- Page 1 and 2:
This project is funded by the Europ
- Page 3 and 4:
EuropeAid/132630/C/SER/Multi CLEANE
- Page 5 and 6:
Table of contents Executive Summary
- Page 7 and 8:
4.3. Renewable energy development .
- Page 9 and 10:
2.2.1 Template 2.2.1 Proposed Commu
- Page 11 and 12:
List of tables Table 1: Emission fa
- Page 13 and 14:
Industry; d) Transport; e) Waste an
- Page 15 and 16:
Section I: Governorate climate and
- Page 17 and 18:
(MCEI) is responsible for drawing u
- Page 19 and 20:
implementing the NEEAP and using sm
- Page 21 and 22:
previously set by H.E. General Fara
- Page 23 and 24:
8. Construct 4500 housing units in
- Page 25 and 26:
2. Promote the integration of energ
- Page 27 and 28:
The SEAU will be in charge of all G
- Page 29 and 30:
To ensure the success of project im
- Page 31 and 32:
Financing the SECAP The Governorate
- Page 33 and 34:
consumption and GHG emissions. 1.2.
- Page 35 and 36:
1.3.1.2 Employment statistics The e
- Page 37 and 38:
Value provided Method Final value E
- Page 39 and 40:
* Emissions from livestock and anim
- Page 41 and 42:
average emissions per capita in Egy
- Page 43 and 44: 10% 10% Governorate (Municipal) Bui
- Page 45 and 46: Agriculture 1 692 0 2 622 0 0 0 0 4
- Page 47 and 48: Figure 11: Impression of the City o
- Page 49 and 50: 4. Planned actions for the city of
- Page 51 and 52: This commitment to act on its own p
- Page 53 and 54: EGP 340,910 (€ 16,148), offering
- Page 55 and 56: places and avenues where the new li
- Page 57 and 58: - Get a good understanding of the b
- Page 59 and 60: energy conservation, energy efficie
- Page 61 and 62: only possible when real alternative
- Page 63 and 64: 155 boats with an average fuel cons
- Page 65 and 66: Luxor and, by the way, a very effic
- Page 67 and 68: 4.2.3.3 Medium-term actions (3 to 1
- Page 69 and 70: electricity used in tertiary buildi
- Page 71 and 72: 4.2.5.2 Possible actions As agricul
- Page 73 and 74: a feed in tariff policy. If this po
- Page 75 and 76: producing solar heater in small wor
- Page 77 and 78: TRANSPORT Common charter for servic
- Page 79 and 80: Figure 14: Seasonal (winter: Decemb
- Page 81 and 82: 2.2. Climate Change Impacts in Egyp
- Page 83 and 84: cause mortalities 18 . In line with
- Page 85 and 86: 36 million from 1950 to 2010, popul
- Page 87 and 88: harbour) in Alexandria 45 . Moreove
- Page 89 and 90: The national strategy, its goals an
- Page 91 and 92: The key players of this strategy st
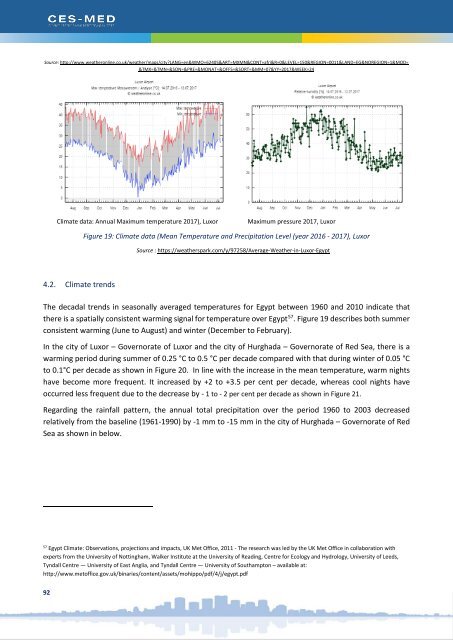
- Page 93: a. Ambient temperature (2000-2012)
- Page 97 and 98: a. Dry-bulb temperature (°C) scena
- Page 99 and 100: • “C”, corresponds to complet
- Page 101 and 102: Future Cities Adaptation Compass To
- Page 104: Receptors Extreme weather event Pot
- Page 108: Receptors Extreme weather event Riv
- Page 112: Receptors Extreme weather event Pot
- Page 115 and 116: Storms - Higher maintenance cost -
- Page 117 and 118: Storms Floods - Damages/ loss of ha
- Page 119 and 120: esult of a partnership between Egyp
- Page 121 and 122: necessary adaptation policies. Prov
- Page 123 and 124: 2. Build institutional and technica
- Page 125 and 126: Alert / Communication / Education D
- Page 127 and 128: Table 17: Suggested adaptation acti
- Page 129 and 130: Adoption of methods to reduce water
- Page 131 and 132: Section V: Project Fiches City of L
- Page 133 and 134: Strategy - Transport Strategy and A
- Page 135 and 136: in the Nile river is absolutely cen
- Page 137 and 138: • Structuring the urban transport
- Page 139 and 140: 5. Assumptions and risks • Mobili
- Page 141 and 142: Loans and potential borrower Expect
