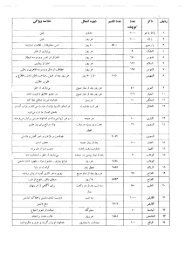
- Page 2:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 6:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 10:
Contents PREFACE ix ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
- Page 14:
Contents 9.4 Building construction
- Page 18:
Preface Introduction to Fire Safety
- Page 22:
About the authors Andrew Furness is
- Page 26:
Illustrations credits Figure 5.1 Co
- Page 30:
Illustrations credits Principles of
- Page 34:
Fire safety foundations To enable s
- Page 38:
There can also be signifi cant emot
- Page 42:
REDUNDANCIES REDUCED CASH FLOW INCR
- Page 46:
If a prosecution is brought for a b
- Page 50:
Figure 1.11 Employers are responsib
- Page 54:
Health and safety arrangements Empl
- Page 58:
fi re specifi c issues that the RRF
- Page 62:
Door closer Fire door Keep shut Fig
- Page 66:
Figure 1.19 Stair lift in situation
- Page 70:
So, whom would she sue for her loss
- Page 74:
Once the court has established negl
- Page 78:
Figure 1.25 Powers of enforcement a
- Page 82:
140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Figure 1.
- Page 86:
External factors Internal factors A
- Page 90:
the company had fully complied with
- Page 94:
Figure 2.1 ACoP of Management of he
- Page 98:
The organisation element of a safet
- Page 102:
detached building, which included o
- Page 106:
Organising for safety 3.1 Introduct
- Page 110:
Directors and senior managers often
- Page 114:
➤ Ensuring access and egress and
- Page 118:
Table 3.1 A summary of individuals
- Page 122:
and inform employers and other self
- Page 126:
Figure 3.8 Safety representatives h
- Page 130:
➤ To consider enforcing authority
- Page 134:
If a piece of work equipment that i
- Page 138:
4. First aid information 5. Fire fi
- Page 142:
Figure 3.13 Designers have a respon
- Page 146:
3.11 Example NEBOSH questions for C
- Page 150:
Safety culture 4.1 Introduction The
- Page 154:
There are various ‘safety climate
- Page 158:
the culture because if there is dis
- Page 162:
Communication is defi ned as: The i
- Page 166:
emergency medical care and rescue w
- Page 170:
on how much people will remember. A
- Page 174:
Individual factors affecting the sc
- Page 178:
on the culture of an organisation.
- Page 182:
Figure 4.11 Consultation with emplo
- Page 186:
esponsibilities are added such as a
- Page 190:
4.9 Human failure Human beings are
- Page 194:
safety in a way that takes their wh
- Page 198: Principles of risk assessment 5.1 I
- Page 202: 5.2.6 Risk control systems (RCS) Th
- Page 206: ➤ Safety representatives ➤ Desi
- Page 210: ➤ Location inspection: ➤ Site s
- Page 214: There are a number of methods for e
- Page 218: Semi-quantitative analysis The use
- Page 222: the risk controls, particularly wit
- Page 226: the hazards that arise from the act
- Page 230: No. Hazards Persons at risk Risk ra
- Page 234: General principles of control 6.1 I
- Page 238: Consultation and the arrangements f
- Page 242: needs. This assessment must also ta
- Page 246: High 100% Level of supervision Low
- Page 252: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 256: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 260: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 264: 7 Principles 7.1 Introduction Previ
- Page 268: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 272: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 276: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 280: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 284: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 288: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 292: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 296: Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 300:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 304:
8 Causes Identifying sources of fue
- Page 308:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 312:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 316:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 320:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 324:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 328:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 332:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 336:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 340:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 344:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 348:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 352:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 356:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 360:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 364:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 368:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 372:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 376:
9 Fire The design, construction, la
- Page 380:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 384:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 388:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 392:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 396:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 400:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 404:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 408:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 412:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 416:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 420:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 424:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 428:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 432:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 436:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 440:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 444:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 448:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 452:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 456:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 460:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 464:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 468:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 472:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 476:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 480:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 484:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 488:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 492:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 496:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 500:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 504:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 508:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 512:
10 Safety The safety of people in t
- Page 516:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 520:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 524:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 528:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 532:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 536:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 540:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 544:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 548:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 552:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 556:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 560:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 564:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 568:
11 Monitoring, While there is no sp
- Page 572:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 576:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 580:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 584:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 588:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 592:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 596:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 600:
12 Reactive The investigation of fi
- Page 604:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 608:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 612:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 616:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 620:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 624:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 628:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 632:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 636:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 640:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 644:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 648:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 652:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 656:
13 Environmental Fire not only pose
- Page 660:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 664:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 668:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 672:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 676:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 680:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 684:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 688:
14 Fire 14.1 Introduction As has be
- Page 692:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 696:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 700:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 704:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 708:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 712:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 716:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 720:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 724:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 728:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 732:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 736:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 740:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 744:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 748:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 752:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 756:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 760:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 764:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 768:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 772:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 776:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 780:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 784:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 788:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 792:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 796:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 800:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 804:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 808:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 812:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 816:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 820:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 824:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 828:
Introduction to Fire Safety Managem
- Page 832:
Abbreviations AFFF Aqueous Film For
- Page 836:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 840:
Index BS 5539 Part 1, Monitoring fi
- Page 844:
Index Demolition work, contributes
- Page 848:
Index Fencing, as a security strate
- Page 852:
Index Fire risk assessment process
- Page 856:
Index Hazardous Installation Direct
- Page 860:
Index Montreal Protocol, 221 Motiva
- Page 864:
Index Risk matrix: for determining
- Page 868:
Index SSOW (Safe systems of work),