gambling in alberta - Research Services - University of Lethbridge
gambling in alberta - Research Services - University of Lethbridge
gambling in alberta - Research Services - University of Lethbridge
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
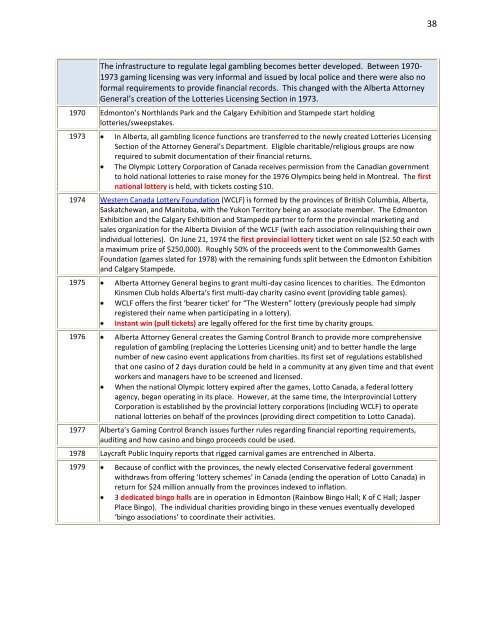
The <strong>in</strong>frastructure to regulate legal <strong>gambl<strong>in</strong>g</strong> becomes better developed. Between 1970-<br />
1973 gam<strong>in</strong>g licens<strong>in</strong>g was very <strong>in</strong>formal and issued by local police and there were also no<br />
formal requirements to provide f<strong>in</strong>ancial records. This changed with the Alberta Attorney<br />
General’s creation <strong>of</strong> the Lotteries Licens<strong>in</strong>g Section <strong>in</strong> 1973.<br />
1970 Edmonton’s Northlands Park and the Calgary Exhibition and Stampede start hold<strong>in</strong>g<br />
lotteries/sweepstakes.<br />
1973 In Alberta, all <strong>gambl<strong>in</strong>g</strong> licence functions are transferred to the newly created Lotteries Licens<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Section <strong>of</strong> the Attorney General’s Department. Eligible charitable/religious groups are now<br />
required to submit documentation <strong>of</strong> their f<strong>in</strong>ancial returns.<br />
The Olympic Lottery Corporation <strong>of</strong> Canada receives permission from the Canadian government<br />
to hold national lotteries to raise money for the 1976 Olympics be<strong>in</strong>g held <strong>in</strong> Montreal. The first<br />
national lottery is held, with tickets cost<strong>in</strong>g $10.<br />
1974 Western Canada Lottery Foundation (WCLF) is formed by the prov<strong>in</strong>ces <strong>of</strong> British Columbia, Alberta,<br />
Saskatchewan, and Manitoba, with the Yukon Territory be<strong>in</strong>g an associate member. The Edmonton<br />
Exhibition and the Calgary Exhibition and Stampede partner to form the prov<strong>in</strong>cial market<strong>in</strong>g and<br />
sales organization for the Alberta Division <strong>of</strong> the WCLF (with each association rel<strong>in</strong>quish<strong>in</strong>g their own<br />
<strong>in</strong>dividual lotteries). On June 21, 1974 the first prov<strong>in</strong>cial lottery ticket went on sale ($2.50 each with<br />
a maximum prize <strong>of</strong> $250,000). Roughly 50% <strong>of</strong> the proceeds went to the Commonwealth Games<br />
Foundation (games slated for 1978) with the rema<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g funds split between the Edmonton Exhibition<br />
and Calgary Stampede.<br />
1975 Alberta Attorney General beg<strong>in</strong>s to grant multi-day cas<strong>in</strong>o licences to charities. The Edmonton<br />
K<strong>in</strong>smen Club holds Alberta’s first multi-day charity cas<strong>in</strong>o event (provid<strong>in</strong>g table games).<br />
WCLF <strong>of</strong>fers the first ‘bearer ticket’ for “The Western” lottery (previously people had simply<br />
registered their name when participat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> a lottery).<br />
Instant w<strong>in</strong> (pull tickets) are legally <strong>of</strong>fered for the first time by charity groups.<br />
1976 Alberta Attorney General creates the Gam<strong>in</strong>g Control Branch to provide more comprehensive<br />
regulation <strong>of</strong> <strong>gambl<strong>in</strong>g</strong> (replac<strong>in</strong>g the Lotteries Licens<strong>in</strong>g unit) and to better handle the large<br />
number <strong>of</strong> new cas<strong>in</strong>o event applications from charities. Its first set <strong>of</strong> regulations established<br />
that one cas<strong>in</strong>o <strong>of</strong> 2 days duration could be held <strong>in</strong> a community at any given time and that event<br />
workers and managers have to be screened and licensed.<br />
When the national Olympic lottery expired after the games, Lotto Canada, a federal lottery<br />
agency, began operat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> its place. However, at the same time, the Interprov<strong>in</strong>cial Lottery<br />
Corporation is established by the prov<strong>in</strong>cial lottery corporations (<strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g WCLF) to operate<br />
national lotteries on behalf <strong>of</strong> the prov<strong>in</strong>ces (provid<strong>in</strong>g direct competition to Lotto Canada).<br />
1977 Alberta’s Gam<strong>in</strong>g Control Branch issues further rules regard<strong>in</strong>g f<strong>in</strong>ancial report<strong>in</strong>g requirements,<br />
audit<strong>in</strong>g and how cas<strong>in</strong>o and b<strong>in</strong>go proceeds could be used.<br />
1978 Laycraft Public Inquiry reports that rigged carnival games are entrenched <strong>in</strong> Alberta.<br />
1979 Because <strong>of</strong> conflict with the prov<strong>in</strong>ces, the newly elected Conservative federal government<br />
withdraws from <strong>of</strong>fer<strong>in</strong>g ‘lottery schemes’ <strong>in</strong> Canada (end<strong>in</strong>g the operation <strong>of</strong> Lotto Canada) <strong>in</strong><br />
return for $24 million annually from the prov<strong>in</strong>ces <strong>in</strong>dexed to <strong>in</strong>flation.<br />
3 dedicated b<strong>in</strong>go halls are <strong>in</strong> operation <strong>in</strong> Edmonton (Ra<strong>in</strong>bow B<strong>in</strong>go Hall; K <strong>of</strong> C Hall; Jasper<br />
Place B<strong>in</strong>go). The <strong>in</strong>dividual charities provid<strong>in</strong>g b<strong>in</strong>go <strong>in</strong> these venues eventually developed<br />
‘b<strong>in</strong>go associations’ to coord<strong>in</strong>ate their activities.<br />
38