Superconducting Technology Assessment - nitrd
Superconducting Technology Assessment - nitrd
Superconducting Technology Assessment - nitrd
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Digital superconducting electronics RSFQ technology has the potential, as identified in the 2003 and 2004 SIA<br />
roadmaps, to be a “successor” technology to CMOS for high-performance applications. The 2004 Update to this<br />
roadmap stated the problem as:<br />
“One difficult challenge related to logic in both near- and the longer-term is to extend CMOS technology to and<br />
beyond the 45 nm node sustaining the historic annual increase of intrinsic speed of high-performance MPUs at<br />
17%. This may require an unprecedented simultaneous introduction of two or more innovations to the device<br />
structure and/or gate materials. Another longer-term challenge for logic is invention and reduction to practice of<br />
a new manufacturable information and signal processing technology addressing ’beyond CMOS‘ applications.<br />
Solutions to the first may be critically important to extension of CMOS beyond the 45 nm node, and solutions to<br />
the latter could open opportunities for microelectronics beyond the end of CMOS scaling.”<br />
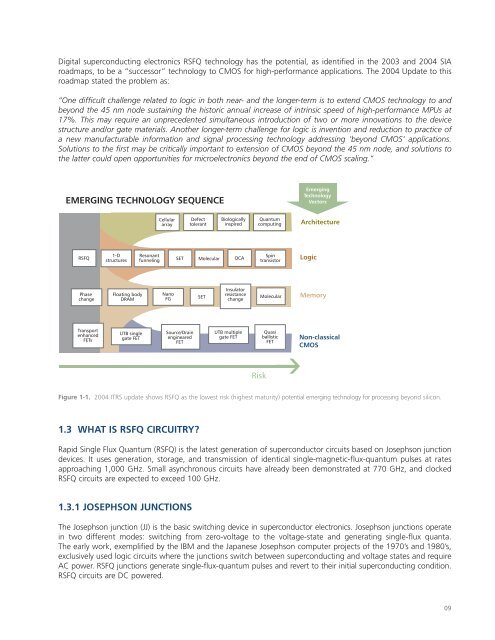
EMERGING TECHNOLOGY SEQUENCE<br />
RSFQ<br />
Phase<br />
change<br />
Transport<br />
enhanced<br />
FETs<br />
1-D<br />
structures<br />
Floating body<br />
DRAM<br />
UTB single<br />
gate FET<br />
Resonant<br />
funneling<br />
Cellular<br />
array<br />
Nano<br />
FG<br />
1.3 WHAT IS RSFQ CIRCUITRY?<br />
Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) is the latest generation of superconductor circuits based on Josephson junction<br />
devices. It uses generation, storage, and transmission of identical single-magnetic-flux-quantum pulses at rates<br />
approaching 1,000 GHz. Small asynchronous circuits have already been demonstrated at 770 GHz, and clocked<br />
RSFQ circuits are expected to exceed 100 GHz.<br />
1.3.1 JOSEPHSON JUNCTIONS<br />
Defect<br />
tolerant<br />
Biologically<br />
inspired<br />
SET Molecular QCA<br />
Source/Drain<br />
engineared<br />
FET<br />
SET<br />
Insulator<br />
resistance<br />
change<br />
UTB multiple<br />
gate FET<br />
Quantum<br />
computing<br />
Spin<br />
transistor<br />
Molecular<br />
The Josephson junction (JJ) is the basic switching device in superconductor electronics. Josephson junctions operate<br />
in two different modes: switching from zero-voltage to the voltage-state and generating single-flux quanta.<br />
The early work, exemplified by the IBM and the Japanese Josephson computer projects of the 1970’s and 1980’s,<br />
exclusively used logic circuits where the junctions switch between superconducting and voltage states and require<br />
AC power. RSFQ junctions generate single-flux-quantum pulses and revert to their initial superconducting condition.<br />
RSFQ circuits are DC powered.<br />
Quasi<br />
ballistic<br />
FET<br />
�<br />
Risk �<br />
Emerging<br />
<strong>Technology</strong><br />
Vectors<br />
Architecture<br />
Logic<br />
Memory<br />
Non-classical<br />
CMOS<br />
Figure 1-1. 2004 ITRS update shows RSFQ as the lowest risk (highest maturity) potential emerging technology for processing beyond silicon.<br />
09