Living Image 3.1
Living Image 3.1
Living Image 3.1
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Living</strong> <strong>Image</strong> ® Software User’s Manual<br />
4.8 Correcting or Filtering <strong>Image</strong> Data<br />
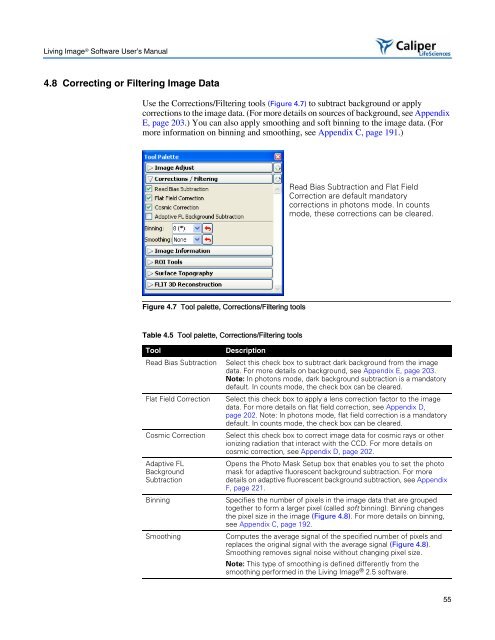
Use the Corrections/Filtering tools (Figure 4.7) to subtract background or apply<br />
corrections to the image data. (For more details on sources of background, see Appendix<br />
E, page 203.) You can also apply smoothing and soft binning to the image data. (For<br />
more information on binning and smoothing, see Appendix C, page 191.)<br />
Figure 4.7 Tool palette, Corrections/Filtering tools<br />
Table 4.5 Tool palette, Corrections/Filtering tools<br />
Tool Description<br />
Read Bias Subtraction Select this check box to subtract dark background from the image<br />
data. For more details on background, see Appendix E, page 203.<br />
Note: In photons mode, dark background subtraction is a mandatory<br />
default. In counts mode, the check box can be cleared.<br />
Flat Field Correction Select this check box to apply a lens correction factor to the image<br />
data. For more details on flat field correction, see Appendix D,<br />
page 202. Note: In photons mode, flat field correction is a mandatory<br />
default. In counts mode, the check box can be cleared.<br />
Cosmic Correction Select this check box to correct image data for cosmic rays or other<br />
ionizing radiation that interact with the CCD. For more details on<br />
cosmic correction, see Appendix D, page 202.<br />
Adaptive FL<br />
Background<br />
Subtraction<br />
Read Bias Subtraction and Flat Field<br />
Correction are default mandatory<br />
corrections in photons mode. In counts<br />
mode, these corrections can be cleared.<br />
Opens the Photo Mask Setup box that enables you to set the photo<br />
mask for adaptive fluorescent background subtraction. For more<br />
details on adaptive fluorescent background subtraction, see Appendix<br />
F, page 221.<br />
Binning Specifies the number of pixels in the image data that are grouped<br />
together to form a larger pixel (called soft binning). Binning changes<br />
the pixel size in the image (Figure 4.8). For more details on binning,<br />
see Appendix C, page 192.<br />
Smoothing Computes the average signal of the specified number of pixels and<br />
replaces the original signal with the average signal (Figure 4.8).<br />
Smoothing removes signal noise without changing pixel size.<br />
Note: This type of smoothing is defined differently from the<br />
smoothing performed in the <strong>Living</strong> <strong>Image</strong> ® 2.5 software.<br />
55