WSHPDR_2013_Final_Report-updated_version
WSHPDR_2013_Final_Report-updated_version
WSHPDR_2013_Final_Report-updated_version
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3.5.6 Lebanon<br />
Joy Balta, Lebanese American University, Lebanon; Kai<br />
Whiting, International Center on Small Hydro Power<br />
Key facts<br />
Population 4,140,289 1<br />
Area 10,400 km 2<br />
Climate Mediterranean; mild to cool, wet<br />
winters with hot, dry summers;<br />
Lebanon mountains experience heavy<br />
winter snows.<br />
Topography Four main geographical regions running<br />
north to south parallel to the<br />
Mediterranean - the coastal plain, the<br />
Lebanon mountain range, the Bekaa<br />
Valley and the Anti-Lebanon range.<br />
Rain<br />
Pattern<br />
Average annual rainfall (1965-1999)<br />
along the coastal zone ranges between<br />
540 mm and 1,110 mm, whereas the<br />
annual average precipitation (rain and<br />
snow) over the mountain area ranges<br />
between 937 mm and 1,854 mm for the<br />
same period. 2<br />
Electricity sector overview<br />
Lebanon lacks all types of major traditional energy<br />
sources, including fossil fuels. 3 Accordingly, 99 per<br />
cent of its primary energy needs is met through the<br />
main electricity company, Electricité du Liban (EDL) by<br />
importing around US$500 million worth of fuel each<br />
year to generate the electricity needed. 4 Renewable<br />
energy currently provides a minor contribution to the<br />
energy balance in Lebanon, its share is less than 5 per<br />
cent of primary energy and less than 10 per cent of<br />
the electricity production.<br />
Hydropower is the only renewable source used in<br />
electricity generation in Lebanon (figure 1), although it<br />
has the potential to benefit from other resources,<br />
particularly solar and wind. 3 Electricity, thus, is mostly<br />
generated from thermal power plants, with a limited<br />
contribution from ageing hydropower installations.<br />
The power supply capacity of 2,100 MW is made up of<br />
1,900 MW thermal power and 200 MW hydropower. 5<br />
Hydropower can, however, be as low as 80 MW in a<br />
dry year. 6 Imports are currently provided by Egypt and<br />
in the past, provided by the Syrian Arab Republic<br />
before the outbreak of civil unrest. 7<br />
The civil war that broke out in 1975 caused vast<br />
destruction to the country’s infrastructure. The war<br />
ceased in 1991, at that point the Lebanese people had<br />
adapted to the absence of stable electricity supply and<br />
have been using private diesel generators.<br />
Between the 1990s and the end of 2000s, successive<br />
governments failed to reform the sector and invest in<br />
infrastructure. In 2011, the Government approved a<br />
policy paper on the electricity sector prepared by the<br />
Minister of Power and Water. It states that the total<br />
energy demand in 2009 was 15,000 GWh, EDL<br />
supplied 11,522 GWh out of the original demand from<br />
different sources. 8 9<br />
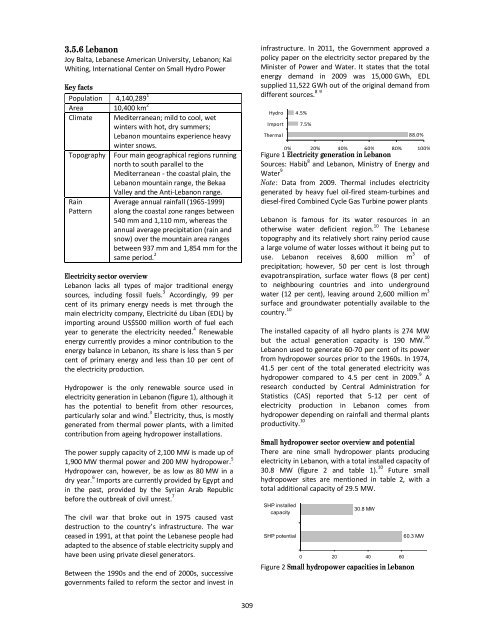
Hydro 4.5%<br />
Import 7.5%<br />
88.0%<br />
Thermal<br />
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%<br />
Figure 1 Electricity generation in Lebanon<br />
Sources: Habib 8 and Lebanon, Ministry of Energy and<br />
Water 9<br />
Note: Data from 2009. Thermal includes electricity<br />
generated by heavy fuel oil-fired steam-turbines and<br />
diesel-fired Combined Cycle Gas Turbine power plants<br />
Lebanon is famous for its water resources in an<br />
otherwise water deficient region. 10 The Lebanese<br />
topography and its relatively short rainy period cause<br />
a large volume of water losses without it being put to<br />
use. Lebanon receives 8,600 million m 3 of<br />
precipitation; however, 50 per cent is lost through<br />
evapotranspiration, surface water flows (8 per cent)<br />
to neighbouring countries and into underground<br />
water (12 per cent), leaving around 2,600 million m 3<br />
surface and groundwater potentially available to the<br />
country. 10<br />
The installed capacity of all hydro plants is 274 MW<br />
but the actual generation capacity is 190 MW. 10<br />
Lebanon used to generate 60-70 per cent of its power<br />
from hydropower sources prior to the 1960s. In 1974,<br />
41.5 per cent of the total generated electricity was<br />
hydropower compared to 4.5 per cent in 2009. 9 A<br />
research conducted by Central Administration for<br />
Statistics (CAS) reported that 5-12 per cent of<br />
electricity production in Lebanon comes from<br />
hydropower depending on rainfall and thermal plants<br />
productivity. 10<br />
Small hydropower sector overview and potential<br />
There are nine small hydropower plants producing<br />
electricity in Lebanon, with a total installed capacity of<br />
30.8 MW (figure 2 and table 1). 10 Future small<br />
hydropower sites are mentioned in table 2, with a<br />
total additional capacity of 29.5 MW.<br />
SHP installed<br />
capacity<br />
SHP potential<br />
30.8 MW<br />
0 20 40 60<br />
60.3 MW<br />
Figure 2 Small hydropower capacities in Lebanon<br />
309