- Page 1 and 2:
DEVELOPMENTAL CRISIS IN EARLY ADULT
- Page 3 and 4:
Acknowledgements I would like to th
- Page 5 and 6:
7 Study 2: Rescuing the Hijacked Se
- Page 7 and 8:
considered to be a constructive par
- Page 9 and 10:
models, psychodynamic theory, socia
- Page 11 and 12:
This literature review will act as
- Page 13 and 14:
stable structures, by the assimilat
- Page 15 and 16:
goal-directed sense, but there is a
- Page 17 and 18:
“Where such a Dream exists, we ar
- Page 19 and 20:
Table I. Caplan’s Four Phases of
- Page 21 and 22:
Table III. O’Connor and Wolfe’s
- Page 23 and 24:
“Having a crisis at the time is n
- Page 25 and 26:
1. Undergoing stressful experiences
- Page 27 and 28:
The store of self-knowledge provide
- Page 29 and 30:
has, according to Booker (2005), ev
- Page 31 and 32:
of which represents a more complex
- Page 33 and 34:
isolated set of me-facts but is dee
- Page 35 and 36:
terms. These kind of popularised th
- Page 37 and 38:
involves genuine integration of com
- Page 39 and 40:
Figure 5. Births within marriage an
- Page 41 and 42:
ecorded by the US Bureau of Labor S
- Page 43 and 44:
group data and statistical analysis
- Page 45 and 46:
cognitive dissonance theory on a si
- Page 47 and 48:
testing and theory-exemplification
- Page 49 and 50:
human agendas that shape knowledge.
- Page 51 and 52:
4. A Composite Qualitative Methodol
- Page 53 and 54:
thesis, and I shall later in this c
- Page 55 and 56:
Nonetheless it could also be argued
- Page 57 and 58:
IPA can employ any written data sou
- Page 59 and 60:
ecommended to use a homogenous samp
- Page 61 and 62:
Case summaries are another written
- Page 63 and 64:
similarities that bind clusters tog
- Page 65 and 66:
conclusions and findings in order t
- Page 67 and 68:
d) Resonance / Impact / Applicabili
- Page 69 and 70:
3. A consent form detailing the key
- Page 71 and 72:
Dear all, I am currently in the 1 s
- Page 73 and 74:
accurately restructure the events,
- Page 75 and 76:
for the whole gender, and then with
- Page 77 and 78:
Neil 30 IT manager N.A. Violet 36 A
- Page 79 and 80:
areas were covered spontaneously as
- Page 81 and 82:
indication of important development
- Page 83 and 84:
starting with female clusters and t
- Page 85 and 86:
6. Study 1 Results: An Emerging Cri
- Page 87 and 88:
This vignette is illustrative and i
- Page 89 and 90:
“By the time I moved into my own
- Page 91 and 92:
New vocational role In Phase 4, cri
- Page 93 and 94:
As Mary’s crisis emerges in her l
- Page 95 and 96:
Angela similarly learned to stand u
- Page 97 and 98:
university to do a degree in psycho
- Page 99 and 100:
of my building, heated through by i
- Page 101 and 102:
married with two children and was a
- Page 103 and 104:
acceptable.” (p.8). George was li
- Page 105 and 106:
“You know, I’d failed, it was t
- Page 107 and 108:
Phase 4 - Post-Crisis: Resolution A
- Page 109 and 110:
Phase 1 - Early Crisis: Constrictio
- Page 111 and 112:
In his early thirties, Leon finally
- Page 113 and 114:
Phase 1 - Early Crisis: Locked In A
- Page 115 and 116:
Phase 3 and 4: Exploration and Reso
- Page 117 and 118:
6.6 Summary of the 4-Phase Pattern
- Page 119 and 120:
can also subtly undermine personal
- Page 121 and 122:
George developed a party-guy person
- Page 123 and 124:
sense of self, but meanwhile the se
- Page 125 and 126:
process in order to help account fo
- Page 127 and 128:
Data Collection In order to gain su
- Page 129 and 130:
Brainstorm memo #2 - “Guy: proces
- Page 131 and 132:
Results 7.3 Summary of Key Events i
- Page 133 and 134:
“That’s a realisation looking b
- Page 135 and 136:
efore the crisis Guy had lost the f
- Page 137 and 138:
that were pushing upon me that this
- Page 139 and 140:
Guy relates this behaviour to his s
- Page 141 and 142:
“I’ve stopped allowing myself t
- Page 143 and 144:
ecause an over-riding life emphasis