- Page 143 and 144: water quality of the surrounding en
- Page 145 and 146:
- Reduce energy consumption in all
- Page 147 and 148:
• Environmental permit: EEAA appr
- Page 149 and 150:
- Minimum NG required per Cruise bo
- Page 151 and 152:
• MoTr through River Transport Au
- Page 153 and 154:
8. Cost estimates Technical support
- Page 155 and 156:
City of Luxor - Governorate of Luxo
- Page 157 and 158:
- Second National Communication on
- Page 159 and 160:
- Reduce fossil fuel consumption in
- Page 161 and 162:
- Directive 2001/42/EC (SEA Directi
- Page 163 and 164:
- Train small local companies that
- Page 165 and 166:
Staff training Governorate (Municip
- Page 167 and 168:
- Lamp replacement by LED 10% 783 k
- Page 169 and 170:
City of Luxor (Governorate of Luxor
- Page 171 and 172:
Laws, Regulations and Decrees Laws
- Page 173 and 174:
lower GHG emissions. This action is
- Page 175 and 176:
Component 2: Develop Solar Water He
- Page 177 and 178:
- Municipality and Governorate - Go
- Page 179 and 180:
• The development of Green hotels
- Page 181 and 182:
- Reduction as related to BAU scena
- Page 183 and 184:
is a need to make use of green labe
- Page 185 and 186:
- Incentives for Generating Electri
- Page 187 and 188:
• Install PV Solar panels and SHW
- Page 189 and 190:
This includes: - Switch from AC/ He
- Page 191 and 192:
The development would require the f
- Page 193 and 194:
• Municipality determination to a
- Page 195 and 196:
Energy savings GWh/y - Lamp replace
- Page 197 and 198:
the workshop participants towards t
- Page 199 and 200:
I. Identification of the target aud
- Page 201 and 202:
From this study concerning the targ
- Page 203 and 204:
- Link to other opportunities and/o
- Page 205 and 206:
2.1.2. Template Proposed Communicat
- Page 207 and 208:
the installation of ordinary lamps
- Page 209 and 210:
- Staff training needs: Coordinatio
- Page 211 and 212:
- Coordinate with the road manageme
- Page 213 and 214:
2.2.2. Template Proposed Communicat
- Page 215 and 216:
3.1. Template Identification of CAP
- Page 217 and 218:
expected in %. 2- Reduce carbon emi
- Page 219 and 220:
staff and household owners and mana
- Page 221 and 222:
Key Message: - Luxor is turning gre
- Page 223 and 224:
References Elkhayt, M. 2016. The Eg
- Page 225 and 226:
Climate Change Legislation in Egypt
- Page 227 and 228:
Table of Contents LIST OF TABLES ..
- Page 229 and 230:
1. Introduction Al-Qurna is one of
- Page 231 and 232:
2 3 (1) Heritage Sites (2) Agricult
- Page 233 and 234:
Consequently, the following will be
- Page 235 and 236:
- Tourism and Heritage problem Lack
- Page 237 and 238:
The introduction of the by road, Lu
- Page 239 and 240:
the constant stream of tourists has
- Page 241 and 242:
Uncoordinated designation for herit
- Page 243 and 244:
d) To mitigate visiting risks throu
- Page 245 and 246:
from the SCA tourist info. Center s
- Page 247 and 248:
- Awareness campaign for SCA staff
- Page 249 and 250:
Provide comfortable environment fri
- Page 251 and 252:
After minimising trips by 40 per ce
- Page 253 and 254:
Public-Private-Partnerships (availa
- Page 255 and 256:
to PV system. Conclusion: - A clean
- Page 257 and 258:
5.1.4 Management of Agriculture was
- Page 259 and 260:
Phase 2: Continue with the rest of
- Page 261 and 262:
5.1.5. Environmental public awarene
- Page 263 and 264:
• Spreading information and train
- Page 265 and 266:
Total cost of Project: 13,000 € D
- Page 267 and 268:
5.2 Project fiches mid-term actions
- Page 269 and 270:
Component 1: Select and formulate t
- Page 271 and 272:
6. Appendix: Luxor Governorate Stra
- Page 273:
Declared by H.E. the governor, Luxo