (
- Page 181 and 182:
The Florescence 159Figure 5.19.Earl
- Page 183 and 184:
"I----_\---~~--.-';--_:::::'y',..~f
- Page 185 and 186:
The Florescence 163rough-sort metho
- Page 187 and 188:
The Florescence 165Ceramics dating
- Page 189 and 190:
The Florescence 167Figure 5.24.Alta
- Page 191 and 192:
The Florescence 169Bonito phase str
- Page 193 and 194:
The Florescence 171Three road-relat
- Page 195 and 196:
The Florescence 173Figure 5.29.Aeri
- Page 197 and 198:
The Florescence 175construction cou
- Page 199 and 200:
Chapter SixThe Classic Adaptation W
- Page 201 and 202:
The Classic Adaptation 179were abov
- Page 203 and 204:
The Classic Adaptation 181upland ar
- Page 205 and 206:
The Classic Adaptation 183Estimated
- Page 207 and 208:
The Classic Adaptation 185which are
- Page 209 and 210:
Table 6.5. (cont'd.)Population Esti
- Page 211 and 212:
Table 6.7. Windes's small-house pop
- Page 213 and 214:
--_._-- -------The Classic Adaptati
- Page 215 and 216:
The Classic Adaptation 193sp.); buc
- Page 217 and 218:
The Classic Adaptation 195e.g., a d
- Page 219 and 220:
The Classic Adaptation 197block siz
- Page 221 and 222:
The Classic Adaptation 199and fir b
- Page 223 and 224:
The Classic Adaptation 201between f
- Page 225 and 226:
340 \I,II320 "• I......---5 - Yea
- Page 227 and 228:
The Classic Adaptation 205in and ar
- Page 229 and 230:
Table 6.8. (cont'd.)FeatureExamples
- Page 231 and 232:
The Classic Adaptation 209gested by
- Page 233 and 234:
The Classic Adaptation 211Table 6.9
- Page 235 and 236:
The Classic Adaptation 213.''-...,,
- Page 237 and 238:
The Classic Adaptation 215chalcedon
- Page 239 and 240:
Table 6.11. Projected ceramic consu
- Page 241 and 242:
The Classic Adaptation 219structure
- Page 243 and 244:
The Classic Adaptation 221Bonito, w
- Page 245 and 246:
The Classic Adaptation 223number of
- Page 247 and 248:
Chapter SevenThe Final Years (A.D.
- Page 249 and 250:
117'1[ .....II)...0"'1.111"'tlll~'[
- Page 251 and 252:
~ ___The Final Years 229RIR2R3__..i
- Page 253 and 254:
The Final Years 2311964) included c
- Page 255 and 256:
The Final Years 233, ,o J 2 3METERS
- Page 257 and 258:
-- -- - - - - -- - ~- -~-------- -
- Page 259 and 260:
_ - ~2 - -1 __ R_4_---J __ R_6_~R3R
- Page 261 and 262:
The Final Years 239most often with
- Page 263 and 264:
The Final Years 241severe drought f
- Page 265 and 266:
The Final Years 243ceramic types, b
- Page 267 and 268:
Chapter EightRelated Communities in
- Page 269 and 270:
Related Communities 247Calendrical0
- Page 271 and 272:
• WALL.ACESKUNK SPRINGS IIIIII ST
- Page 273 and 274:
• ESCALANTE.IDA JEAN• WALLACESK
- Page 275 and 276:
Related Communities 253(Marshall et
- Page 277 and 278:
Related Communities 255foodstuffs k
- Page 279 and 280:
Related Communities 257and cupule w
- Page 281 and 282:
GWeST. ( )~1 PIERRE'S~I ~.~~ ~ .•
- Page 283 and 284:
Related Communities 261possibility
- Page 285 and 286:
Related Communities 263by the Red M
- Page 287:
Related Communities 265when the div
- Page 290 and 291:
268 Chaco Project Synthesismigrated
- Page 292 and 293:
270 Chaco Project Synthesiswas not
- Page 294 and 295:
272 Chaco Project SynthesisCanyon r
- Page 296 and 297:
274 Chaco Project Synthesisgreater
- Page 298 and 299:
276 Chaco Project Synthesislayout,
- Page 300 and 301:
278 Chaco Project Synthesisleadersh
- Page 302 and 303:
-- -~----280 Chaco Project Synthesi
- Page 304 and 305:
282 Chaco Project SynthesisDiscussi
- Page 306 and 307:
284 Chaco Project Synthesissedentiz
- Page 308 and 309:
286 Chaco Project Synthesis• chan
- Page 310 and 311:
288 Chaco Project Synthesiswatered
- Page 312 and 313:
290 Chaco Project SynthesisEven ear
- Page 314 and 315:
292 Chaco Project Synthesis1954:65)
- Page 316 and 317:
294 Chaco Project Synthesisp337123
- Page 318 and 319:
296 Chaco Project Synthesisnecessar
- Page 321 and 322:
Chapter TenHistoric Period StudiesE
