- Page 1 and 2:
Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 3 and 4:
European Commission- Joint Research
- Page 5 and 6:
Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 7 and 8:
At the 2003 Rome Informal Meeting o
- Page 9 and 10:
Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 11 and 12:
Changes in the diurnal variation of
- Page 13 and 14:
Fugure I.2. (a) Maximum grid covera
- Page 15 and 16:
century. This corresponds to a sea
- Page 17 and 18:
Other causes Other causes of climat
- Page 19 and 20:
tropospheric ozone are photochemica
- Page 21 and 22:
Figure. I.4. Radiative forcings and
- Page 23 and 24:
There are two indirect effects of a
- Page 25 and 26:
The projected warming is not unifor
- Page 27 and 28:
water towards the west Pacific caus
- Page 29 and 30:
Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 31 and 32:
Aerosols and climate change in the
- Page 33 and 34:
precipitation intensities have been
- Page 35 and 36:
Chapter III. The Hydrologic Cycle I
- Page 37 and 38:
Figure III.2. Long-term average ann
- Page 39 and 40:
Figure III.4. Projected change in s
- Page 41 and 42:
eduction in the rate of evaporation
- Page 43 and 44:
characteristics may or may not be u
- Page 45 and 46:
temperatures potentially lead to hi
- Page 47 and 48:
Chapter IV.A. Proxy indicators of C
- Page 49 and 50:
Mean Air Temperature (Dec.-March) [
- Page 51 and 52:
correlation coefficient -0.4 -0.3 -
- Page 53 and 54:
Chapter IV. B. The Impact of Climat
- Page 55 and 56:
numbers refer to water bodies bigge
- Page 57 and 58:
Table IV.B.2. Number of large dams*
- Page 59 and 60:
quality degradation and meet the in
- Page 61 and 62:
sufficient resolution and accuracy
- Page 63 and 64:
Windermere in the English Lake Dist
- Page 65 and 66:
their vertical structure. In partic
- Page 67 and 68:
have recently described a method th
- Page 69 and 70:
The available evidence suggests tha
- Page 71 and 72:
1979). In contrast, heavy rain incr
- Page 73 and 74:
The projected increase in the atmos
- Page 75 and 76:
Aulacoseira spp. favour the changed
- Page 77 and 78:
vertical bars are a simple measure
- Page 79 and 80:
values, with an upper limit of 30°
- Page 81 and 82:
Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 83 and 84:
the processes controlling, regional
- Page 85 and 86:
Sea level rise is partially due to
- Page 87 and 88:
Box # 1: The North Sea The North Se
- Page 89 and 90:
and organic material more rapidly t
- Page 91 and 92:
suggesting that climate rather than
- Page 93 and 94:
CO2 2- ). In turn, the alkalinity i
- Page 95 and 96:
looms are often associated with tox
- Page 97 and 98:
events of dense water through the D
- Page 99 and 100:
(1) Are we already observing a resp
- Page 101 and 102:
eastern and western side of the Nor
- Page 103 and 104:
system, their physiology and intern
- Page 105 and 106:
each coastal element be studied and
- Page 107 and 108:
IV.D.1. Introduction Coastal lagoon
- Page 109 and 110:
In the last decade, a general model
- Page 111 and 112:
topics in coastal lagoons (de Wit e
- Page 113 and 114:
Po River Delta lagoons, the long dr
- Page 115 and 116:
esilient to environmental changes a
- Page 117 and 118:
Chapter V.A. Climate Change and Ext
- Page 119 and 120:
It is realized that adaptation to c
- Page 121 and 122:
Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 123 and 124:
member states. Moreover some agenci
- Page 125 and 126: Large, global scale climatic driver
- Page 127 and 128: V.B.5. Climate change and droughts
