Air quality expert group - Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in ... - Defra
Air quality expert group - Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in ... - Defra
Air quality expert group - Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in ... - Defra
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>PM2.5</strong> emissions and receptor modell<strong>in</strong>g<br />
background sites, it was shown that the mass of particles mak<strong>in</strong>g up the<br />
roadside <strong>in</strong>crement (i.e. the difference between the roadside concentration<br />
and the urban background) was comprised almost wholly of elemental carbon<br />
(54.8%), organic carbon (27.4%) and road dust (18.3%) (Harrison et al., 2004).<br />
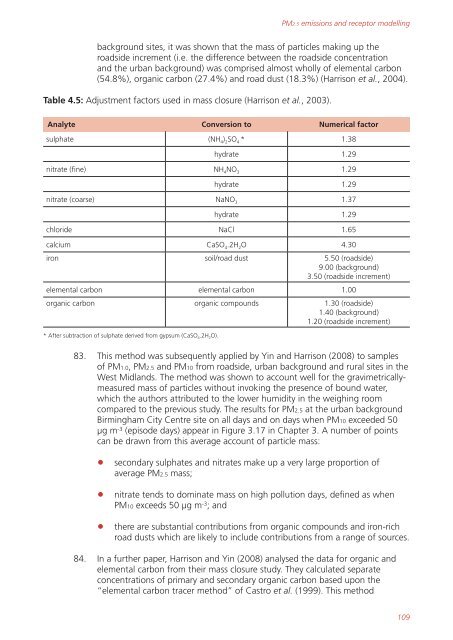
Table 4.5: Adjustment factors used <strong>in</strong> mass closure (Harrison et al., 2003).<br />
Analyte Conversion to Numerical factor<br />
sulphate (NH4) 2SO4 * 1.38<br />
hydrate 1.29<br />
nitrate (f<strong>in</strong>e) NH 4NO 3 1.29<br />
hydrate 1.29<br />
nitrate (coarse) NaNO 3 1.37<br />
hydrate 1.29<br />
chloride NaCl 1.65<br />
calcium CaSO 4.2H 2O 4.30<br />
iron soil/road dust 5.50 (roadside)<br />
9.00 (background)<br />
3.50 (roadside <strong>in</strong>crement)<br />
elemental carbon elemental carbon 1.00<br />
organic carbon organic compounds 1.30 (roadside)<br />
1.40 (background)<br />
1.20 (roadside <strong>in</strong>crement)<br />
* After subtraction of sulphate derived from gypsum (CaSO 4.2H 2O).<br />
83. This method was subsequently applied by Y<strong>in</strong> and Harrison (2008) to samples<br />
of PM1.0, <strong>PM2.5</strong> and PM10 from roadside, urban background and rural sites <strong>in</strong> the<br />
West Midlands. The method was shown to account well for the gravimetricallymeasured<br />
mass of particles without <strong>in</strong>vok<strong>in</strong>g the presence of bound water,<br />
which the authors attributed to the lower humidity <strong>in</strong> the weigh<strong>in</strong>g room<br />
compared to the previous study. The results for <strong>PM2.5</strong> at the urban background<br />
Birm<strong>in</strong>gham City Centre site on all days and on days when PM10 exceeded 50<br />
µg m -3 (episode days) appear <strong>in</strong> Figure 3.17 <strong>in</strong> Chapter 3. A number of po<strong>in</strong>ts<br />
can be drawn from this average account of particle mass:<br />
• secondary sulphates and nitrates make up a very large proportion of<br />
average <strong>PM2.5</strong> mass;<br />
• nitrate tends to dom<strong>in</strong>ate mass on high pollution days, def<strong>in</strong>ed as when<br />
PM10 exceeds 50 µg m -3 ; and<br />
• there are substantial contributions from organic compounds and iron-rich<br />
road dusts which are likely to <strong>in</strong>clude contributions from a range of sources.<br />
84. In a further paper, Harrison and Y<strong>in</strong> (2008) analysed the data for organic and<br />
elemental carbon from their mass closure study. They calculated separate<br />
concentrations of primary and secondary organic carbon based upon the<br />
“elemental carbon tracer method” of Castro et al. (1999). This method<br />
109