- Page 323 and 324:
Historic Period Studies 301control
- Page 325 and 326:
Historic Period Studies 303Chaco Pr
- Page 327 and 328:
Historic Period Studies 305Figure 1
- Page 329 and 330:
Historic Period Studies 307Figure 1
- Page 331 and 332:
Historic Period Studies 309lived in
- Page 333 and 334:
Historic Period Studies 311Warburto
- Page 335 and 336:
Figure 10.9.Map 2, locating Histori
- Page 337 and 338:
Figure 10.11. Map 4, locating Histo
- Page 339 and 340:
Figure 10.13. Map 6, locating Histo
- Page 341 and 342:
Figure 10.15. Map 8, which combines
- Page 343 and 344:
Historic Period Studies 321(_ 29SJI
- Page 345 and 346:
Historic Period Studies 323informat
- Page 347 and 348:
Historic Period Studies 325as stove
- Page 349 and 350:
Historic Period Studies 327them els
- Page 351 and 352:
Historic Period Studies 329the case
- Page 353 and 354:
Chapter ElevenThe Chaco Project fro
- Page 355 and 356:
A Broader Perspective 333Among arch
- Page 357 and 358:
A Broader Perspective 335Assuming t
- Page 359 and 360:
Table 11.2. Population thresholds i
- Page 361 and 362:
A Broader Perspective 339whom fall
- Page 363 and 364:
A Broader Perspective 341Table 11.3
- Page 365 and 366:
A Broader Perspective 343that is re
- Page 367 and 368:
Appendix AExcavated Sites in Chaco
- Page 369 and 370:
Table A.1. (cont'd.)Site Name Site
- Page 371 and 372:
Table A.2. (cont'd.)Site Name Site
- Page 373 and 374:
Table A.3. Sites excavated or exami
- Page 375 and 376:
Table A.3. (cont' d.)Site Name Site
- Page 377 and 378:
Table A.4. Sites excavated or exami
- Page 379 and 380:
Table AA. (cont'd.)Site Name Site N
- Page 381 and 382:
Table A.5. (cont'd.)Site No. Site N
- Page 383 and 384:
Table A.S. (cont'd.)5ite No. 5ite N
- Page 385 and 386:
Appendix BChronology ChartsThrougho
- Page 387 and 388:
Appendix B 365Table B.3. Dominant c
- Page 389 and 390:
Table B.4. (cont'd.)Pecos Classific
- Page 391 and 392:
Appendix CThe Chaco Synthesis Proje
- Page 393 and 394:
Appendix C 371Table C.l. The organi
- Page 395 and 396:
Appendix C 373Table C.3. The Chaco
- Page 397 and 398:
Appendix C 375Table C.5. Chaco, Mes
- Page 399 and 400:
Appendix C 377Table C.7. The capsto
- Page 401:
Appendix C 379Table C.S.In Search o
- Page 404 and 405:
382 Chaco Project SynthesisArcheolo
- Page 406 and 407:
384 Chaco Project SynthesisBinford,
- Page 408 and 409:
386 Chaco Project SynthesisMexico,
- Page 410 and 411:
388 Chaco Project SynthesisMonument
- Page 412 and 413:
390 Chaco Project SynthesisDoyel, D
- Page 414 and 415:
392 Chaco Project SynthesisUniversi
- Page 416 and 417:
-~ -- - -- ------394 Chaco Project
- Page 418 and 419:
396 Chaco Project SynthesisAmerican
- Page 420 and 421:
398 Chaco Project SynthesisMiscella
- Page 422 and 423:
400 Chaco Project SynthesisKlausner
- Page 424 and 425:
402 Chaco Project SynthesisLoose, R
- Page 426 and 427:
404 Chaco Project SynthesisPrice, p
- Page 428 and 429:
406 Chaco Project Synthesis1984 The
- Page 430 and 431:
408 Chaco Project SynthesisOrtiz, A
- Page 432 and 433:
410 Chaco Project SynthesisPsycholo
- Page 434 and 435:
412 Chaco Project SynthesisSchoenwe
- Page 436 and 437:
414 Chaco Project SynthesisSprague,
- Page 438 and 439:
416 Chaco Project Synthesis2000 Mac
- Page 440 and 441:
418 Chaco Project Synthesis1970b As
- Page 442 and 443:
420 Chaco Project SynthesisWhaley,
- Page 444 and 445:
-----------------------422 Chaco Pr
- Page 447 and 448:
Indexabandonment, and dispersion, 2
- Page 449 and 450:
Index 427bow and arrow, 63, 99Bradf
- Page 451 and 452:
Index 429demography: community, mar
- Page 453 and 454:
Index 431Hack, J. T., 32Half House,
- Page 455 and 456:
Index 433Little Colorado (River) ar
- Page 457 and 458:
Index 435population as a system, 33
- Page 459 and 460:
Index 437264, and nearest-neighbor
- Page 461 and 462:
Index 43929Mc391 structure, 30929SJ
- Page 464:
-----