- Page 129 and 130: Evacuation from forest fires at Mas
- Page 131 and 132: In European forest policy, water is
- Page 133 and 134: Drought mitigation and the involvem
- Page 135 and 136: DSS-DROUGHT A Decision Support Syst
- Page 137 and 138: Chapter V .C. Climate Change, Ecolo
- Page 139 and 140: The quality class boundaries within
- Page 141 and 142: An example of this kind of relation
- Page 143 and 144: Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 145 and 146: Regions 1 to 5 represent mainly a m
- Page 147 and 148: een observed in southwestern countr
- Page 149 and 150: Table V.D.2: Percentage area affect
- Page 151 and 152: Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 153 and 154: Lake Surface Temperature [°C] Desc
- Page 155 and 156: Case Study: Esthwaite Water, Cumbri
- Page 157 and 158: Residence time (days) Chlorophyll (
- Page 159 and 160: Case Study: Lake Erken, Sweden ►
- Page 161 and 162: TP (µg l -1 ) Modelling To analyse
- Page 163 and 164: Data availability and investigation
- Page 165 and 166: smaller volume of water. The warmer
- Page 167 and 168: Chapter VI.B. Climate Change and th
- Page 169 and 170: Concerning the flora of the lagoon
- Page 171 and 172: Figure VI.B.2: Frequency of “bora
- Page 173 and 174: Climate Change and the European Wat
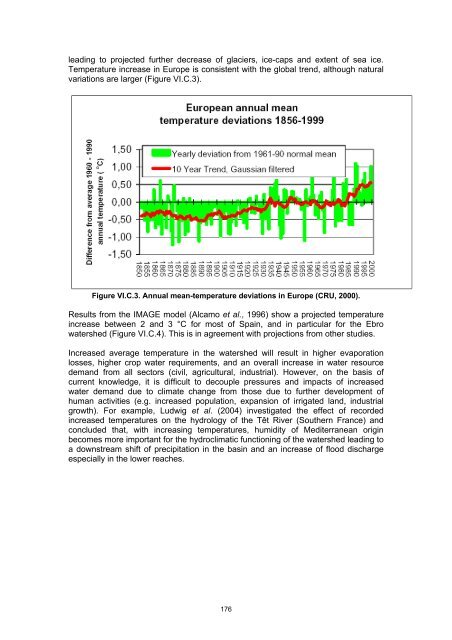
- Page 175: Figure VI.C.2. Daily flows in Ebro
- Page 179 and 180: factors including an appropriate su
- Page 181 and 182: with the lower limit range indicate
- Page 183 and 184: Chapter VI.C. The Effects of Climat
- Page 185 and 186: the main carrier of nutrients to gr
- Page 187 and 188: system pathway shows an increase of
- Page 189 and 190: Table-VI.C.7: Main factors and cons
- Page 191 and 192: Chapter VI.D. Climate Change and th
- Page 193 and 194: Atmospheric deposition to marine wa
- Page 195 and 196: Many studies during the 90’s have
- Page 197 and 198: Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 199 and 200: severe flooding were investigated (
- Page 201 and 202: Table VI.E.1. Waterborne pathogens
- Page 203 and 204: Chapter VI.F. Climate Change, Extre
- Page 205 and 206: Areas behind the dikes broken in 20
- Page 207 and 208: Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 209 and 210: Second, the chemical is transported
- Page 211 and 212: POPs exist in the atmosphere in the
- Page 213 and 214: and ice have quite a low capacity t
- Page 215 and 216: Table VI.F.1. Priority substances i
- Page 217 and 218: Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 219 and 220: 22. Monteith, J.L., 1965. Evaporati
- Page 221 and 222: 31. Rodionov, S.N. 1994. Global and
- Page 223 and 224: 28. Dokulil, M.T., 2003. Algae as e
- Page 225 and 226: 63. Hejzlar, J., Dubrovský, M. Buc
- Page 227 and 228:
99. Melack, J.M., J. Dozier, C.R. G
- Page 229 and 230:
136. Straile, D. & Adrian, R. 2000.
- Page 231 and 232:
14. Blaas, M., Kerkhoven, D., and d
- Page 233 and 234:
60. McCleery, R. H. and Perrins, C.
- Page 235 and 236:
105. UNESCO 2003. The integrated st
- Page 237 and 238:
ecosystems and the landscape and de
- Page 239 and 240:
2. Carter, T.R., Saarikko, R.A., an
- Page 241 and 242:
24. Hydrographisches Zentralbüro 1
- Page 243 and 244:
European Coastal Lagoons: The Influ
- Page 245 and 246:
4. Bouma MJ, Sondrop HE, van der Ka
- Page 247 and 248:
variable trophic status: a paired l
- Page 249 and 250:
Climate Change and the European Wat
- Page 251 and 252:
France GIANMARCO GIORDANI Departmen
- Page 253:
Chapter VI.E. Climate Change and Wa