- Page 145 and 146:
transformation and development, rat
- Page 147 and 148:
8. Study 3: Crisis, Persona and the
- Page 149 and 150:
Peer pressure Need for social acce
- Page 151 and 152:
At the time of the crisis, Frank wa
- Page 153 and 154:
Frank’s young Dream was to become
- Page 155 and 156:
sham or an act. This dissonant dysf
- Page 157 and 158:
the ranks. Nobody tells you that yo
- Page 159 and 160:
“What I often refer to is a dress
- Page 161 and 162:
Claire described the business world
- Page 163 and 164:
a cellar, it’s really suffocating
- Page 165 and 166:
environment, during which time she
- Page 167 and 168:
and is no longer so concerned with
- Page 169 and 170:
understanding early adult crisis. T
- Page 171 and 172:
it leads to a lack of inner-outer b
- Page 173 and 174:
they can be channelled to support a
- Page 175 and 176:
9. A Conjectural Model of Early Adu
- Page 177 and 178:
The motivation for entering into th
- Page 179 and 180:
Phase 2: Separation Life Situation:
- Page 181 and 182:
training programme, a philosophy de
- Page 183 and 184:
“But I am going for jobs for diff
- Page 185 and 186:
9.3 Eight Theoretical Precepts on C
- Page 187 and 188:
homogeneity. For Jung, the removal
- Page 189 and 190:
assertiveness, for to act in accord
- Page 191 and 192:
throughout, and while this may glos
- Page 193 and 194:
lifespan and the context of relatio
- Page 195 and 196:
oth phases there is the description
- Page 197 and 198:
“In order to make commitments to
- Page 199 and 200:
Interactive Model and Smith’s Int
- Page 201 and 202:
economic groups get married earlier
- Page 203 and 204:
The Participant Feedback Exercise Y
- Page 205 and 206:
Question 3 asked whether the model
- Page 207 and 208:
10.9 Reflexive Considerations: The
- Page 209 and 210:
work that suggested crisis does occ
- Page 211 and 212:
may be of benefit to bring others i
- Page 213 and 214:
In sum, the current study provides
- Page 215 and 216:
References Ainsworth, M. (1967). In
- Page 217 and 218:
Cabrera, N.J., Tamis-LeMonda, C.S.,
- Page 219 and 220:
Festinger, L., Riecken, H.W. & Scha
- Page 221 and 222:
Hudson, W.C. (1978). Persona and De
- Page 223 and 224:
Lincoln, Y.S. & Guba, E.G. (1985).
- Page 225 and 226:
Polkinghorne, D.E. (1988). Narrativ
- Page 227 and 228:
Smith, J. (1991). Conceiving Selves
- Page 229 and 230:
Appendices 224
- Page 231 and 232:
SELF - process and structure • Wh
- Page 233 and 234: “Dancing became absolutely phenom
- Page 235 and 236: STUDY 3 - First Interview Schedule
- Page 237 and 238: o How would you describe your new j
- Page 239 and 240: Materialism • How do you think yo
- Page 241 and 242: • Are you still as driven by mone
- Page 243 and 244: Mark Interview 2 Schedule Pre-Crisi
- Page 245 and 246: Victoria - Interview 2 guide Pre-Cr
- Page 247 and 248: Claire - Interview 2 guide Pre-cris
- Page 249 and 250: Lilly - Interview 2 Schedule Pre-Cr
- Page 251 and 252: Information Sheet for Studies 1 and
- Page 253 and 254: APPENDIX C School of Psychology Bir
- Page 255 and 256: and so there was unused freedom. Lo
- Page 257 and 258: 5/02/05 As the crisis progresses, G
- Page 259 and 260: Violet memos 09.02.05 Once again we
- Page 261 and 262: acceptance of genuine possibility,
- Page 263 and 264: All these ladies and gents went bac
- Page 265 and 266: accompany the post-partition state.
- Page 267 and 268: lack of available time to pursue an
- Page 269 and 270: Pragmatism and Pluralism properties
- Page 271 and 272: Cyclical and iterative nature of re
- Page 273 and 274: Gemma Interview 10 Case Summary Gem
- Page 275 and 276: Coding Frame and Quotes 1. Backgrou
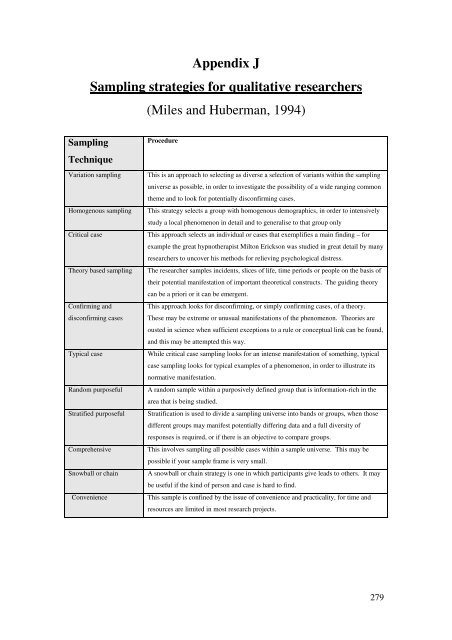
- Page 277 and 278: were trying to crush it too.” 4
- Page 279 and 280: 3d) Separation from old self 3e) Ne
- Page 281 and 282: Rob kids Working as advertising exe
- Page 283: Table XIX: Case Ordered Matrix of P