Inside Pages9Final.indd - Ministry of Power
Inside Pages9Final.indd - Ministry of Power
Inside Pages9Final.indd - Ministry of Power
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
20<br />
MINISTRY OF POWER<br />
way <strong>of</strong> one for two matching grants. FY 2000-01 has been<br />
fixed as base year. Expected outlay under the incentive<br />
component is Rs. 20,000 Crore. The Minstry has appointed<br />
M/S CARE and M/S ICRA for third party scrutiny <strong>of</strong> the<br />
incentive claims <strong>of</strong> the utilities.<br />
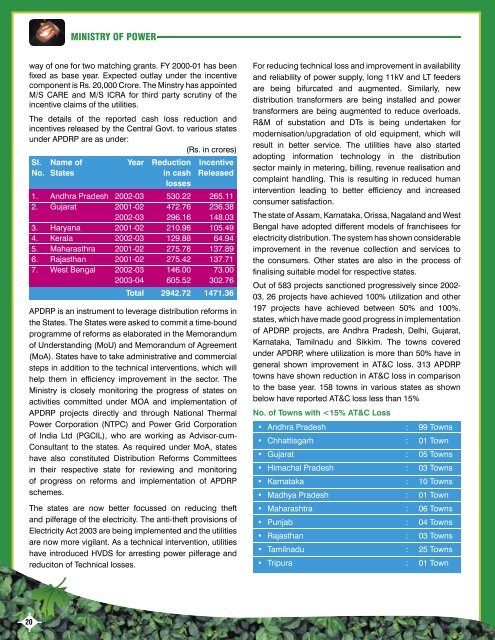
The details <strong>of</strong> the reported cash loss reduction and<br />
incentives released by the Central Govt. to various states<br />
under APDRP are as under:<br />
(Rs. in crores)<br />
Sl. Name <strong>of</strong> Year Reduction Incentive<br />
No. States in cash Released<br />
losses<br />
1. Andhra Pradesh 2002-03 530.22 265.11<br />
2. Gujarat 2001-02 472.76 236.38<br />
2002-03 296.16 148.03<br />
3. Haryana 2001-02 210.98 105.49<br />
4. Kerala 2002-03 129.88 64.94<br />
5. Maharasthra 2001-02 275.78 137.89<br />
6. Rajasthan 2001-02 275.42 137.71<br />
7. West Bengal 2002-03 146.00 73.00<br />
2003-04 605.52 302.76<br />
Total 2942.72 1471.36<br />
APDRP is an instrument to leverage distribution reforms in<br />
the States. The States were asked to commit a time-bound<br />
programme <strong>of</strong> reforms as elaborated in the Memorandum<br />
<strong>of</strong> Understanding (MoU) and Memorandum <strong>of</strong> Agreement<br />
(MoA). States have to take administrative and commercial<br />
steps in addition to the technical interventions, which will<br />
help them in efficiency improvement in the sector. The<br />
<strong>Ministry</strong> is closely monitoring the progress <strong>of</strong> states on<br />
activities committed under MOA and implementation <strong>of</strong><br />
APDRP projects directly and through National Thermal<br />
<strong>Power</strong> Corporation (NTPC) and <strong>Power</strong> Grid Corporation<br />
<strong>of</strong> India Ltd (PGCIL), who are working as Advisor-cum-<br />
Consultant to the states. As required under MoA, states<br />
have also constituted Distribution Reforms Committees<br />
in their respective state for reviewing and monitoring<br />
<strong>of</strong> progress on reforms and implementation <strong>of</strong> APDRP<br />
schemes.<br />
The states are now better focussed on reducing theft<br />
and pilferage <strong>of</strong> the electricity. The anti-theft provisions <strong>of</strong><br />
Electricity Act 2003 are being implemented and the utilities<br />
are now more vigilant. As a technical intervention, utilities<br />
have introduced HVDS for arresting power pilferage and<br />
reduciton <strong>of</strong> Technical losses.<br />
For reducing technical loss and improvement in availability<br />
and reliability <strong>of</strong> power supply, long 11kV and LT feeders<br />
are being bifurcated and augmented. Similarly, new<br />
distribution transformers are being installed and power<br />
transformers are being augmented to reduce overloads.<br />
R&M <strong>of</strong> substation and DTs is being undertaken for<br />
modernisation/upgradation <strong>of</strong> old equipment, which will<br />
result in better service. The utilities have also started<br />
adopting information technology in the distribution<br />
sector mainly in metering, billing, revenue realisation and<br />
complaint handling. This is resulting in reduced human<br />
intervention leading to better efficiency and increased<br />
consumer satisfaction.<br />
The state <strong>of</strong> Assam, Karnataka, Orissa, Nagaland and West<br />
Bengal have adopted different models <strong>of</strong> franchisees for<br />
electricity distribution. The system has shown considerable<br />
improvement in the revenue collection and services to<br />
the consumers. Other states are also in the process <strong>of</strong><br />
finalising suitable model for respective states.<br />
Out <strong>of</strong> 583 projects sanctioned progressively since 2002-<br />
03, 26 projects have achieved 100% utilization and other<br />
197 projects have achieved between 50% and 100%.<br />
states, which have made good progress in implementation<br />
<strong>of</strong> APDRP projects, are Andhra Pradesh, Delhi, Gujarat,<br />
Karnataka, Tamilnadu and Sikkim. The towns covered<br />
under APDRP, where utilization is more than 50% have in<br />
general shown improvement in AT&C loss. 313 APDRP<br />
towns have shown reduction in AT&C loss in comparison<br />
to the base year. 158 towns in various states as shown<br />
below have reported AT&C loss less than 15%<br />
No. <strong>of</strong> Towns with